Every error recognizes with a specific number. This Error Number function will help us to fetch that error number when the SQL server identifies errors during the query execution. This Error Number function works within the scope of a TRY CATCH block.
For example, we write a series of statements inside the TRY block. And if the SQL Server finds an error, then ERROR_NUMBER inside the CATCH block will be executed and returns the corresponding error.
SQL ERROR NUMBER Function Syntax
The basic syntax of the Error_Number in SQL Server is as shown below:
ERROR_NUMBER()
TIP: The ERROR_NUMBER() function takes no arguments and returns an integer value as the output.
Following SQL statement will return the Error Numbers (message_id) and the corresponding text (ERROR_MESSAGE). Here, we highlighted the well know error number 8134, which is the Divide by Zero error encountered
SELECT * FROM sys.messages
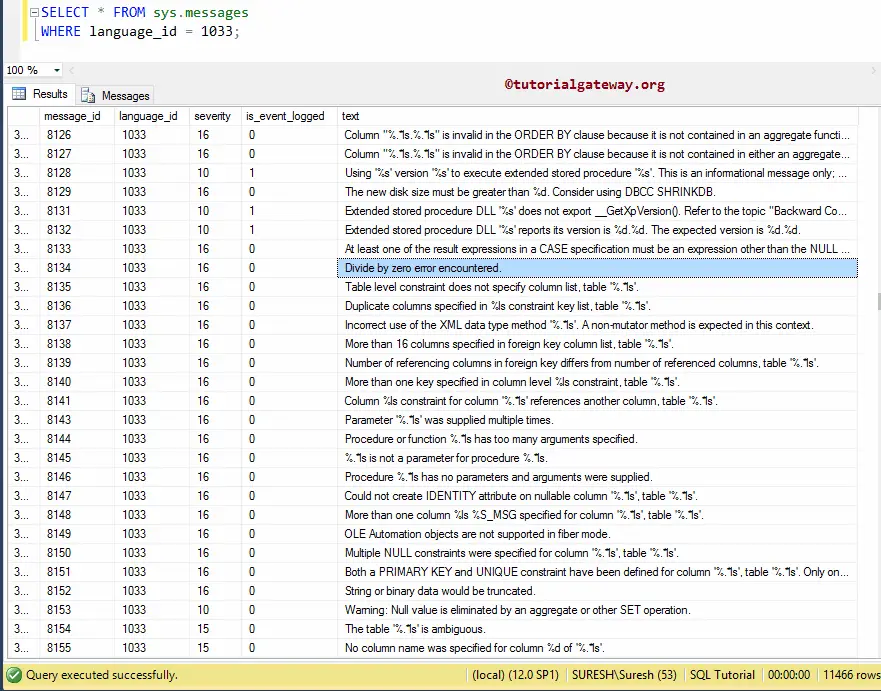
SQL ERROR NUMBER example
In this example, we are going to show you how to use the Error_Number function to return the error number.
BEGIN TRY
DECLARE @Number tinyint,
@Result tinyint;
SET @Number = 252;
SET @Result = @Number + 10;
SELECT @Number AS Number,
@Result AS Result;
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
PRINT N'Error Number = ' + CAST(ERROR_NUMBER() AS nvarchar(100));
END CATCH
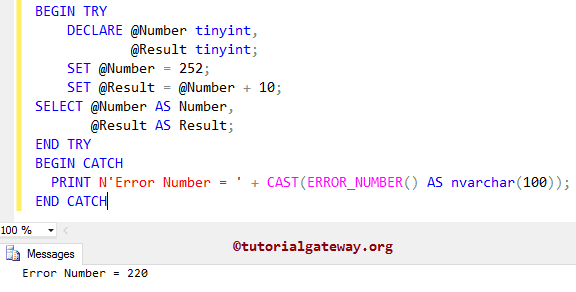
First, we declared two tinyint variables.
DECLARE @Number tinyint,
@Result tinyint;
Next, we assigned 252 to the Number variable and 262 to the Result variable.
SET @Number = 252; SET @Result = @Number + 10;
As we all know, that tinyint holds numbers from 0 to 255 means Overflow. So, it exits from the TRY block and executes the statement inside our CATCH block, which is:
PRINT N'Error Number = ' + CAST(ERROR_NUMBER() AS nvarchar(100));
ERROR NUMBER example 2
In this example, we are going to find the result of 1/0.
BEGIN TRY SELECT 1/0 AS Result; END TRY BEGIN CATCH SELECT ERROR_NUMBER() AS ErrorNumber; END CATCH
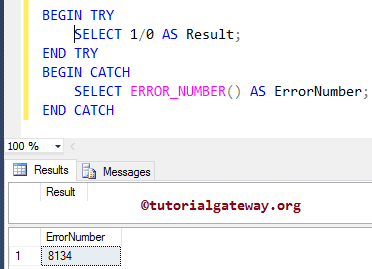
Within the TRY block, we are finding the result of 1/0
SELECT 1/0 AS Result;
We all know that the above SQL Server statement will throw an error. So, the Error Number inside the CATCH block will execute.
SELECT ERROR_NUMBER() AS ErrorNumber;
