In real-time, a function in C may define with or without parameters, and it may or may not return a value. It entirely depends upon the user requirement. In C Programming, as per our requirement, we can define the User-defined functions in multiple ways. The following are a list of available types of Functions in C
- Function with no argument and no Return value.
- With no argument and with a Return value.
- With argument and No Return value.
- With argument and Return value.
From the above, 1 and 3 types of functions in c do not return any value when we call them. So, We use the void return type while defining those.
When we call the 2 and 4 types of functions in C, they will return some value. That’s why we have to use the appropriate data type (int, float, double, etc.) as a return type while defining the function. We use the return keyword inside it to return some value when we call from the main() or any subfunctions.
Types of Functions in C Programming
The following examples will explain to you the available function types in C programming.
C Function with No argument and No Return value
In this method, We won’t pass any arguments to the function while defining, declaring, or calling it. This type of functions in C will not return any value when we call the function from main() or any sub-function. When we are not expecting any return value, we need some statements to print as output. Then, this type of function is very useful.
No argument and No Return value Example
In these types of Functions in C program, We are going to calculate the Sum of 2 integer values and print the output from the udfs itself.
#include<stdio.h>
// Declaration
void Addition();
void main()
{
printf("\n ............. \n");
Addition();
}
void Addition()
{
int Sum, a = 10, b = 20;
Sum = a + b;
printf("\n Sum of a = %d and b = %d is = %d", a, b, Sum);
}
.............
Sum of a = 10 and b = 20 is = 30Within these types of Functions in C example, If you observe the main(), We haven’t passed any arguments /parameters to the Addition()
Within the Addition func, we declared the integer variables of the sum, a, b, and we assigned 10 to a and 20 to b. In the next C Programming line, we calculate the sum using the Arithmetic operator ( + )
Sum = a + b
= 10 + 20
= 30
Below printf statement is used to print the output.
printf("\n Sum of a = %d and b = %d is = %d", a, b, Sum);
Whenever we call the Addition (), it will print the same output because the values of a and b are fixed inside the uff block.
C Function with no argument and with Return value
In this method, We won’t pass any arguments while defining, declaring, or calling the function. This C type of function will return some value when we call it from the main() or any sub method.
The Data Type of the return value will depend upon the return type of function declaration. For instance, if the return type is int, then the return value will be int.
In this C Types of Functions program, We are going to calculate the multiplication of 2 integers using the udf without arguments and return keywords.
#include<stdio.h>
int Multiplication();
int main()
{
int Multi;
Multi = Multiplication();
printf("\n Multiplication of a and b is = %d \n", Multi );
return 0;
}
int Multiplication()
{
int Multi, a = 20, b = 40;
Multi = a * b;
return Multi;
}
Multiplication of a and b is = 800 If you observe the main(), we declare the integer variable Multi. We assigned it to the return value of the Multiplication(). Because UDFs also return integer value only.
Multi = Multiplication();
We haven’t passed any arguments /parameters to the Multiplication()
In the next line, the printf statement is to print the output
printf("\n Multiplication of a and b is = %d \n", Multi);
Whenever we call the Multiplication (), it will print the above statement.
Within the Multiplication (), we declared the integer variables of Multi, a, b, and we assigned 20 to a and 40 to b.
In the next line, we Multiplied both a and b using the Arithmetic operator ( * )
Multi = a * b
= 20 * 40
= 800
Whenever we call the Multiplication (), it prints the same output because the values of a and b are the same inside the method body.
C Function with argument and No Return value
If you observe the above two types of functions in C, No matter how many times you executive, it will give the same output. We don’t have any control over the values of variables a and b because they are fixed values.
In real-time, we mostly deal with dynamic data means we have to allow the user to enter his own values rather than fixed ones.
This method allows us to pass the arguments to the function while calling it. But, This C type of function will not return any value when we call it from main () or any sub method.
If we want to allow the user to pass his data to the arguments, but we are not expecting any return value, this type of function is very useful in real time.
These Types of Functions in C program allows the user to enter 2 integers. Next, We are going to pass those values to the user-defined function to calculate the sum.
#include<stdio.h>
void Addition(int, int);
void main()
{
int a, b;
printf("\n Please Enter two integer values \n");
scanf("%d %d",&a, &b);
//Calling with dynamic values
Addition(a, b);
}
void Addition(int a, int b)
{
int Sum;
Sum = a + b;
printf("\n Additiontion of %d and %d is = %d \n", a, b, Sum);
}
Please Enter two integer values
40
90
Additiontion of 40 and 90 is = 130 If you observe the main(), We declared the integer variables a and b. This program allows the user to enter 2 integers as a and b.
printf("\n Please Enter two integer values \n");
scanf("%d %d",&a, &b);
In the next line, we called the Addition (int a, int b) with the user entered values.
Addition(a, b);
Within the Addition (int a, int b),
We declared the integer variables of Sum, and also we have integer (a, b) arguments in the function. It means this will allow the user to pass 2 integers.
Next, we added both a and b using the Arithmetic operator ( + ). In the next line, the printf statement is to print the output
printf("\n Additiontion of %d and %d is = %d \n", a, b, Sum);
C Function with argument and Return value
This method allows us to pass the arguments to the function while calling it. This type of function in C will return some value when we call it from the main () or any subfunction. The data Type of the return will depend upon the return type of function declaration. For instance, if the return type is int then the return value will be int.
This type of user-defined function is called a fully dynamic one, and it provides maximum control to the end user.
This Types of Functions in C program allows the user to enter 2 integers. And then, We are going to pass those values to the UDFs to multiply them and return the output using the return keyword.
#include<stdio.h>
int Multiplication(int, int);
int main()
{
int a, b, Multi;
printf("\n Please Enter two integer values \n");
scanf("%d %d",&a, &b);
//Calling the with dynamic values
Multi = Multiplication(a, b);
printf("\n Multiplication of %d and %d is = %d \n", a, b, Multi);
return 0;
}
int Multiplication(int a, int b)
{
int Multi;
Multi = a * b;
return Multi;
}
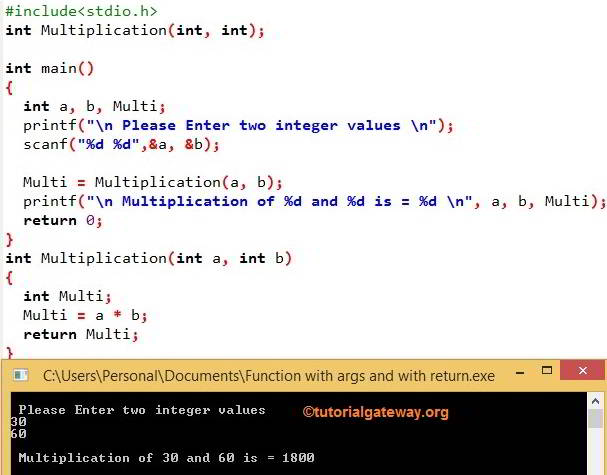
If you observe the main(), We declared the integer variables Multi, a, and b. This program allows the user to enter 2 integers as a and b.
printf("\n Please Enter two integer values \n");
scanf("%d %d",&a, &b);
In the next line, we assigned the return value of the Multiplication(int a, int b) to the Multi integer. It is because the user-defined function also returns integers only.
Multi = Multiplication(a, b);
We passed the user inputs as the arguments /parameters to the Multiplication(int a, int b). In the next line, the printf statement prints the output.
printf("\n Multiplication of a and b is = %d \n", Multi);
Within the Multiplication (), we declared the integer variables of Multi, and also we have two integers (a, b) arguments. It means this will allow the user to pass two integers. In the next line, we Multiplied both a and b using the Arithmetic operator ( * )

Comments are closed.