The SQL ASCII function is used to return the ASCII code of the leftmost character of a character expression. The syntax of the ASCII Function is
SELECT ASCII (Character_Expression) FROM [Source]
Character_Expression: Please specify the valid Expression for which you want to find the ASCII code. This SQL Function will return the ASCII code of the leftmost character of this expression. The Character_Expression can be a Char or Varchar. The return value of this string function will be INT.
SQL ASCII Function Example
The Function returns the ASCII code of the leftmost character of the given expression. The following query will show multiple ways to use this method.
TIP: Please refer to the Table to check the character codes of each character.
DECLARE @i VARCHAR(25)
DECLARE @j INT
-- Initialize the variables.
SET @i = 'a'
SET @j = 1
SELECT ASCII(@i) AS Result1,
ASCII(@j) AS Result2 ;
SELECT ASCII('efgh') AS Result3;
SELECT ASCII('789') AS Result4;
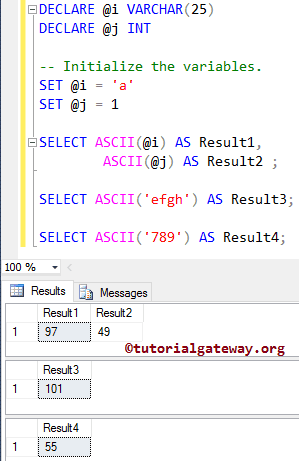
We are finding the ASCII code of the alphabet ‘a’ and integer 1. We also assigned new names to the result as ‘Result1’, and ‘Result2’ using the ALIAS Column in the SQL Server.
SELECT ASCII(@i) AS Result1,
ASCII(@j) AS Result2 ;
In the following line, we used the SQL ASCII function directly on a group of characters (word). Here, it will return the leftmost character (i.e., e), and that should be 101
SELECT ASCII('efgh') AS Result3;
Next, we used it directly on the integer. Here, String Functions will return the leftmost character (i.e., 7), and that should be 55
SELECT ASCII('789') AS Result4;
How to use ASCII Function in a While loop?
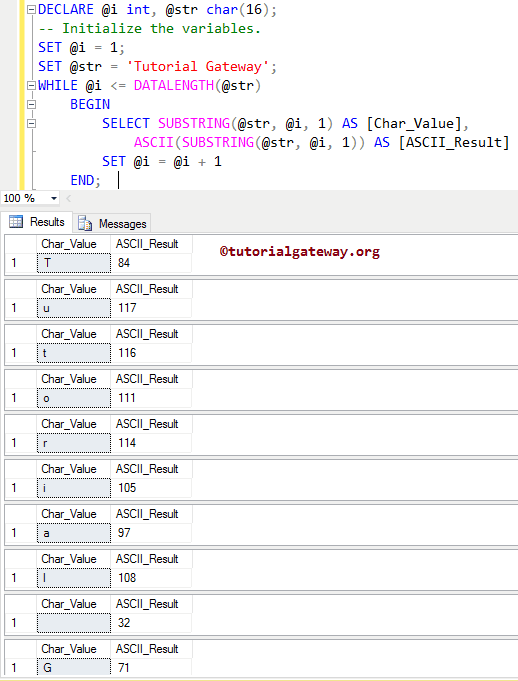
In this example, We are going to use the ASCII function inside the WHILE LOOP. I suggest you refer to both the SUBSTRING and WHILE LOOP articles.
DECLARE @i int,
@str char(16);
-- Initialize the variables.
SET @i = 1;
SET @str = 'Tutorial Gateway';
WHILE @i <= DATALENGTH(@str)
BEGIN
SELECT SUBSTRING(@str, @i, 1) AS [Char_Value],
ASCII(SUBSTRING(@str, @i, 1)) AS [ASCII_Result]
SET @i = @i + 1
END;
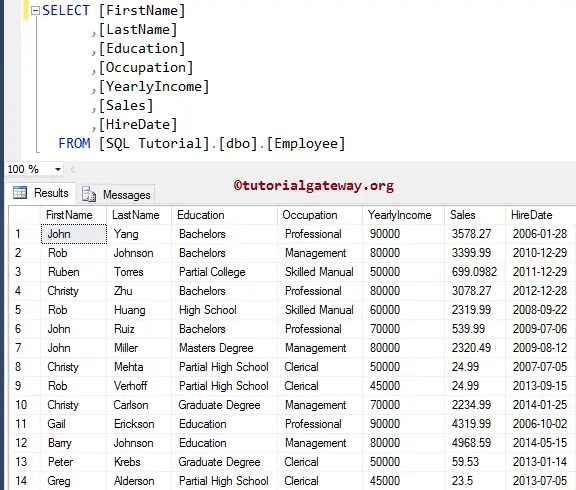
How to get the ASCII values of a Table Column?
In this example, we are going to implement the SQL Server ASCII function on the column. For this, We use the below-shown data.
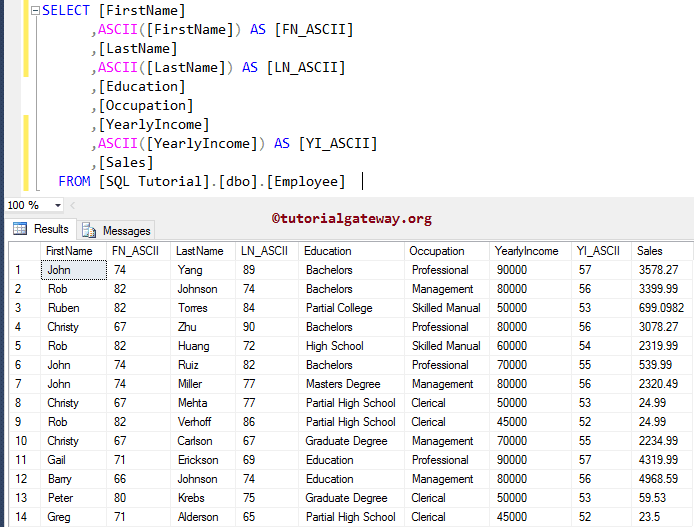
The following statement will return the ASCII code of the leftmost character in the [FirstName] column and [LastName] column and the leftmost number in the [YearlyIncome] column.
SELECT [FirstName]
,ASCII([FirstName]) AS [FN_ASCII]
,[LastName]
,ASCII([LastName]) AS [LN_ASCII]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,ASCII([YearlyIncome]) AS [YI_ASCII]
,[Sales]
FROM [Employee]
As you can see from the image, 74 is the code of J, 89 is for Y, and 57 is for 9.