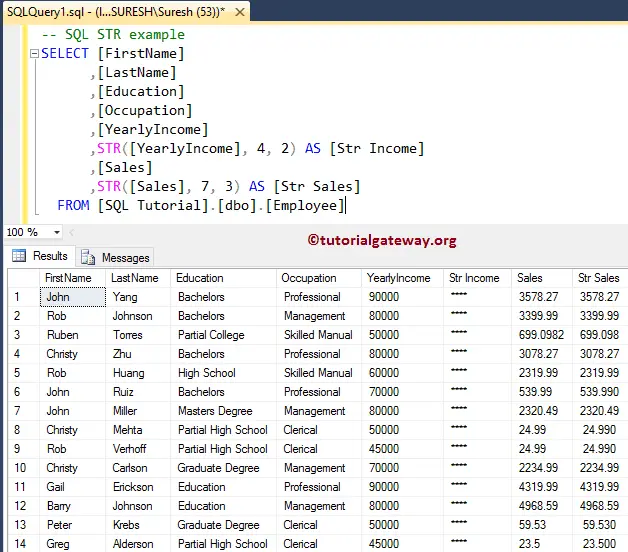
The SQL Server STR is a String Function used to return the string representation of the numeric expression. The syntax of the SQL STR function is shown below.
SELECT STR(Float_Expression, Length, Decimal) FROM [Source]
This SQL String STR function will return VARCHAR. The list of arguments available for STR is:
- Float_Expression: Please specify the valid Expression for which you want to convert as character data. Please specify any expression of a Float data type with decimal points.
- length: This is an optional argument representing the total string length. The value assigned to the length argument includes a decimal point, sign, spaces, and digits. If you omit this argument, then it will assign the default length as 10.
- decimal: This is an optional argument, representing the total number of decimal places to display by the string result. The value assigned to the decimal argument must be less than or equal to 16, and if you assign more than 16, then the result will be truncated to 16.
SQL Server STR Function Example
The SQL STR Function returns the string representation of the float values. The following query will show you multiple ways to use this function.
DECLARE @Num FLOAT SET @Num = 786.387 -- No Length, Decimal arguments. @Num value will be rounded SELECT STR(@Num) AS Result1 -- Length = 7, No Decimal argument. -- Although length is 7, @Num value will be rounded because decimal places defaults value is 0 SELECT STR(@Num, 7) AS Result2 SELECT STR(@Num, 7, 0) AS Result3 -- Length = 7, Decimals = 1, 2 Resulting string will return 1 and 2 decimal values SELECT STR(@Num, 7, 1) AS Result4 SELECT STR(@Num, 7, 2) AS Result5 SELECT STR(@Num, 6, 1) AS Result6 -- Length = 5, Decimals = 3. SELECT STR(@Num, 5, 3) AS Result7
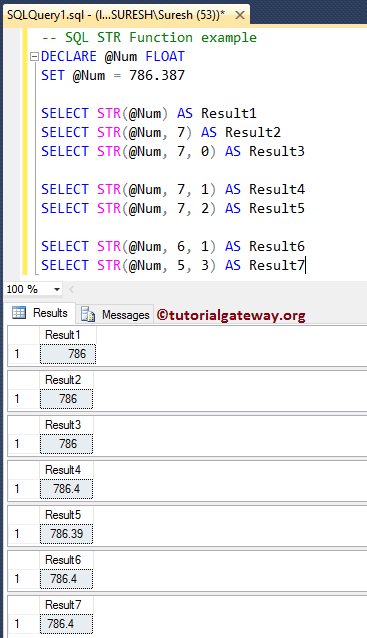
Within this SQL STR function example query, For both the statements, Length = 7, and for the first one No Decimal argument, for the second statement decimal = 0. Although the length value is 7, the @Num value is rounded because the decimal places default value is 0.
SELECT STR(@Num, 7) AS Result2 SELECT STR(@Num, 7, 0) AS Result3
Here, Length = 5, and Decimals = 3. Although the decimal value is 3, the @Num value is rounded to one because the length value is 5 (and the length of 786.4 is 5, including the decimal point)
SELECT STR(@Num, 5, 3) AS Result7
SQL Server STR Function Example 2
In this example, we will use the STR function with uneven lengths and decimals values.
SELECT STR(786.387) AS Result1 SELECT STR(786.387, 3) AS Result2 SELECT STR(786.387, 2) AS Result3 SELECT STR(786.387, 2, 2) AS Result4 SELECT STR(786.387, 9, 5) AS Result5 SELECT STR(FLOOR(786.387), 9, 4) AS Result6 SELECT STR(CEILING(786.387), 9, 4) AS Result7
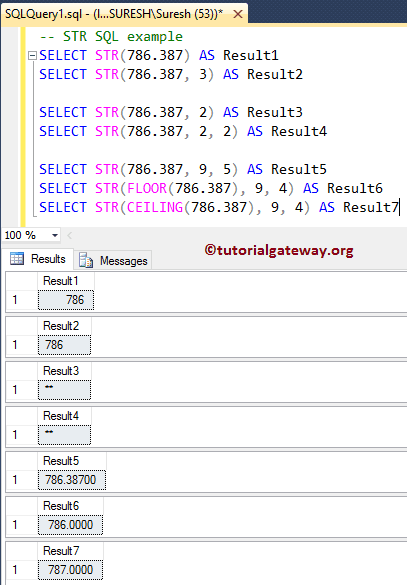
Here, we are assigning the length value less than the left-hand side of the decimal point. The SQL Server will return the output as **
SELECT STR(786.387, 2) AS Result3 SELECT STR(786.387, 2, 2) AS Result4
Next, we apply the SQL STR function to Floor and ceiling values. Though the values are rounded to the nearest values, this String Function is returning 4 zeros after the decimal point because we assigned the decimal argument to 4, and length = 9 (length of 787.0000 is 9, including the decimal point)
SELECT STR(FLOOR(786.387), 9, 4) AS Result6 SELECT STR(CEILING(786.387), 9, 4) AS Result7
STR Function Example 3
In this example, we will implement the SQL STR function on the numeric columns. For this demo, We are going to use the below-shown data.
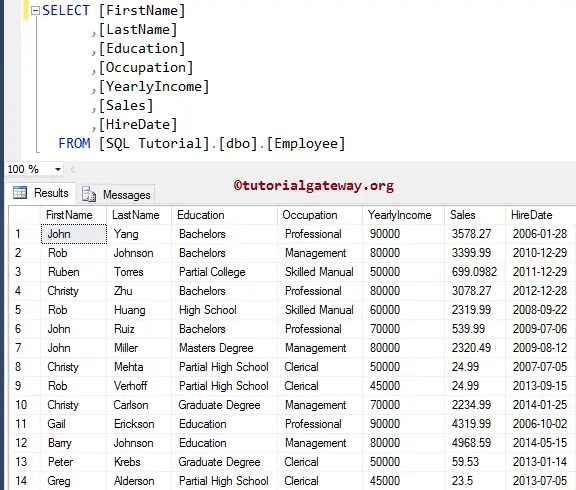
The following SQL STR string function statement will return the string representation of the [Yearly Income] and [Sales] columns.
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,STR([YearlyIncome], 4, 2) AS [Str Income]
,[Sales]
,STR([Sales], 7, 3) AS [Str Sales]
FROM [Employee]
From the below screenshot, you can observe that str Income is returning **** because we assigned the length value less than the yearly income value.