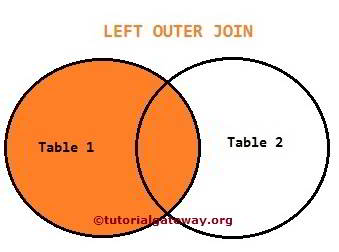
The SQL Server Left Outer Join returns all the rows or records present in the Left table and matches rows from the right table. The visual representation of this is shown below
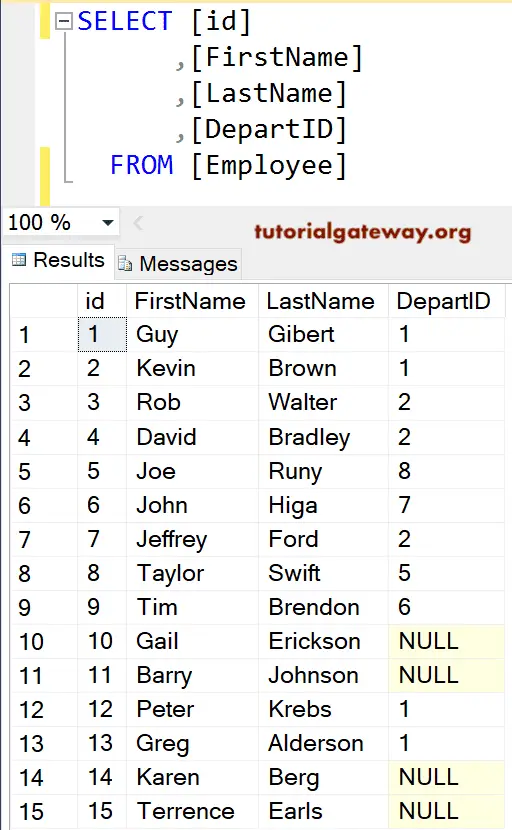
The above image displays all the records present in Table1 and matching records from Table2. All the Unmatched rows from the right table will fill with NULL Values. The syntax of the SQL Server Left Join clause is
-- Syntax
SELECT Table1.Column(s), Table2.Column(s),
FROM Table1
LEFT OUTER JOIN
Table2 ON
Table1.Common_Column = Table2.Common_Column
--OR We can Simply Write it as
SELECT Table1. Column(s), Table2. Column(s),
FROM Table1
LEFT JOIN
Table2 ON
Table1.Common_Column = Table2.Common_Column
The Left join in SQL Server can also be called a Left outer join. So it is optional to use the Outer Keyword. For this example, We use the Employee is:
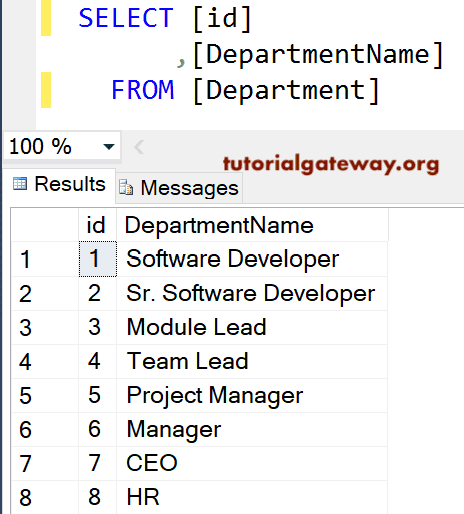
Department
SQL Server Left Join Select All Columns
The following query will display all the columns present in Employees and matching records from Department tables.
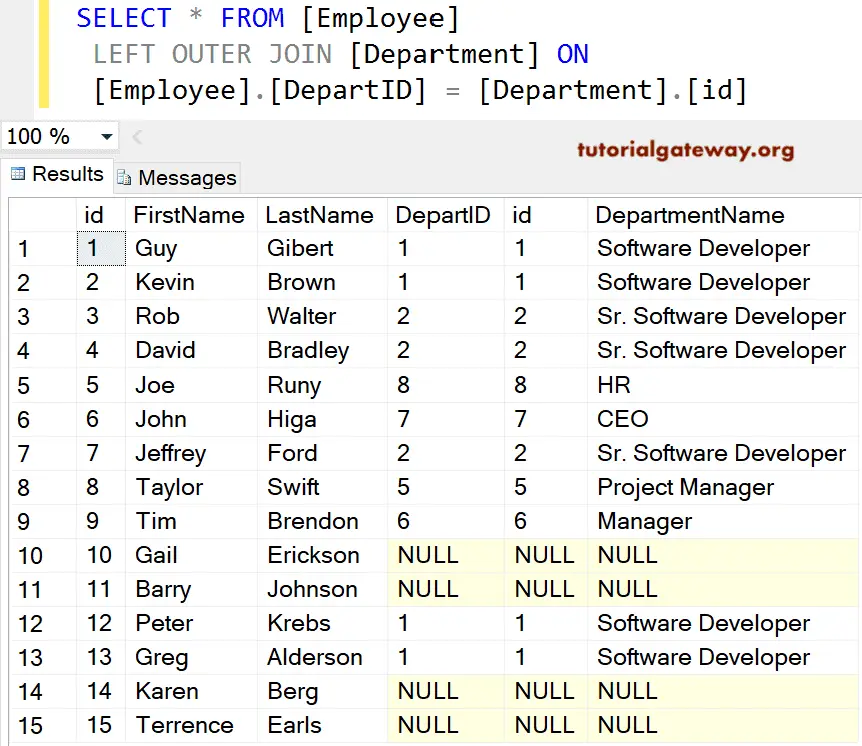
SELECT *
FROM [Employee]
LEFT OUTER JOIN
[Department] ON
[Employee].[DepartID] = [Department].[id]
Avoid Outer keyword
Let me remove the Outer keyword from the SQL LEFT JOIN, which is optional, and it works well. As you can see, it returns rows from both tables in the result set.
SELECT *
FROM [Employee]
LEFT JOIN
[Department] ON
[Employee].[DepartID] = [Department].[id]
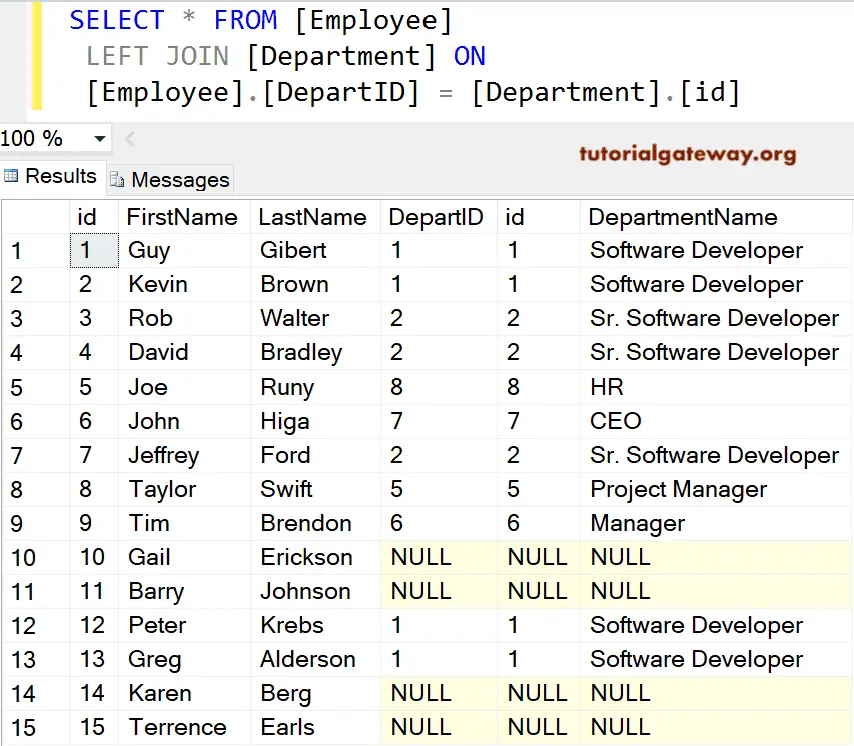
If you observe the above screenshot, We have 15 records in the Employee table. And the SQL Left Join is displaying 15 records, but for [DepartID], id, [Department Name], it displays NULL Values for ID numbers 10, 11, 14, and 15. It is because the Department Id for them in the Employee table is NULLS, so there are no matching records in the right table.
The [Department ID] column is repeated twice, which is annoying to the user. By selecting individual column names, we can avoid unwanted ones. So, please avoid SELECT * Statements.
SQL Server Left Join Select Few Columns
Please place the required columns after the SELECT Statement to avoid unwanted Server columns in Joins.
-- Select Few Columns Example
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[DepartmentName]
FROM [Employee]
LEFT JOIN
[Department] ON
[Employee].[DepartID] = [Department].[id]
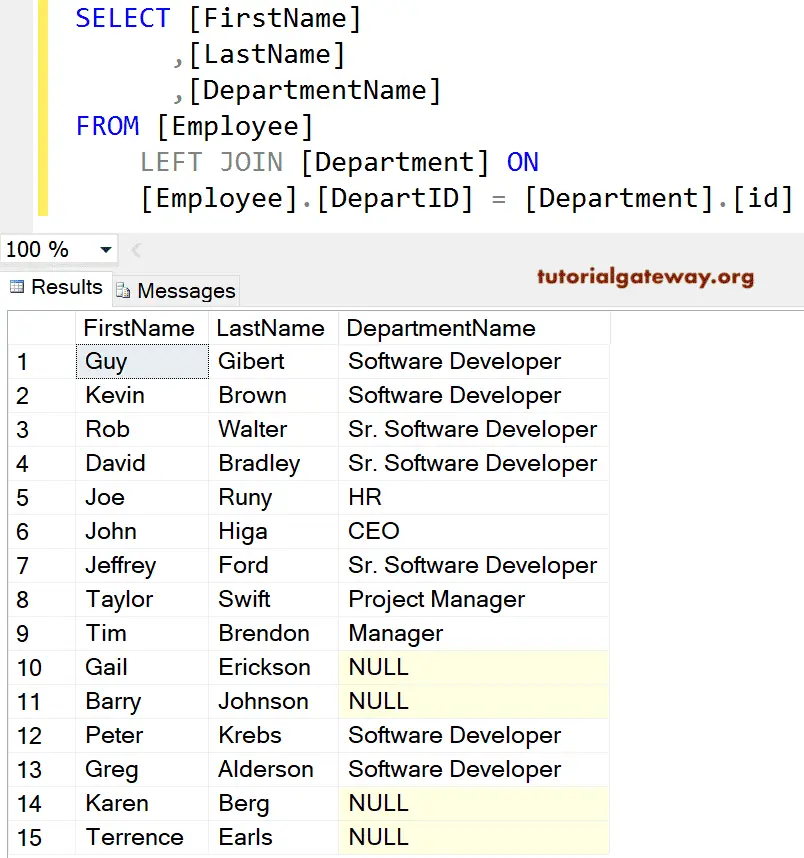
The above query work as long as the column names from both tables are different like above. If we have identical Column names in both tables, it will throw an error. For instance, we are using the above query. But, we added the id from the department table as an additional column.
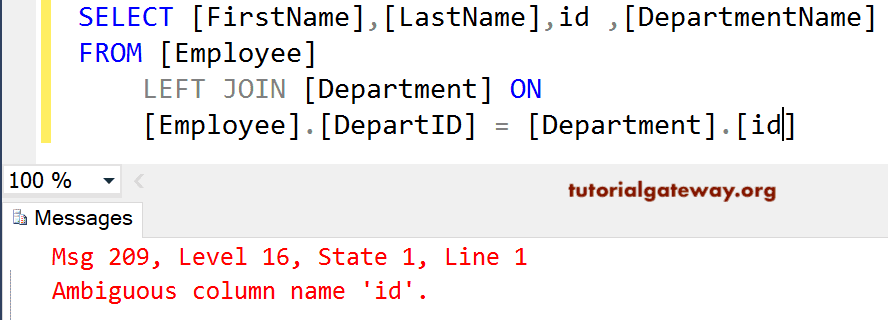
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,id
,[DepartmentName]
FROM [Employee]
LEFT OUTER JOIN
[Department] ON
[Employee].[DepartID] = [Department].[id]
As you can see, SQL Server Left Join throws an error, Ambiguous column name id. It is because the id is present in both tables. And the server doesn’t understand which column you are requesting it to retrieve.
To resolve this sort of issue, forever use the table name before the column name. The following query uses the ALIAS table name before the column names. By this method, we can inform you that we are looking for an id related to the department. We can rewrite the above query as:
SELECT Emp.[FirstName] AS [First Name]
,Emp.[LastName] AS [Last Name]
,Dept.id
,Dept.[DepartmentName] AS [Department Name]
FROM [Employee] AS Emp
LEFT JOIN
[Department] AS Dept ON
Emp.[DepartID] = Dept.[id]
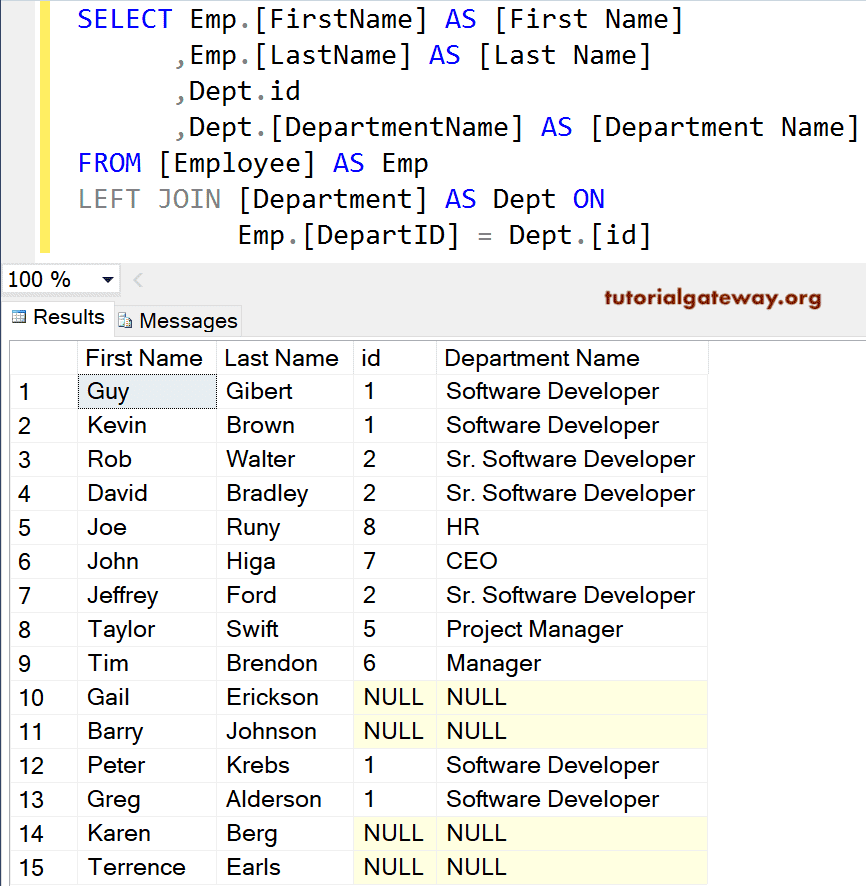
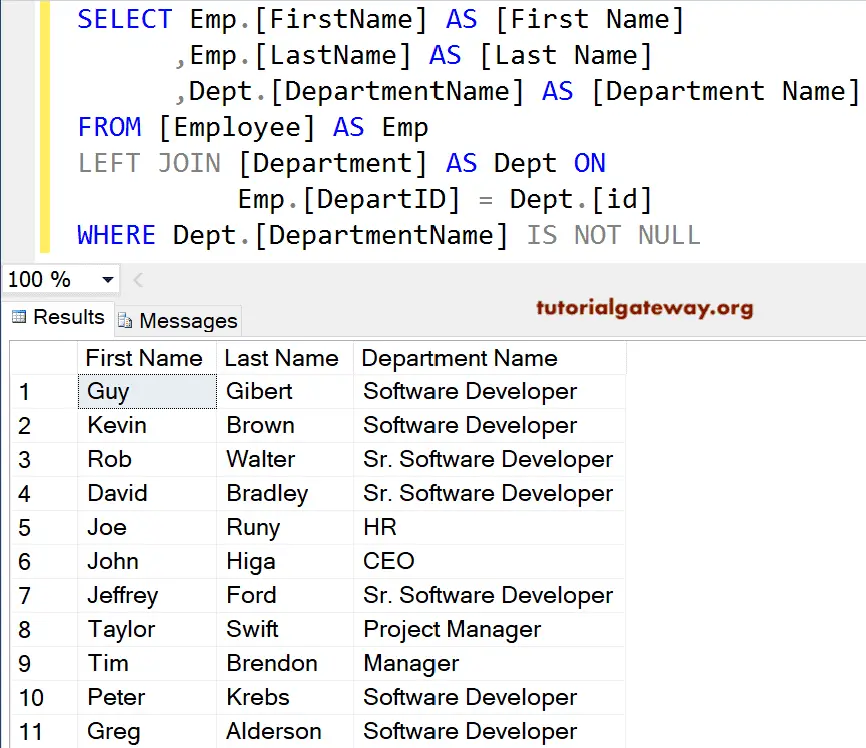
The SQL Server Left Outer Join also permits us to use the Where Clause to limit the number of rows returned by it. Here, we use the WHERE Clause along with this.
SELECT Emp.[FirstName] AS [First Name]
,Emp.[LastName] AS [Last Name]
,Dept.[DepartmentName] AS [Department Name]
FROM [Employee] AS Emp
LEFT JOIN
[Department] AS Dept ON
Emp.[DepartID] = Dept.[id]
WHERE Dept.[DepartmentName] IS NOT NULL
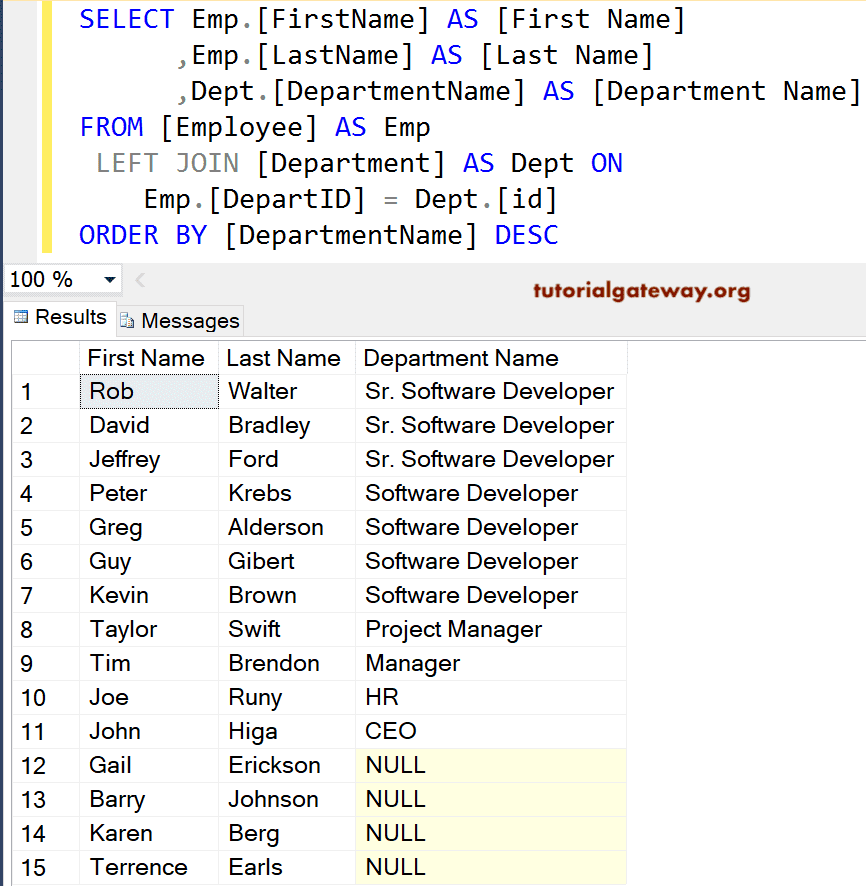
It also allows us to use Order By Clause to rearrange the order of the records.
SELECT Emp.[FirstName] AS [First Name]
,Emp.[LastName] AS [Last Name]
,Dept.[DepartmentName] AS [Department Name]
FROM [Employee] AS Emp
LEFT JOIN
[Department] AS Dept ON
Emp.[DepartID] = Dept.[id]
ORDER BY [DepartmentName] ASC