The SQL CHOOSE function is the new built-in Logical function introduced in SQL Server 2012. This Choose function returns the item at the specified index from the list of items.
SQL CHOOSE Syntax
The syntax of the CHOOSE Logical Function in SQL Server is shown below.
CHOOSE (Index, Value1, Value2, ....,ValueN)
Index: Please specify the index position of the required item. The index position should start at 1.
- If the specified index value has a numeric data type other than an integer, the numeric value will implicitly convert to an integer type. For example, 10.68 will convert to 10.
- If there are no items in the specified index or index out of range, then CHOOSE function returns a NULL value.
Value1, Value2…,ValueN are the array of items.
SQL CHOOSE Function example
This example will show you the working functionality of CHOOSE function.
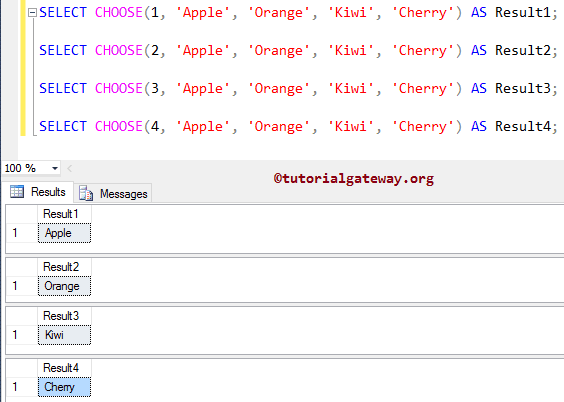
SELECT CHOOSE(1, 'Apple', 'Orange', 'Kiwi', 'Cherry') AS Result1; SELECT CHOOSE(2, 'Apple', 'Orange', 'Kiwi', 'Cherry') AS Result2; SELECT CHOOSE(3, 'Apple', 'Orange', 'Kiwi', 'Cherry') AS Result3; SELECT CHOOSE(4, 'Apple', 'Orange', 'Kiwi', 'Cherry') AS Result4;
SQL CHOOSE Function Index Out of Range
In this example, we are going to use the CHOOSE function with index value 0, negative index values, and non-indexing values.
SELECT CHOOSE(0, 'Apple', 'Orange', 'Kiwi', 'Cherry') AS Result1; SELECT CHOOSE(-2, 'Apple', 'Orange', 'Kiwi', 'Cherry') AS Result2; SELECT CHOOSE(6, 'Apple', 'Orange', 'Kiwi', 'Cherry') AS Result3;
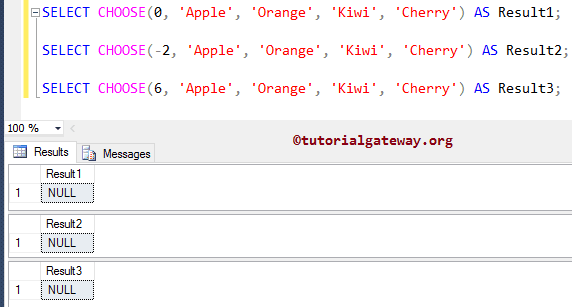
Within this choose function example, the below statement is returning a NULL value because the index value should start with one or greater than 1.
SELECT CHOOSE(0, 'Apple', 'Orange', 'Kiwi', 'Cherry') AS Result1; SELECT CHOOSE(-2, 'Apple', 'Orange', 'Kiwi', 'Cherry') AS Result2;
Below SQL Server statement is returning a NULL value because we are passing the index value as six. And we don’t have any item in the sixth position.
SELECT CHOOSE(6, 'Apple', 'Orange', 'Kiwi', 'Cherry') AS Result3;
Decimal values
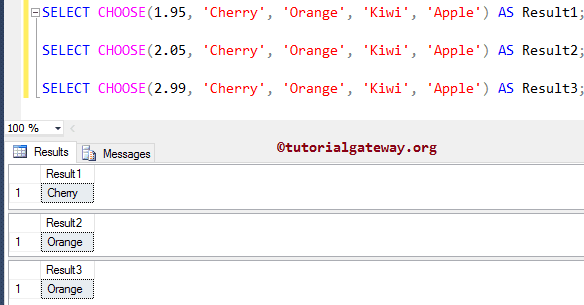
In this example, we are going to use the SQL Server CHOOSE function with numeric or decimal values. Here, decimal values will round to an integer. It means 1.95 will round to 1, 2.05, and 2.99 rounded to 2.
SELECT CHOOSE(1.95, 'Cherry', 'Orange', 'Kiwi', 'Apple') AS Result1; SELECT CHOOSE(2.05, 'Cherry', 'Orange', 'Kiwi', 'Apple') AS Result2; SELECT CHOOSE(2.99, 'Cherry', 'Orange', 'Kiwi', 'Apple') AS Result3;
SQL CHOOSE Function String values
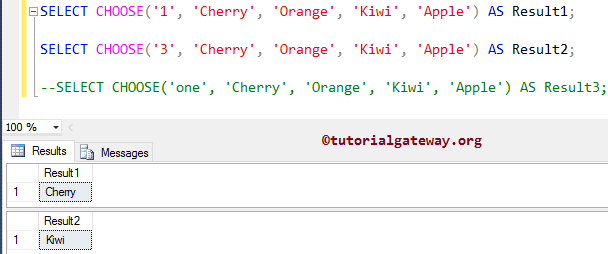
In this example, we use the CHOOSE function with string values. Here varchar 1 and 3 will be converted to the integer data type.
SELECT CHOOSE('1', 'Cherry', 'Orange', 'Kiwi', 'Apple') AS Result1;
SELECT CHOOSE('3', 'Cherry', 'Orange', 'Kiwi', 'Apple') AS Result2;
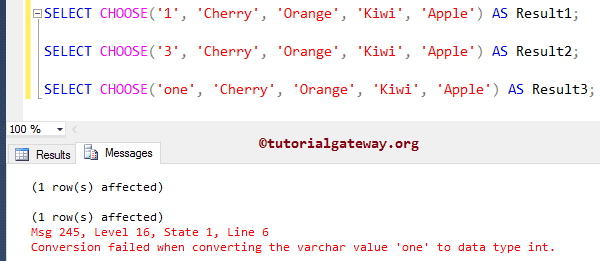
Here SQL Server is unable to convert the Varchar value one to an integer data type. So, it is throwing an error.
SELECT CHOOSE('one', 'Cherry', 'Orange', 'Kiwi', 'Apple') AS Result3;
Practical example
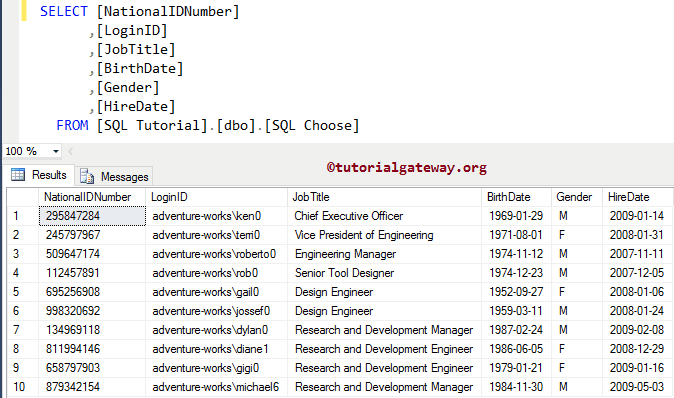
In this example, we are using the AdventureWorks database, and the query we used to extract the data is as shown below:
SELECT TOP 10
[NationalIDNumber]
,[LoginID]
,[JobTitle]
,[BirthDate]
,[Gender]
,[HireDate]
FROM [AdventureWorks2014].[HumanResources].[Employee]
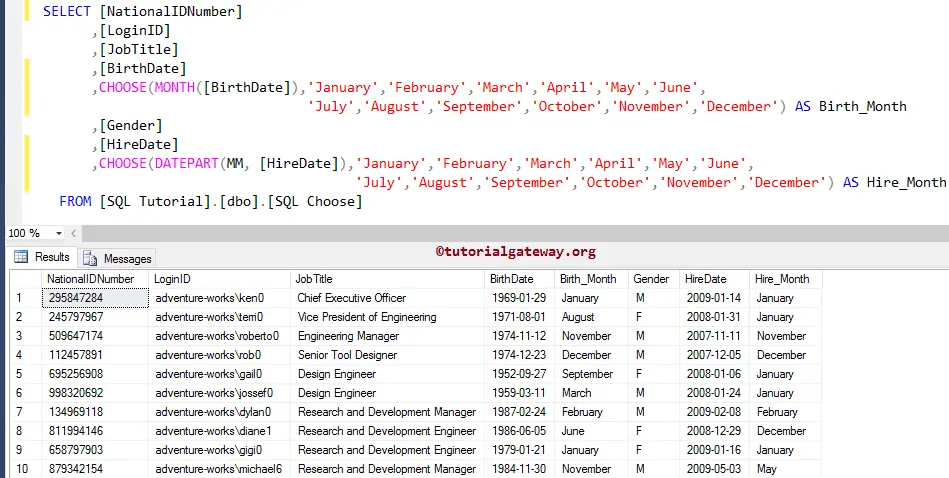
The following screenshot will show you the data inside the table. In this example, we will use the SQL server CHOOSE function to convert the Month numbers to January, February so on.
From the below code snippet, you can observe that we can extract the Month number using the built-in function MONTH and DATEPART. That’s why we used both the functions
SELECT [NationalIDNumber]
,[LoginID]
,[JobTitle]
,[BirthDate]
,CHOOSE(MONTH([BirthDate]),'January','February','March','April','May','June',
'July','August','September','October','November','December') AS Birth_Month
,[Gender]
,[HireDate]
,CHOOSE(DATEPART(MM, [HireDate]),'January','February','March','April','May','June',
'July','August','September','October','November','December') AS Hire_Month
FROM [SQL Tutorial].[dbo].[SQL Choose]