This SQL Sever String Function is used to format the specified value in the given way or dates and numbers using culture. And the syntax of the Format Function is
Format(Value, Format, Culture)
- Value: Please specify a valid Expression of the supporting Data Type.
- Format: Please specify a valid .NET Framework string.
- Culture: This is an optional argument and user for regional or country-specific changes.
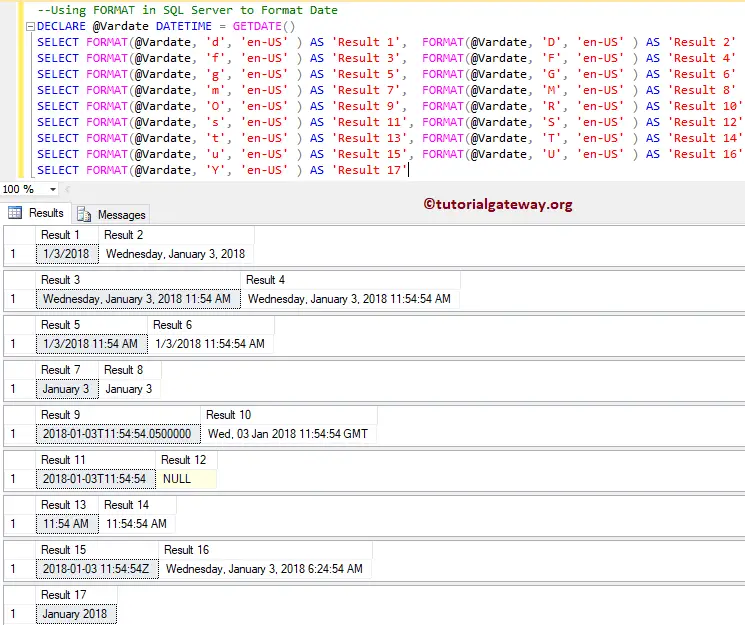
SQL Format Date Example
In this String Function example, we first declared a Datetime variable and assigned GETDATE() to it. Here, we are going to use the function to return the date in different formats. I suggest you refer to the SQL Standard Date Time Format article to understand the string formats we used in this example.
DECLARE @Vardate DATETIME = GETDATE() SELECT FORMAT(@Vardate, 'd', 'en-US' ) AS 'Result 1', FORMAT(@Vardate, 'D', 'en-US' ) AS 'Result 2' SELECT FORMAT(@Vardate, 'f', 'en-US' ) AS 'Result 3', FORMAT(@Vardate, 'F', 'en-US' ) AS 'Result 4' SELECT FORMAT(@Vardate, 'g', 'en-US' ) AS 'Result 5', FORMAT(@Vardate, 'G', 'en-US' ) AS 'Result 6' SELECT FORMAT(@Vardate, 'm', 'en-US' ) AS 'Result 7', FORMAT(@Vardate, 'M', 'en-US' ) AS 'Result 8' SELECT FORMAT(@Vardate, 'O', 'en-US' ) AS 'Result 9', FORMAT(@Vardate, 'R', 'en-US' ) AS 'Result 10' SELECT FORMAT(@Vardate, 's', 'en-US' ) AS 'Result 11', FORMAT(@Vardate, 'S', 'en-US' ) AS 'Result 12' SELECT FORMAT(@Vardate, 't', 'en-US' ) AS 'Result 13', FORMAT(@Vardate, 'T', 'en-US' ) AS 'Result 14' SELECT FORMAT(@Vardate, 'u', 'en-US' ) AS 'Result 15', FORMAT(@Vardate, 'U', 'en-US' ) AS 'Result 16' SELECT FORMAT(@Vardate, 'Y', 'en-US' ) AS 'Result 17'
SQL Server Format Date using Culture
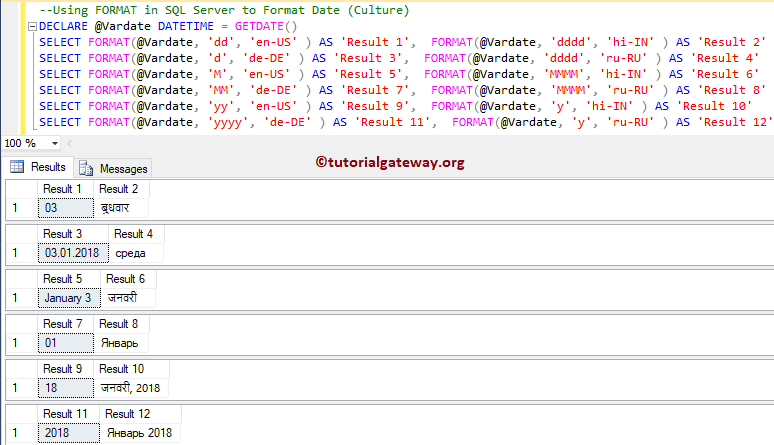
In this example, we are going to use the third argument, culture. By this, you can display the month name or day name in the native language—something like Day name in Japanese, Chinese, Hindi, Russian, Korean, etc.
DECLARE @Vardate DATETIME = GETDATE() SELECT FORMAT(@Vardate, 'dd', 'en-US' ) AS 'Result 1', FORMAT(@Vardate, 'dddd', 'hi-IN' ) AS 'Result 2' SELECT FORMAT(@Vardate, 'd', 'de-DE' ) AS 'Result 3', FORMAT(@Vardate, 'dddd', 'ru-RU' ) AS 'Result 4' SELECT FORMAT(@Vardate, 'M', 'en-US' ) AS 'Result 5', FORMAT(@Vardate, 'MMMM', 'hi-IN' ) AS 'Result 6' SELECT FORMAT(@Vardate, 'MM', 'de-DE' ) AS 'Result 7', FORMAT(@Vardate, 'MMMM', 'ru-RU' ) AS 'Result 8' SELECT FORMAT(@Vardate, 'yy', 'en-US' ) AS 'Result 9', FORMAT(@Vardate, 'y', 'hi-IN' ) AS 'Result 10' SELECT FORMAT(@Vardate, 'yyyy', 'de-DE' ) AS 'Result 11', FORMAT(@Vardate, 'y', 'ru-RU' ) AS 'Result 12'
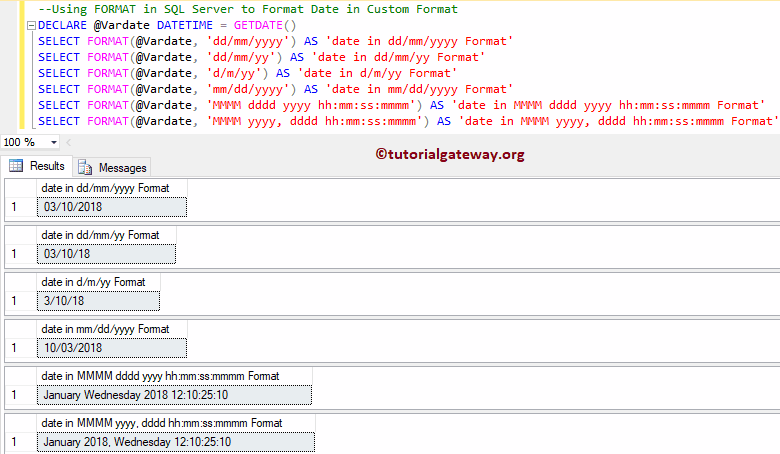
In this section, we are going to define custom date-time formats. By this, you can determine the SQL custom formats to display the date and time.
DECLARE @Vardate DATETIME = GETDATE() SELECT FORMAT(@Vardate, 'dd/mm/yyyy') AS 'date in dd/mm/yyyy Format' SELECT FORMAT(@Vardate, 'dd/mm/yy') AS 'date in dd/mm/yy Format' SELECT FORMAT(@Vardate, 'd/m/yy') AS 'date in d/m/yy Format' SELECT FORMAT(@Vardate, 'mm/dd/yyyy') AS 'date in mm/dd/yyyy Format' SELECT FORMAT(@Vardate, 'MMMM dddd yyyy hh:mm:ss:mmmm') AS 'date in MMMM dddd yyyy hh:mm:ss:mmmm Format' SELECT FORMAT(@Vardate, 'MMMM yyyy, dddd hh:mm:ss:mmmm') AS 'date in MMMM yyyy, dddd hh:mm:ss:mmmm Format'
SQL Format Currency using Culture
In this case, we are going to format the Currency values based on the specified culture.
DECLARE @Sales INT = 3325 SELECT FORMAT(@Sales, 'c', 'en-US' ) AS 'USA Currency' SELECT FORMAT(@Sales, 'c', 'ru-RU' ) AS 'Russian Currency' SELECT FORMAT(@Sales, 'c', 'hi-IN' ) AS 'Indian Currency' SELECT FORMAT(@Sales, 'c', 'de-DE' ) AS 'Indian Currency'
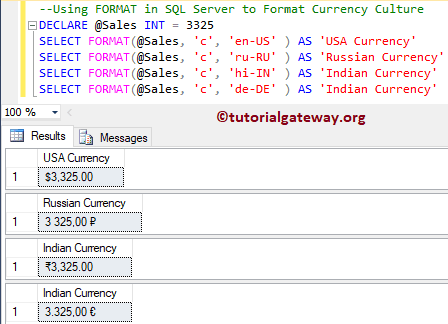
In this SQL example, we use this to format the Currency. Using this approach, you can simply display the country’s Currency symbols before the Money or Value.
DECLARE @Sales DECIMAL(8, 4) = 3325.2569 SELECT FORMAT(@Sales, 'c' ) AS 'Result 1' SELECT FORMAT(@Sales, 'c0' ) AS 'Result 2' SELECT FORMAT(@Sales, 'c1' ) AS 'Result 3' SELECT FORMAT(@Sales, 'c2' ) AS 'Result 4' SELECT FORMAT(@Sales, 'c3' ) AS 'Result 5' SELECT FORMAT(@Sales, 'c4' ) AS 'Result 6'
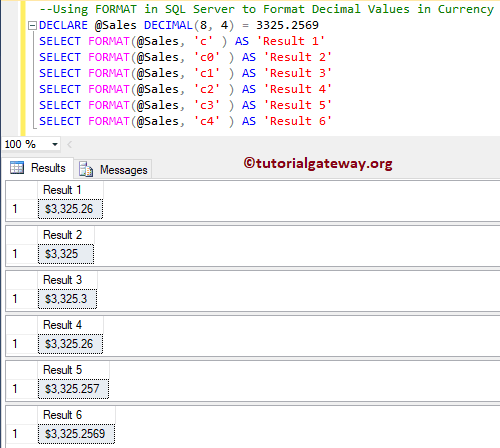
Sql Server Format Currency Decimals
In this example, we are going to format the decimal values in Currency using this.
DECLARE @Sales DECIMAL(8, 4) = 3325.2569 SELECT FORMAT(@Sales, 'c', 'en-US' ) AS 'Result 1' SELECT FORMAT(@Sales, 'c0', 'hi-IN' ) AS 'Result 2' SELECT FORMAT(@Sales, 'c1', 'ru-RU') AS 'Result 3' SELECT FORMAT(@Sales, 'c2', 'fr-FR' ) AS 'Result 4' SELECT FORMAT(@Sales, 'c3', 'de-DE') AS 'Result 5' SELECT FORMAT(@Sales, 'c4', 'zh-CN') AS 'Result 6'
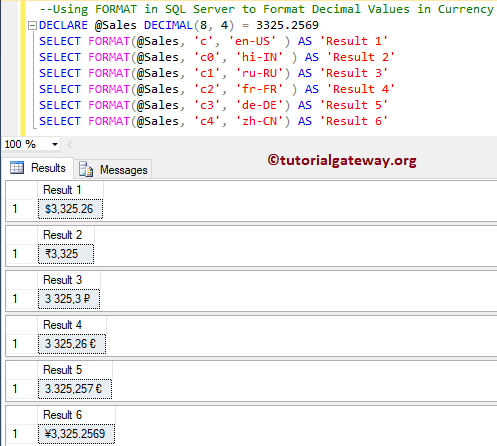
Using Culture
In this example, we will use the function to format Numbers. Culture specifies the number formats. I mean, some countries separate 100s, and others separate 1000s, etc.
DECLARE @Number DECIMAL(11, 4) = 1453325.2569 SELECT FORMAT(@Number, 'N', 'en-US') AS 'Result 1' SELECT FORMAT(@Number, 'N', 'en-IN' ) AS 'Result 2' SELECT FORMAT(@Number, 'N', 'ru-RU') AS 'Result 3' SELECT FORMAT(@Number, 'N', 'fr-FR' ) AS 'Result 4' SELECT FORMAT(@Number, 'N', 'de-DE') AS 'Result 5' SELECT FORMAT(@Number, 'N', 'zh-CN') AS 'Result 6'
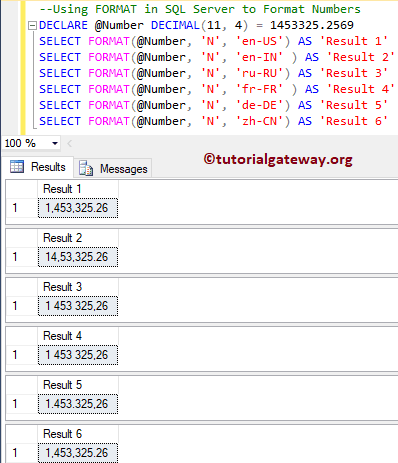
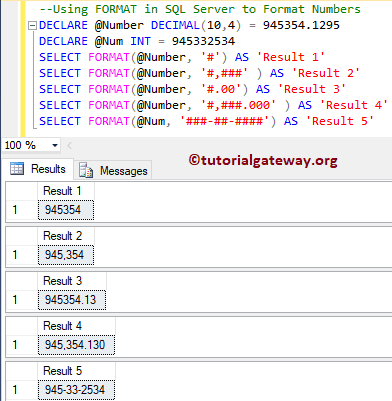
Format Numbers
In this example, we are going to format numbers. To format the numbers, you can use the # symbols. Or, you can also use 0 to specify the number of decimal values.
DECLARE @Number DECIMAL(10,4) = 945354.1295 DECLARE @Num INT = 945332534 SELECT FORMAT(@Number, '#') AS 'Result 1' SELECT FORMAT(@Number, '#,###' ) AS 'Result 2' SELECT FORMAT(@Number, '#.00') AS 'Result 3' SELECT FORMAT(@Number, '#,###.000' ) AS 'Result 4' SELECT FORMAT(@Num, '###-##-####') AS 'Result 5'