The SQL Server PERCENT_RANK is one of the Analytic functions, which will calculate the relative rank of each row. This function will return the rank from a range of values greater than 0 and less than 1. The basic syntax of the SQL PERCENT_RANK is:
SELECT PERCENT_RANK()
OVER (
PARTITION_BY_Clause
ORDER_BY_Clause
)
FROM [Source]
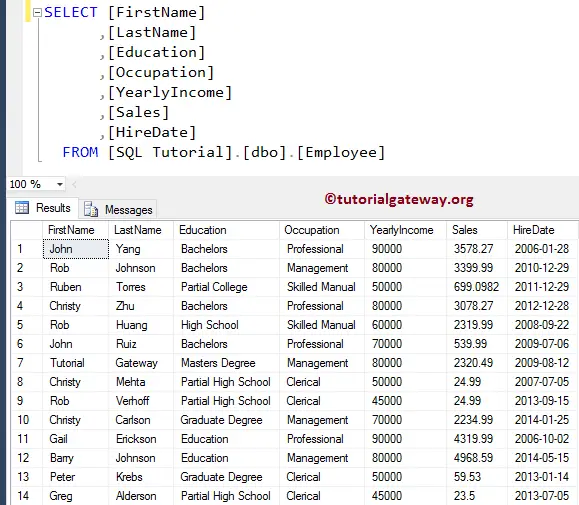
We are going to use the below-shown data for this demonstration
SQL PERCENT_RANK without Partition By Clause
In this example, we will show what will happen if we omit the Partition By Clause in the PERCENT_RANK Function.
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
,PERCENT_RANK() OVER (ORDER BY [Sales] ASC) AS PercentRank
FROM [Employee]
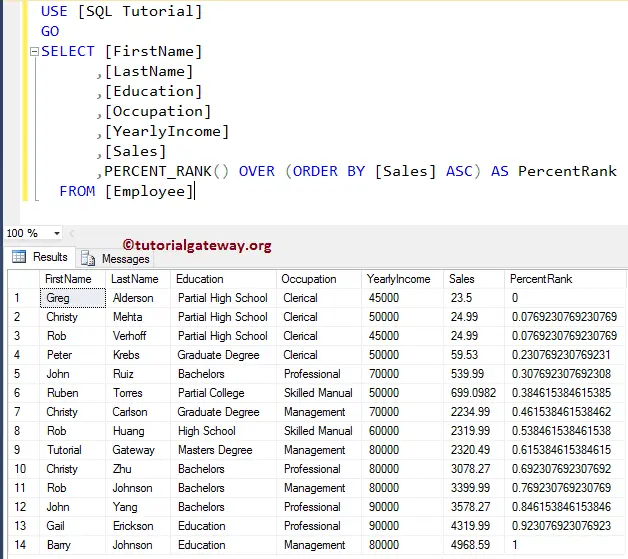
The Order By Clause Sort the Employee table Ascending order using their Sales Amount
ORDER BY [Sales] ASC
Next, the SQL PERCENT_RANK function returns the percentage ranks as the output. Here, a row with the highest sales will assign 1 as the rank, and 0 is the percentile rank for the least sales.
PERCENT_RANK() OVER (ORDER BY [Sales] ASC) AS PercentRank
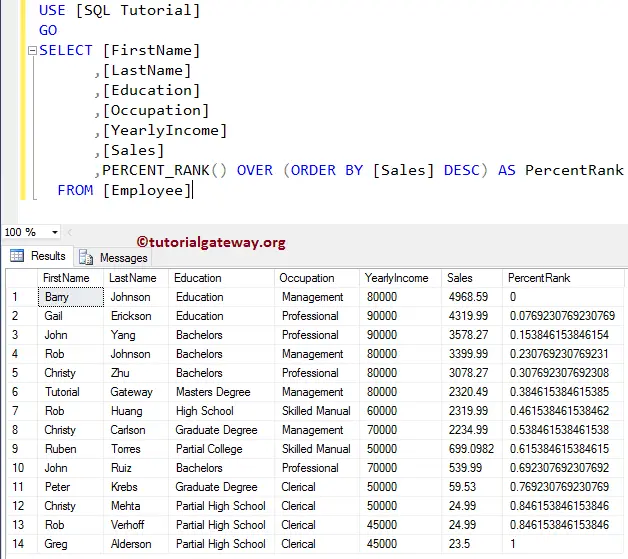
Let me change the Order by clause from Ascending order to Descending. As you can see, it ranks the least value as 1 and the highest value as 0.
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
,PERCENT_RANK() OVER (ORDER BY [Sales] DESC) AS PercentRank
FROM [Employee]
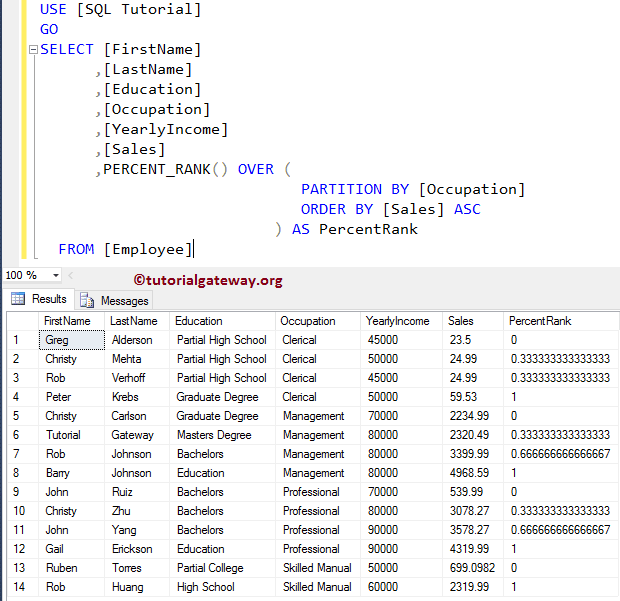
SQL PERCENT_RANK with Partition By Example
How do return the percentage ranks for the partitioned records? The following PERCENT_RANK query will partition the data by Occupation using their Sales amount, and then written the percent ranks for each partition independently.
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
,PERCENT_RANK() OVER (
PARTITION BY [Occupation]
ORDER BY [Sales] ASC
) AS PercentRank
FROM [Employee]
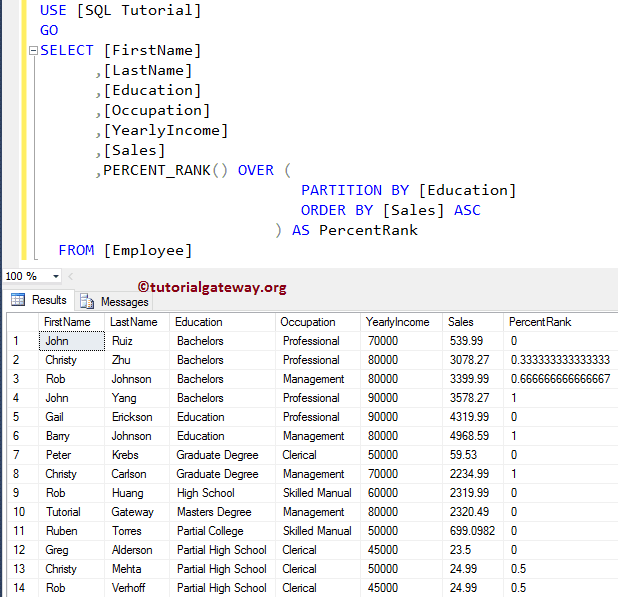
To make sure you understand well. We are changing the SQL Server Group value from Occupation to Education.
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
,PERCENT_RANK() OVER (
PARTITION BY [Education]
ORDER BY [Sales] ASC
) AS PercentRank
FROM [Employee]

Comments are closed.