In real-time, dealing with table NULL values is very difficult when performing aggregations, comparisons, or mathematical calculations. The SQL COALESCE function is one of the few options to deal with NULLS. This article will show you how to use the COALESCE function, syntax, benefits, and handling table nulls with an example.
The SQL Server COALESCE function returns the first not Null value from the series of expressions. It allows you to replace the NULL value with alternative non-empty values. The SQL COALESCE function accepts multiple expressions as the input parameter and evaluates them in the order they provide. It simply returns the first not Null value, and if all the expressions are NULLs, it returns NULL as the output.
The basic syntax behind this function is:
COALESCE (expression1, expression2, ......, expressionN)
SQL COALESCE Function example
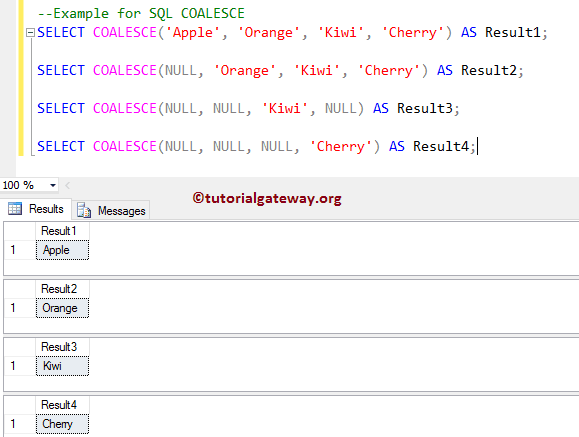
Use this SQL Coalesce on String data. The first statement returns Apple as the Output because this function will return the first non empty value.
The second SQL Server statement returns Orange as the Output. Because the first one is Null, the function always returns the first not empty value.
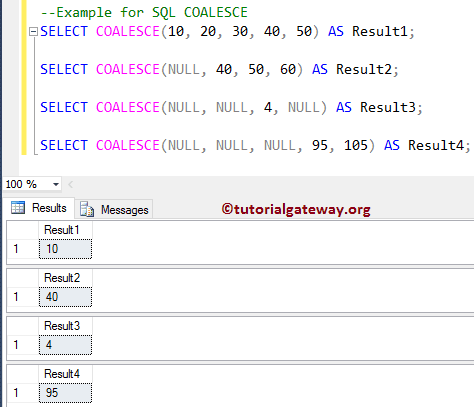
The working functionality of Coalesce on Numerical values
SQL COALESCE Practical example
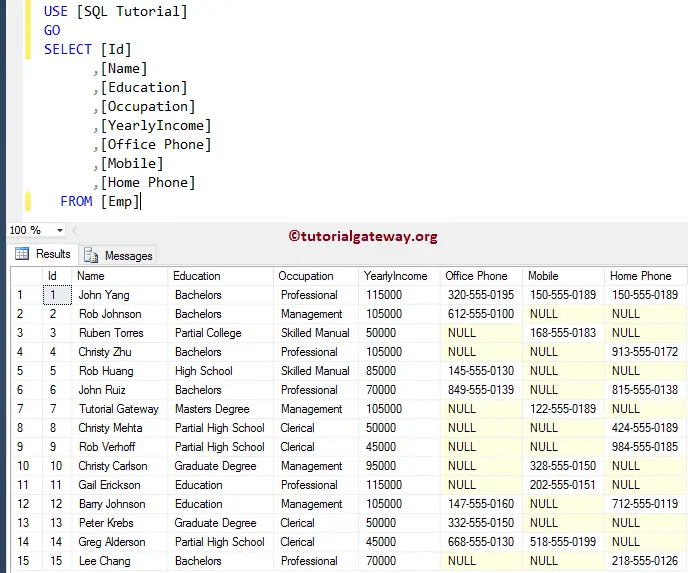
How to write this SQL Server Coalesce function on a table with a practical example that you might see in real-time. For this demonstration, we use the [Emp] table.
The following screenshot shows you the data inside the Emp table. As you can see, it has 15 records.
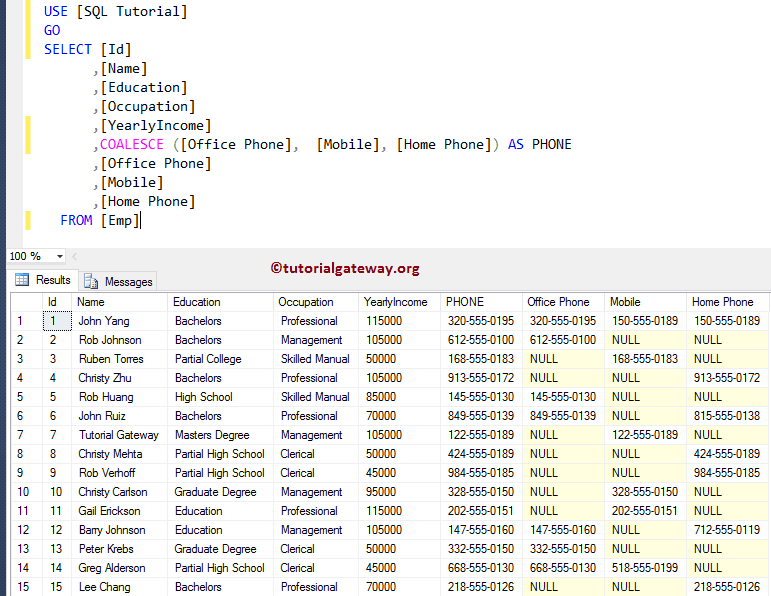
In this example, we will use the SQL Coalesce function to find out the contact number of each employee:
- If an employee has an Office number, the function returns the office number.
- If an employee does not have an Office number but has a Mobile, this function displays the Mobile.
- And, If our employee in the Emp table does not have an Office or Mobile number but has a Home phone, it displays the Home number.
- If an employee has an Office, Mobile, and Home, then it will return the first non-empty, i.e., office number.
SELECT [Id]
,[Name]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,COALESCE ([Office Phone], [Mobile], [Home Phone]) AS PHONE
,[Office Phone]
,[Mobile]
,[Home Phone]
FROM [Emp]

Comments are closed.