The SQL PARSE function is a Conversions Function used to convert the String data to the requested data type and returns the result as an expression. It is recommended to use this SQL PARSE function to convert the string data to either Date time, or Number type.
SQL PARSE Function Syntax
The syntax of the SQL Server PARSE Function is
PARSE (String_Value AS Data_Type [USING Culture]) -- For example SELECT PARSE (String_Column_Value AS Data_Type USING 'en-US') AS [result_name] FROM [Source]
- Data_Type: Data Type to which you want to convert the String_Value
- Culture: This is an optional parameter. By default, it uses the current session language.
SQL PARSE Function Example 1
The SQL Server Parse Function is mainly used to convert the string into date and time, and numeric values. The following Parse function query parses integer or string to decimal and string to DateTime.
If the Parse function is unable to convert the string into the desired data type. Or if we pass the non-convertible string, or if we pass NULL value, then this Parse function will return Error.
DECLARE @str AS VARCHAR(50)
SET @str = '11122'
SELECT PARSE(@str AS INT) AS Result;
-- Direct Inputs
SELECT PARSE('1234' AS DECIMAL(10, 2)) AS Result;
SELECT PARSE('06/03/2017' AS DATETIME) AS Result;
SELECT PARSE('06/03/2017' AS DATETIME2) AS Result;
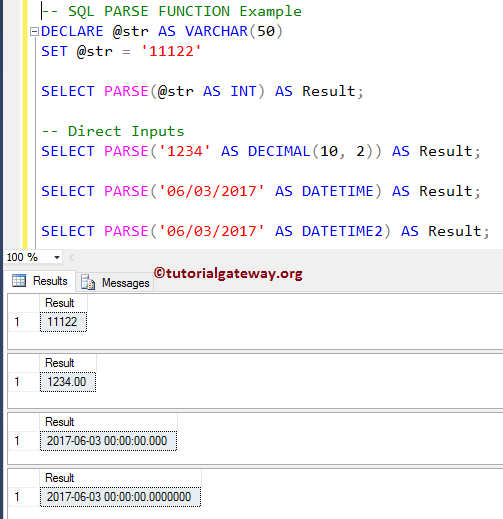
We are converting the string value to an integer and used ALIAS Column in SQL Server to name it as ‘Result’.
SELECT TRY_PARSE(@str AS INT) AS Result;
In the next line, We used the SQL PARSE function directly on string value and converting it to decimal value with precision 2
SELECT PARSE('1234' AS DECIMAL(10, 2)) AS Result;
Next, we are converting the string to DateTime and datetime2 Data Type.
SELECT PARSE('06/03/2017' AS DATETIME) AS Result;
SELECT PARSE('06/03/2017' AS DATETIME2) AS Result;
PARSE Function Example 2
In this SQL Parse function example, we will work with NULL values and non-convertible strings.
DECLARE @strval AS VARCHAR(50) SET @strval = NULL SELECT PARSE(@strval AS INT) AS Result;
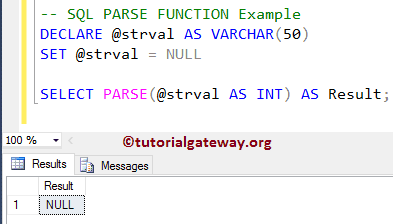
Let us use what happens if we pass the NULL value as the direct input
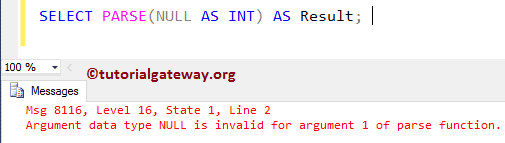
SELECT PARSE(NULL AS INT) AS Result;
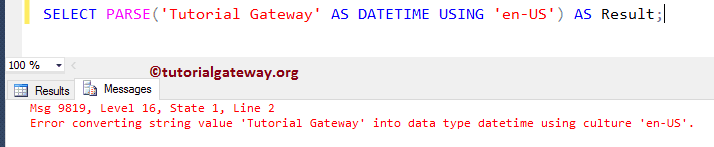
We tried to convert the ‘Tutorial Gateway’ string to date time. It is not possible, so this SQL parse function is returning Error as output.
SELECT PARSE('Tutorial Gateway' AS DATETIME USING 'en-US') AS Result;