This function converts an expression from one data type to another. If the SQL Server cannot CONVERT an expression into the desired data type, then it returns an Error. For this SQL convert demonstration, we use the Employee table.
SQL Server CONVERT Function Syntax
The syntax of the SQL CONVERT Function
CONVERT (Data_Type [(Length)], Expression, [Style]) -- For example SELECT CONVERT (VARCHAR(50), 245) AS [resultName] FROM [Source]
- Data_Type: Specify the Data Type to which you want to transform an expression
- Length: It is an optional parameter of integer type. You can use this parameter to specify the length of the target data type. By default, it is 30.
- An expression that you want to convert into the desired data type.
- Style: use this optional parameter of integer type to define the style.
SQL CONVERT Function to format Date
The list of formatting styles is available in the SQL Server CONVERT function.
| Without Century (yy) | With Century (yyyy) | Standard | Input/Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| – | 0 to 100 | This is the Default for both datetime and smalldatetime | mon dd yyyy hh:miAM (or PM) |
| 1 | 101 | The U.S. | 1 = mm/dd/yy 101 = mm/dd/yyyy |
| 2 | 102 | ANSI | 2 = yy.mm.dd 102 = yyyy.mm.dd |
| 3 | 103 | British/French | 3 = dd/mm/yy 103 = dd/mm/yyyy |
| 4 | 104 | German | 4 = dd.mm.yy 104 = dd.mm.yyyy |
| 5 | 105 | Italian | 5 = dd-mm-yy 105 = dd-mm-yyyy |
| 6 | 106 | – | 6 = dd mon yy 106 = dd mon yyyy |
| 7 | 107 | – | 7 = Mon dd, yy 107 = Mon dd, yyyy |
| 8 | 108 | – | hh:mi:ss |
| – | 9 or 109 | Default + milliseconds | mon dd yyyy hh:mi:ss:mmmmAM (or PM) |
| 10 | 110 | USA | 10 = mm-dd-yy 110 = mm-dd-yyyy |
| 11 | 111 | JAPAN | 11 = yy/mm/dd 111 = yyyy/mm/dd |
| 12 | 112 | ISO | 12 = yymmdd 112 = yyyymmdd |
| – | 13 or 113 | Europe Default + millisecond | dd mon yyyy hh:mi:ss:mmm(24h) |
| 14 | 114 | – | hh:mi:ss:mmm(24h) |
| – | 20 or 120 | ODBC canonical | yyyy-mm-dd hh:mi:ss(24h) |
| – | 21 or 121 | ODBC canonical with milliseconds. This is the Default for time, date, datetime2, and datetimeoffset | yyyy-mm-dd hh:mi:ss.mmm(24h) |
| – | 126 | ISO8601 | yyyy-mm-ddThh:mi:ss.mmm (no Spaces) |
| – | 127 | ISO8601 with time zone Z | yyyy-mm-ddThh:mi:ss.mmmZ (no Spaces) |
| – | 130 | Hijri | dd mon yyyy hh:mi:ss:mmmAM |
| – | 131 | Hijri | dd/mm/yyyy hh:mi:ss:mmmAM |
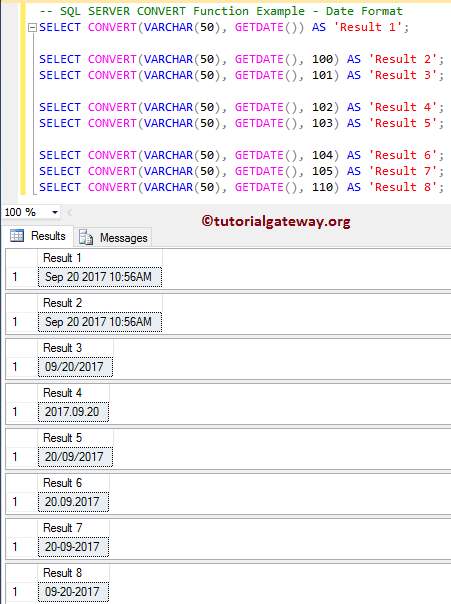
SQL CONVERT Function to Format DATE
In this example, we use the SQL CONVERT function on GETDATE() to return the date in different formats.
SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(50), GETDATE()) AS 'Result 1'; SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(50), GETDATE(), 100) AS 'Result 2'; SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(50), GETDATE(), 101) AS 'Result 3'; SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(50), GETDATE(), 102) AS 'Result 4'; SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(50), GETDATE(), 103) AS 'Result 5'; SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(50), GETDATE(), 104) AS 'Result 6'; SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(50), GETDATE(), 105) AS 'Result 7'; SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(50), GETDATE(), 110) AS 'Result 8';
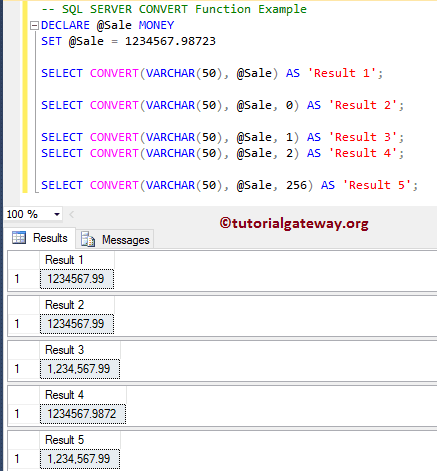
SQL Server CONVERT Money Format Example
If an expression is a money or small money, then we can use the style argument to stylize. The list of money formatting styles that are available in the SQL Server CONVERT function is.
| Value | Output |
|---|---|
| 0 | It will only return two digits after the decimal point |
| 1 | It will separate every three digits by placing a comma. It will also return two digits after the decimal point. |
| 2 | This return four digits after the decimal point |
| 126 | This is equivalent to 2 when you are changing to char or varchar. |
DECLARE @Sale MONEY SET @Sale = 1234567.98723 SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(50), @Sale) AS 'Result 1'; SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(50), @Sale, 0) AS 'Result 2'; SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(50), @Sale, 1) AS 'Result 3'; SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(50), @Sale, 2) AS 'Result 4'; SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(50), @Sale, 256) AS 'Result 5';
SQL Convert float values Example
We can use the style argument when an expression is float or real. The following are the formatting styles that are available in the SQL CONVERT function.
| Value | Output |
|---|---|
| 0 | This returns a maximum of 6 digits |
| 1 | It always returns 16 digits. Always use Scientific notation |
| 2 | It always returns 16 digits. Always use in Scientific notation |
| 3 | It returns eight digits. Always use Scientific notation |
DECLARE @Sale FLOAT SET @Sale = 1234567.98723 SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(50), @Sale) AS 'Result 1'; SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(50), @Sale, 0) AS 'Result 2'; SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(50), @Sale, 1) AS 'Result 3'; SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(50), @Sale, 2) AS 'Result 4'; SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(50), @Sale, 3) AS 'Result 5';

Null Values Example
In this SQL convert function example, we will work with NULL values.
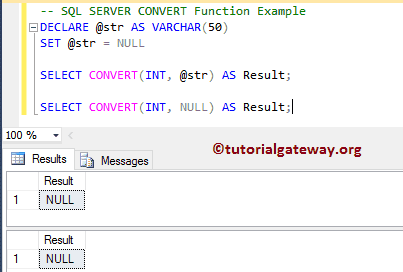
DECLARE @str AS VARCHAR(50) SET @str = NULL SELECT CONVERT(INT, @str) AS Result; SELECT CONVERT(INT, NULL) AS Result;
Suppose we use the SQL Server Convert function to change the ‘Tutorial Gateway’ string to date time. As you can see, it is impossible, so it returns an Error as output.
SELECT CONVERT(INT, 'Tutorial Gateway') AS Result;
Execute the above Transact query.
Msg 245, Level 16, State 1, Line 2
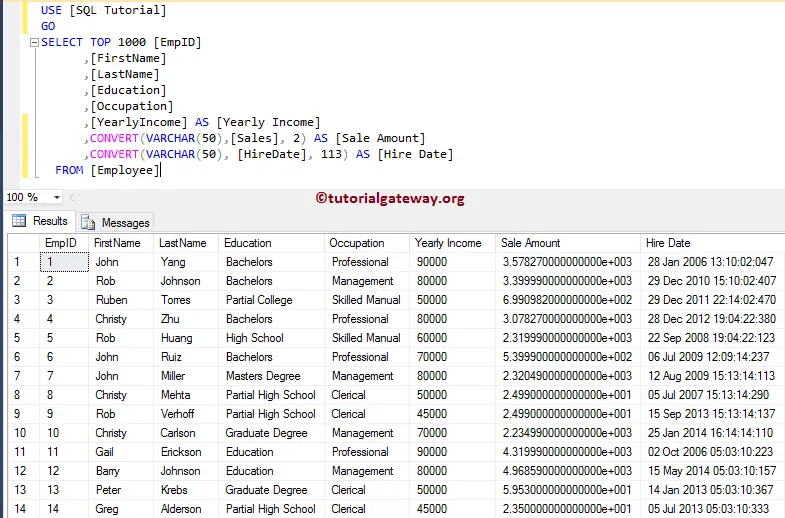
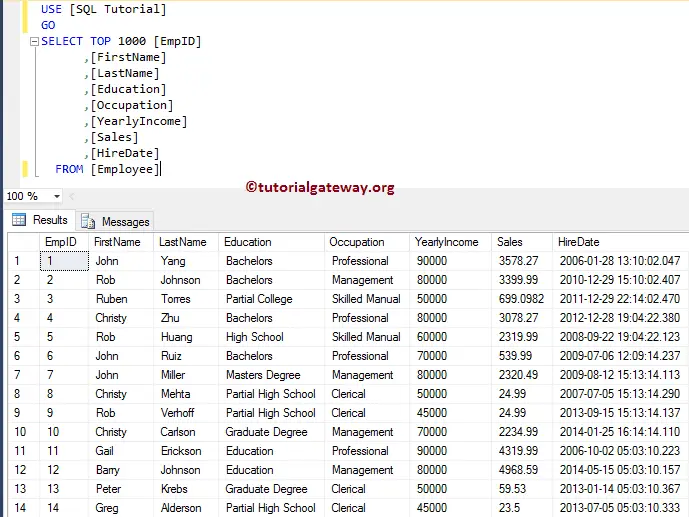
Failed converting the Varchar value 'Tutorial Gateway' to data type int.We will apply this to our Employee table in this SQL Server Convert Function example.
SELECT TOP 1000 [EmpID]
,[FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome] AS [Yearly Income]
,CONVERT(VARCHAR(50),[Sales], 2) AS [Sale Amount]
,CONVERT(VARCHAR(50), [HireDate], 113) AS [Hire Date]
FROM [Employee]