The SQL Server Instead Of INSERT Trigger will fire before the Insert operation on a table starts. The SQL Instead of Insert Triggers can be created in Tables and Views. In general, we use them on View. For this SQL Server Instead Of INSERT Trigger demonstration, We use the below-shown tables.
Here, our task is to create SQL INSTEAD OF INSERT TRIGGER on this Employee table. And by using this INSTEAD Of INSERT Triggers, we want to restrict the records inserting into Employee Table. Also insert records into the Audit table, along with the audit information
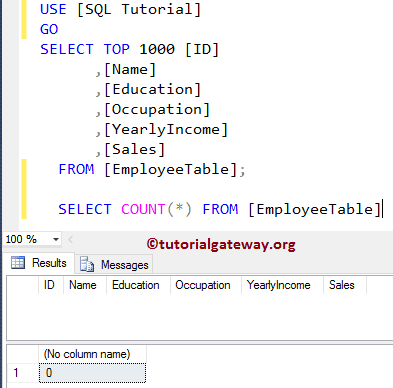
and our Employee Table Audit is also empty
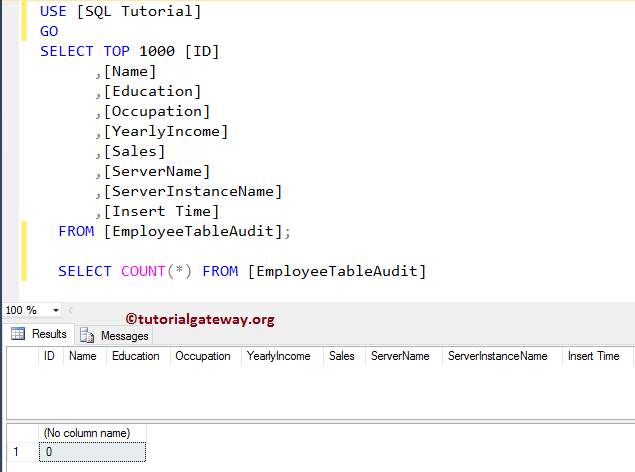
Instead Of INSERT Triggers in SQL Server Example
Next, we will create Instead of insert Triggers in SQL Server on the Employee table using the CREATE TRIGGER statement.
Remember, this trigger will fire before the Insert operation on the Employee table starts. Once it completes inserting into the Employee Audit table, it will begin to insert into the Employee table. And if it fails for some reason, it won’t insert into the Employee table.
TIP: You can refer Views, TRIGGERS, INSTEAD OF DELETE TRIGGERS, and INSTEAD OF UPDATE TRIGGERS articles in SQL Server.
From the below code snippet, you can see that we are using the INSERT INTO SELECT Statement to select all the records that are inserting into the Employee table, and then
- We are inserting the records whose yearly Income is less than or equal to 70000 into the Audit table, and.
- Whose yearly Income is greater than 70000 into the Employee table
-- Example for INSTEAD OF INSERT Triggers in SQL Server
CREATE TRIGGER InsteadOfINSERTTriggerExample on [EmployeeTable]
INSTEAD OF INSERT
AS
BEGIN
INSERT INTO [EmployeeTableAudit](
[ID],
[Name],
[Education],
[Occupation],
[YearlyIncome],
[Sales],
[ServerName],
[ServerInstanceName],
[Insert Time])
SELECT ID,
Name,
Education,
Occupation,
YearlyIncome,
Sales,
CAST( SERVERPROPERTY('MachineName') AS VARCHAR(50)),
CAST( SERVERPROPERTY('ServerName') AS VARCHAR(50)),
GETDATE()
FROM INSERTED
WHERE YearlyIncome <= 70000;
PRINT 'We Successfully Fired Our INSTEAD OF INSERT Triggers in SQL Server.';
INSERT INTO [EmployeeTable](
[Name],
[Education],
[Occupation],
[YearlyIncome],
[Sales])
SELECT Name,
Education,
Occupation,
YearlyIncome,
Sales
FROM INSERTED
WHERE YearlyIncome > 70000;
END
GO
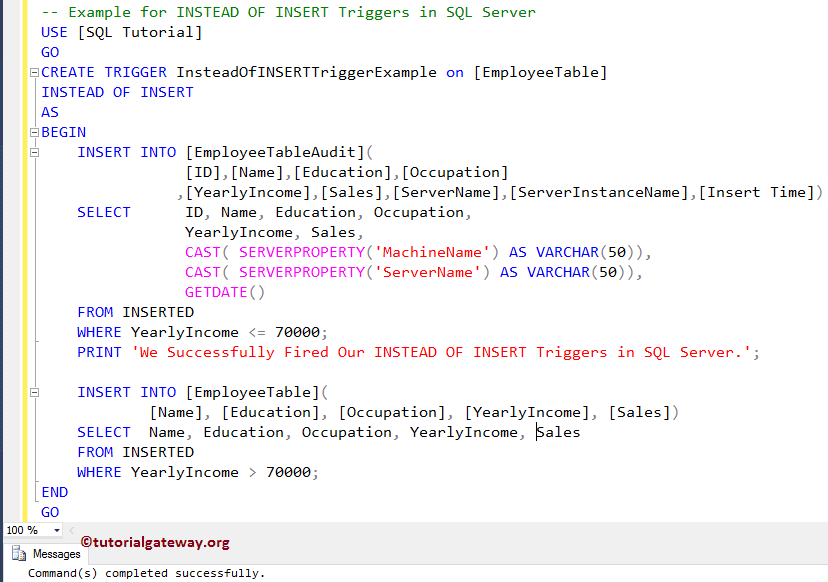
Here, we used the INSERT Statement to insert the selected values into the Employee Table. And the following statements will return the Machine Name and the server name. This information might be helpful for the audit
SERVERPROPERTY('MachineName'),
SERVERPROPERTY('ServerName')
Let me show you the newly created Instead Of INSERT Triggers in SQL Server by opening the Object Explorer. Next, Go to the SQL Tutorial Database, expand the Employee Table, and then expand the Triggers Folder
For the SQL Server Instead Of INSERT Triggers demo, we are inserting 14 records in the Employee into the Employee table to check whether the Instead of insert Trigger triggered or not.
-- Example for Instead of INSERT Triggers in SQL Server
INSERT INTO [EmployeeTable] ([Name]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales])
SELECT [Firstname] + ' '[LastName]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
FROM [Employee]
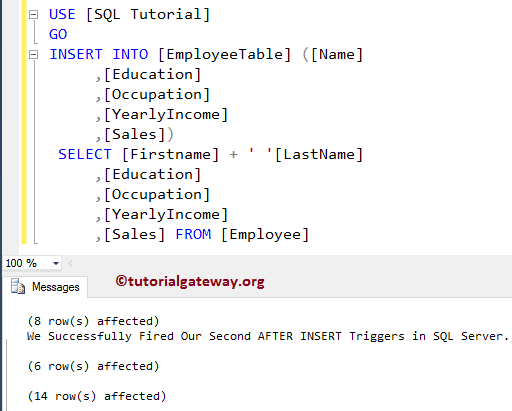
From the above screenshot, you can see that our SQL Server Instead Of INSERT Triggers triggered. And, instead of inserting 14 records into the Employee table, it inserted 8 records into the Audit Table and 6 records into the Employee table. Please use the following SQL Query to check the inserted records in the Employee table
-- Example for SQL Instead of INSERT Triggers
SELECT [ID]
,[Name]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
FROM [EmployeeTable]
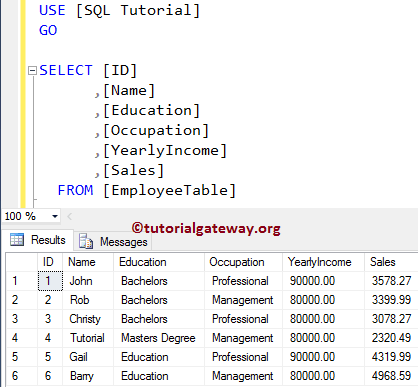
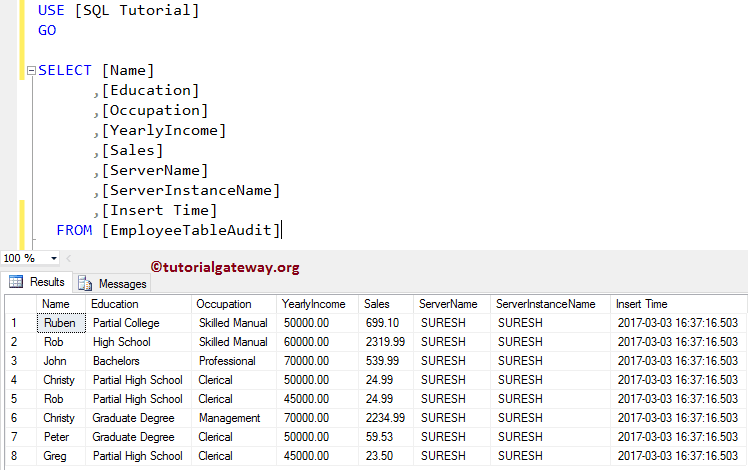
Next, check the records in the Employee table Audit using the following query.
-- Example for SQL Instead of INSERT Triggers
SELECT [Name]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
,[ServerName]
,[ServerInstanceName]
,[Insert Time]
FROM [EmployeeTableAudit]
You can also try with the conditions, something like: Insert the records into Employee table whose Yearly Income is greater than 7000. Otherwise, throw an error (or message), etc.

Comments are closed.