The UDF or User Defined Functions in SQL Server are like scalar methods in any other programming language that accepts the parameters, perform complex calculations, and return the result value.
Types of Functions in SQL Server
There are two types of SQL Server functions:
- Built-in system.
- User defined.
SQL Server User Defined Functions
SQL Server allows us to create our methods called user defined functions. For example, if we want to perform some complex calculations, then we can place them in a separate method and store them in the database. Whenever we need the calculation, we can call it. There are three types of functions:
Scalar: It returns a single value. Generally, we have to define the body between BEGIN … END blocks, but for the SQL Server user defined inline scalar function, you can omit them. We can use any data type as the return type except text, image, ntext, cursor, and timestamp.
Table Valued: It is a user defined function that returns a table.
Inline Table valued: It returns a table data type based on a single SELECT Statement.
SQL Server Built-in Functions
All the built-ins supported by Microsoft are called System functions. We don’t have to bother about the logic inside them because they cannot be modified. For example, Mathematical, Ranking, and String are some of the many built-in functions.
The aggregate functions to find the sum, minimum value, and average value is mostly used in system methods. And finding the current system date and time is also the most frequent one.
Advantages of SQL User Defined Functions
- The SQL Server User defined functions prevent us from writing the same logic multiple times.
- Within the Database, you can create the method once and call it n number of times.
- They reduce the compilation time of queries by catching the execution plan and reusing them.
- This UDF can help us to separate the complex calculations from the regular query so that we can understand and debug the query quicker and better.
- It reduces the network traffic because of its cache plan
- They are also used in the WHERE Clause as well. By this, we can limit the number of rows sent to the client.
SQL UDFs Syntax
The syntax of the SQL Server user defined functions or UDF is
CREATE FUNCTION Name(@Parameter_Name Data_type,
.... @Parameter_Name Data_type
)
RETURNS Data_Type
AS
BEGIN
-- Function_Body
RETURN Data
END
- Return_Type:
- Data Type: Please specify the data type of return value. For example, VARCHAR, INT, FLOAT, etc.
- Data: Please specify the return value, and it should match the Data Type. It can be a single value or a Table.
- Name: You can specify any name you wish to give other than the system reserved keywords. Please try to use meaningful names so that you can identify them easily.
- @Parameter_Name: Every method accepts zero or more parameters; it completely depends upon the user’s requirements. While declaring the parameters, don’t forget the appropriate data type. For example (@name VARCHAR(50), @number INT)
- Function_Body: Any query or any complex mathematical calculations you want to implement in this particular method.
Let us see how to create or write different types of user defined Functions in SQL Server with an example.
For this SQL UDF demonstration, we will use the [MyEmployee table] and [Department] table in our Database.
TIP: Please refer to Alter UDFs article to understand, How to Rename, Modify, or Delete SQL Server UDFs.
From the below figure, you can observe that the [MyEmployee table] table has fourteen records
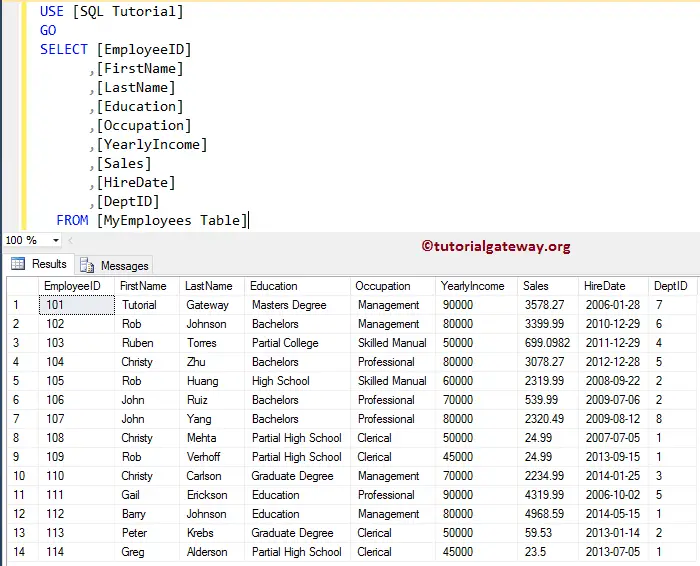
And [Department] table has eight records.
Create SQL User Defined Scalar Function example
These are very useful when you want to return a single value as the resultant. For example, total sales, total investments, loss, expenditure, etc.
Create Scalar Function with No parameters example
In this simple example, we will show you how to create the Sum Scalar functions without any parameters.
From the below aggregate query, you can observe that we are summing the Yearly Income of the MyEmployee table.
-- Scalar example
CREATE FUNCTION NoParameters ()
RETURNS INT
AS
BEGIN
RETURN (SELECT SUM([YearlyIncome]) FROM [MyEmployees Table])
END
Messages
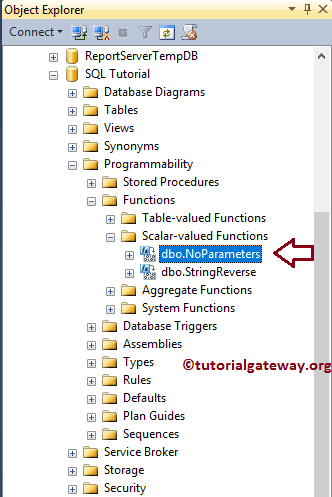
-------
Command(s) completed successfully.Let me show you, How our newly created one looks in the Management Studio
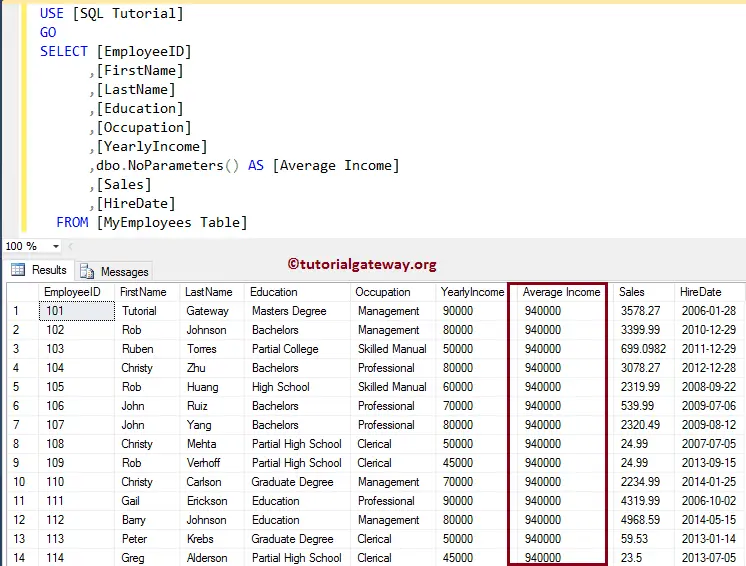
Let us see the Output of the Sum
SELECT [EmployeeID]
,[FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,dbo.NoParameters() AS [Average Income]
,[Sales]
,[HireDate]
FROM [MyEmployees Table]
Create SQL Scalar Function with parameters example
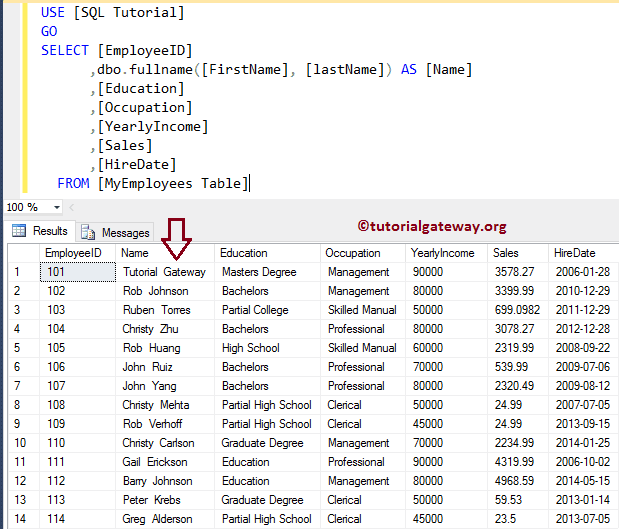
In this example, we will show you, How to create a Scalar function with parameters. From the below query, you can observe that we are concatinating First name and Last Name.
NOTE: We are using the SPACE to provide the space between the First name and last name.
-- Scalar example
CREATE FUNCTION fullName (@firstName VARCHAR(50), @lastName VARCHAR(50))
RETURNS VARCHAR(200)
AS
BEGIN
RETURN (SELECT @firstName + SPACE(2) + @lastName )
END
Let us see the Output by using the below query
SELECT [EmployeeID]
-- Passing Parameters to fullname Function
,dbo.fullname([FirstName], [lastName]) AS [Name]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
,[HireDate]
FROM [MyEmployees Table]
Create SQL User Defined Scalar Function Where Clause
The following SQL scalar functions where clause example will accept the varchar as the parameter. And it finds the sum of the Sales amount, whose Occupation is equal to the parameter that we pass.
-- Scalar example
CREATE FUNCTION average (@Occupation VARCHAR(50))
RETURNS FLOAT
AS
BEGIN
RETURN (SELECT SUM([Sales]) FROM [MyEmployees Table]
WHERE [Occupation] = @Occupation)
END
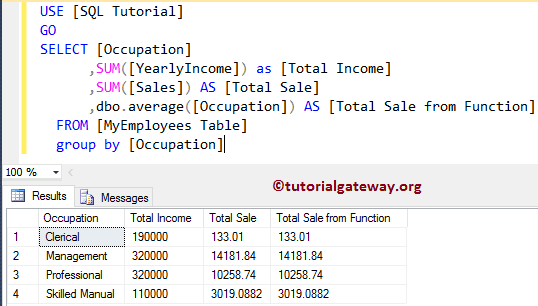
Let us see the Output.
SELECT [Occupation]
,SUM([YearlyIncome]) as [Total Income]
,SUM([Sales]) AS [Total Sale]
,dbo.average([Occupation]) AS [Total Sale from Function]
FROM [MyEmployees Table]
group by [Occupation]
Use in Where Clause Example
In this example, we show you how to use the Scalar UDF in the WHERE Clause
CREATE FUNCTION AverageSale ()
RETURNS FLOAT
AS
BEGIN
RETURN (SELECT AVG([Sales]) FROM [MyEmployees Table])
END
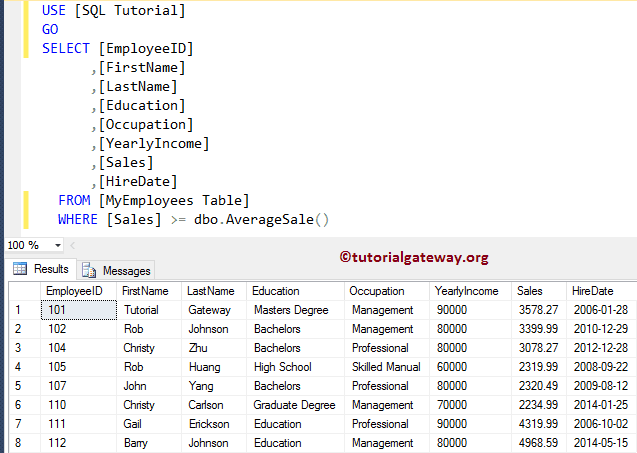
Let us see the Output
SELECT [EmployeeID]
,[FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
,[HireDate]
FROM [MyEmployees Table]
WHERE [Sales] >= dbo.AverageSale()
Create SQL User Defined Inline Table valued Functions examples
The Inline UDF returns a table data type as the return value based on a single SELECT Statement.
Inline with No parameters example
In this simple example, we will show you, How to create a SQL Inline table valued function without any parameters. From the below query, you can observe that we are selecting the top 10 records from the MyEmployee table.
-- Inline example
CREATE FUNCTION TopTenCustomers ()
RETURNS TABLE
AS
RETURN (
SELECT TOP 10 [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
,[HireDate]
FROM [MyEmployees Table]
)
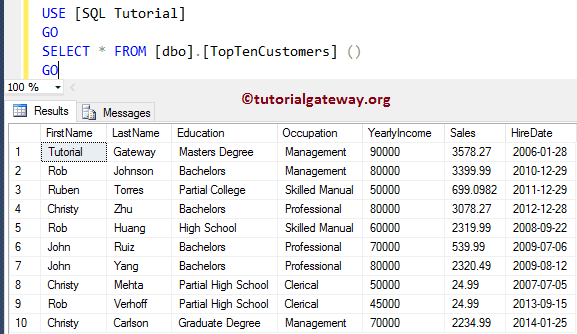
Let us see the Output.
SELECT * FROM [dbo].[TopTenCustomers] () GO
SQL Server User Defined Inline Function with Parameters Example
This example shows how to create an Inline table valued functions with parameters.
From the below query, you can see we are selecting the records from both tables using INNER JOIN, whose Occupation is equal to a parameter that we pass.
-- Inline example
CREATE FUNCTION CustomerbyDepartment (@profession VARCHAR(50))
RETURNS TABLE
AS
RETURN (
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Occupation]
,[Education]
,dept.DepartmentName AS Department
,[YearlyIncome] AS Income
,[Sales]
FROM [MyEmployees Table]
INNER JOIN
Department AS dept ON
Dept.[id] = [MyEmployees Table].DeptID
WHERE [Occupation] = @profession
)
Let us see the Output of the Inline table valued.
SELECT * FROM [dbo].[CustomerbyDepartment] ('Management')
GO
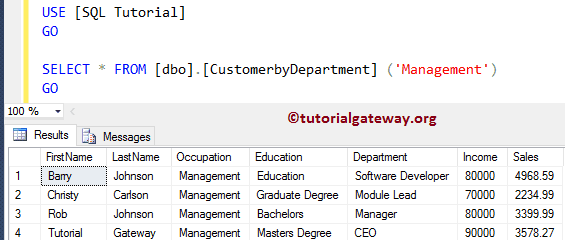
SQL Server User Defined Multi select Table valued Examples
The Multiple select table valued one returns the tabular result set. However, unlike the inline table valued, we can use multiple select statements inside the body.
This Multi select table valued function example will show you how to use Multiple statements in one UDF.
-- Table Valued example
CREATE FUNCTION CustomerDepartment()
RETURNS @customers TABLE
(
[EmployeeID] [smallint] NOT NULL,
[FirstName] [nvarchar](30) NULL,
[LastName] [nvarchar](40) NULL,
[Education] [nvarchar](255) NULL,
[Occupation] [nvarchar](255) NULL,
[YearlyIncome] [float] NULL,
[Sales] [float] NULL,
[HireDate] [date] NULL,
[DepartmentName] [VARCHAR](50) NULL
)
AS BEGIN
INSERT INTO @customers
SELECT [EmployeeID]
,[FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
,[HireDate]
,dept.DepartmentName
FROM [MyEmployees Table]
INNER JOIN
Department AS dept ON
Dept.[id] = [MyEmployees Table].DeptID
-- Updating the Records
UPDATE @customers SET [YearlyIncome] = [YearlyIncome] + 35200
WHERE [Sales] > (SELECT AVG(Sales) FROM [MyEmployees Table])
RETURN
END
Within this example, First, we are creating a table variable called @customers using the following statement.
@customers TABLE
Next, we insert the records from the [MyEmployee Table] and [Department] tables into the @customers table variable.
INSERT INTO @customers SELECT
Next, we are updating the Yearly income of all the customers present in the @customers table variable whose yearly income is greater than the average sales.
UPDATE @customers SET [YearlyIncome] = [YearlyIncome] + 35200 WHERE [Sales] > (SELECT AVG(Sales) FROM [MyEmployees Table])
Let us see the Output.
SELECT * FROM [dbo].[CustomerDepartment] () GO
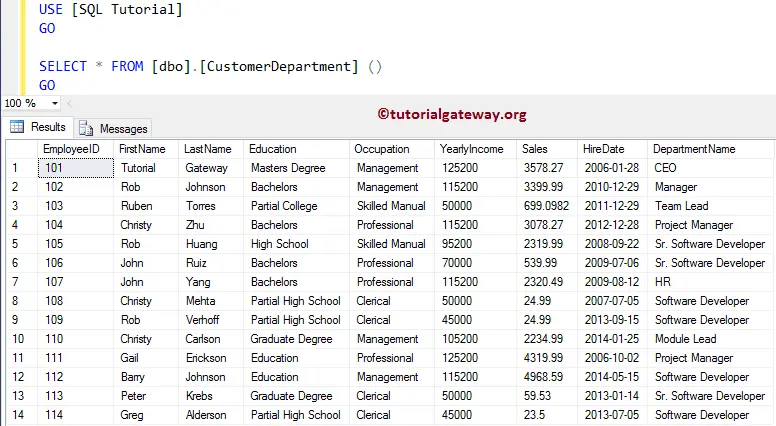
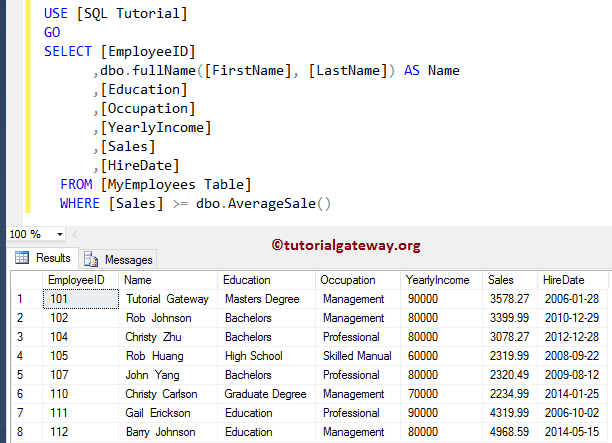
Multiple User Defined Functions in SQL Server
How to use multiple UDFs in a single SELECT Statement.
SELECT [EmployeeID]
,dbo.fullName([FirstName], [LastName]) AS Name -- First UDF
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
,[HireDate]
FROM [MyEmployees Table]
WHERE [Sales] >= dbo.AverageSale() -- Second UDF
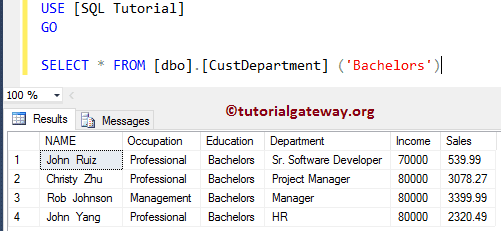
One SQL UDF inside another UDF
In this simple SQL UDF example, we will show you, How to nest or insert one User defined inside another.
CREATE FUNCTION CustDepartment (@education VARCHAR(50)) RETURNS TABLE AS RETURN ( SELECT dbo.fullName([FirstName],[LastName]) AS NAME ,[Occupation] ,[Education] ,dept.DepartmentName AS Department ,[YearlyIncome] AS Income ,[Sales] FROM [MyEmployees Table] INNER JOIN Department AS dept ON Dept.[id] = [MyEmployees Table].DeptID WHERE [Education] = @education )
Let us see the Output of the Nested functions.
SELECT * FROM [dbo].[CustDepartment] ('Bachelors')
Alter User Defined Functions in SQL
In the previous section, we explained creating User Defined Functions. Let us see how to alter User Defined Functions in SQL Server, such as renaming, modifying, and deleting the existing UDFs.
To view the existing functions in SQL Server, Please select the Database with UDFs. From the screenshot below, you can observe that our database has all the functions we created earlier.
To execute the existing functions, select the one you want to execute (AverageSale). Next, right-click on it and select the Script Function as -> SELECT To -> New Query Window Editor.
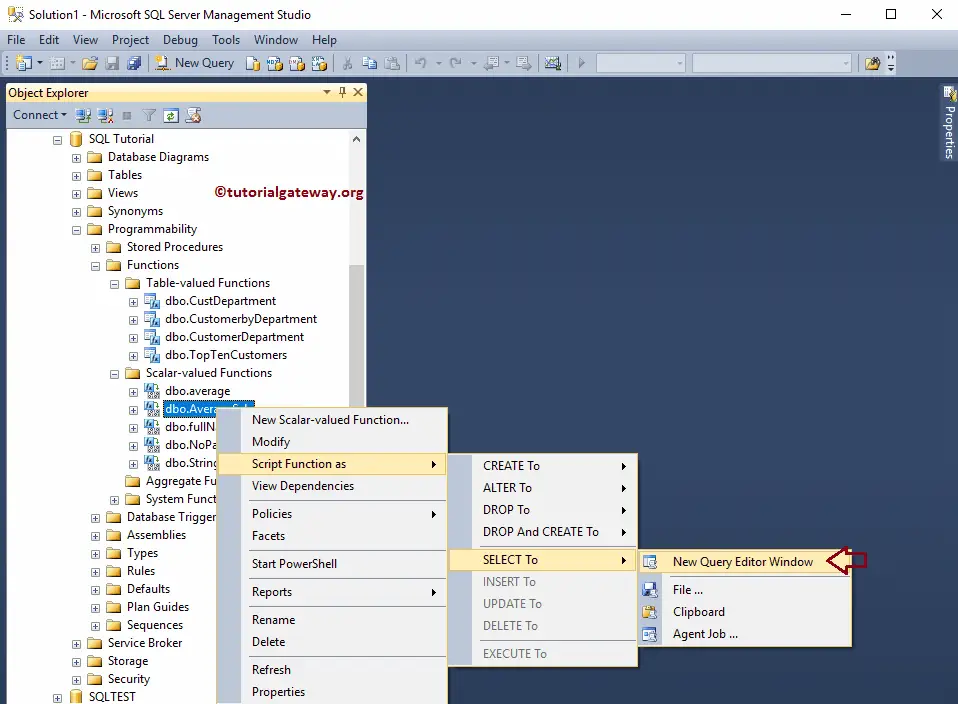
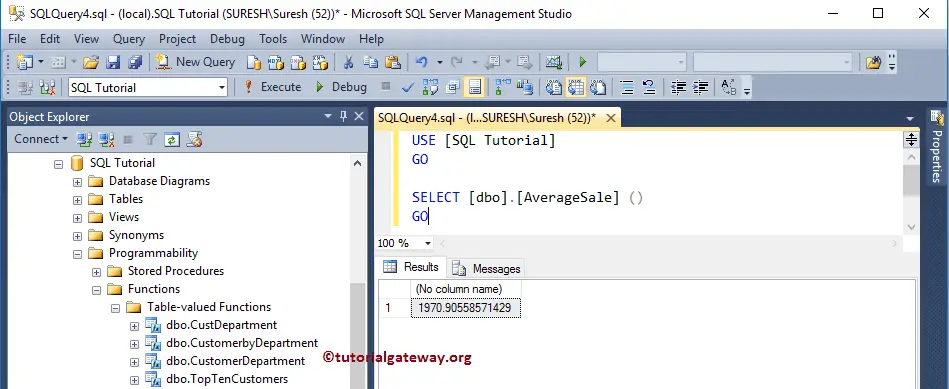
Once you select the New Query Window Editor option, Select from the query will return automatically by the SSMS.
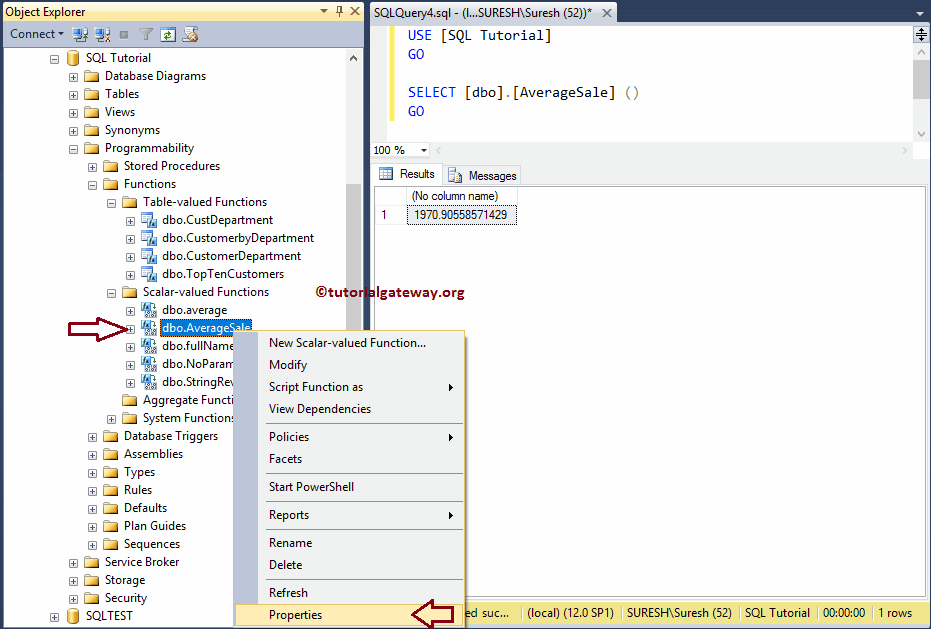
Properties of SQL User Defined Functions using SSMS
First, Right-click on the required name and select the SQL Server properties option.
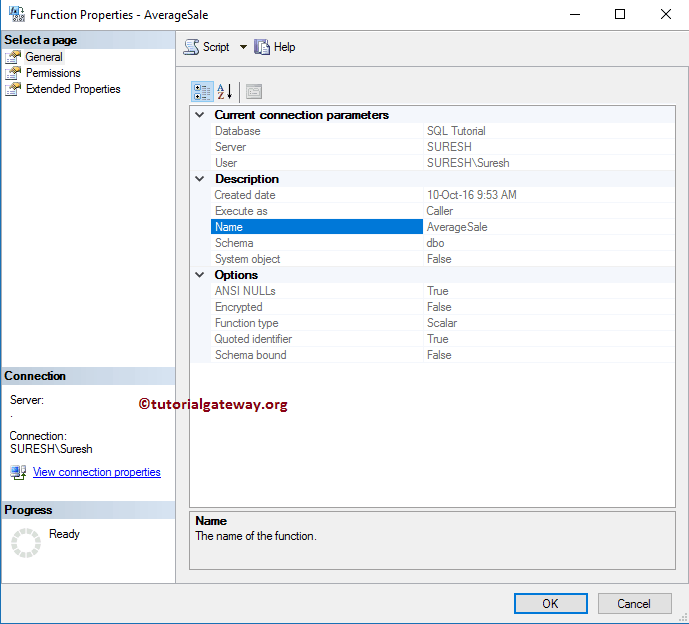
Once you click on the Properties option, a new window called Function Properties opens. The following is the list of SQL Server Function Properties, and they are:
- Database: It shows the database name containing the specified function. Here, it is AverageSale.
- Server: The name of the current Instance.
- User: It shows the name of the current user
- Created Date: It displays the created date.
- Name: It shows the name of the current one. i.e., AverageSale
- Schema: It displays the schema that we used for it.
- System Object: It shows Boolean value True or False, indicating whether the current one is a System Object or Not.
- ANSI NULLs: Displays Boolean value True or False, indicating whether the object was created with ANSI NULLs or Not.
- Function type: It shows whether the function is SCALAR or Table-Valued Functions
Properties of SQL User Defined Functions using Query
How to find the definition of a SQL User Defined Functions using the OBJECT_DEFINITION.
-- It Returns the AverageSale function Definition
SELECT OBJECT_DEFINITION (OBJECT_ID('dbo.AverageSale')) AS ObjectDefinition;
GO
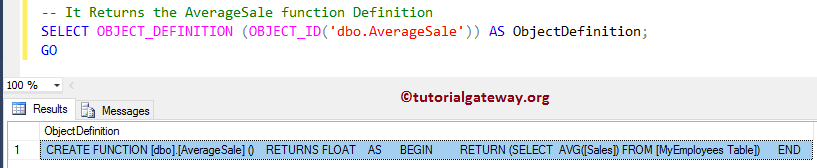
The following query returns the remaining properties of SQL UDFs.
-- It Returns the AverageSale Name & it's Properties
SELECT smo.OBJECT_ID,
OBJECT_NAME(smo.OBJECT_ID) AS OBJECT_NAME,
Obj.TYPE,
Obj.TYPE_DESC,
obj.create_date,
smo.uses_ansi_nulls,
smo.uses_quoted_identifier,
smo.is_schema_bound,
smo.execute_as_principal_id
FROM sys.sql_modules AS smo
JOIN sys.objects AS Obj ON smo.OBJECT_ID = Obj.OBJECT_ID
WHERE smo.OBJECT_ID = OBJECT_ID('dbo.AverageSale')
ORDER BY Obj.TYPE
GO
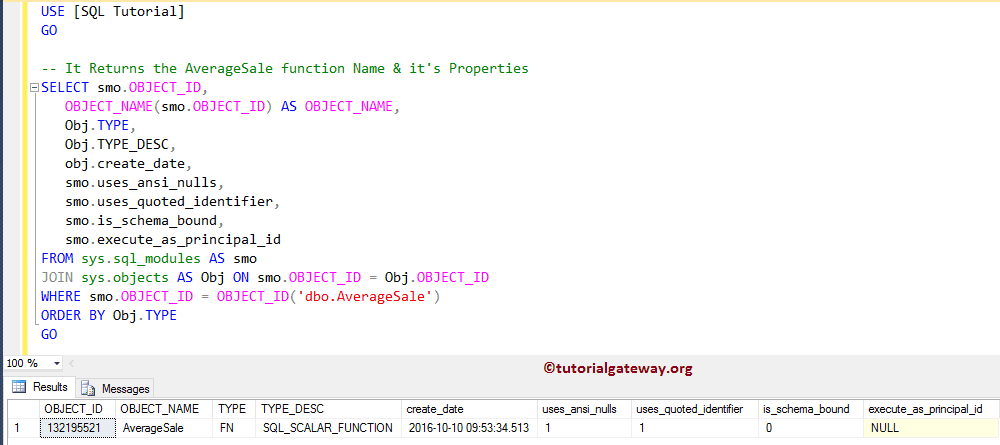
TIP: You can also return the definition by adding: smo.DEFINITION inside the Select Statement.
Rename User Defined Functions in SQL Server
To rename the User Defined Functions using the Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio, right-click on the one you want to modify (AverageSale) and select the Rename option.
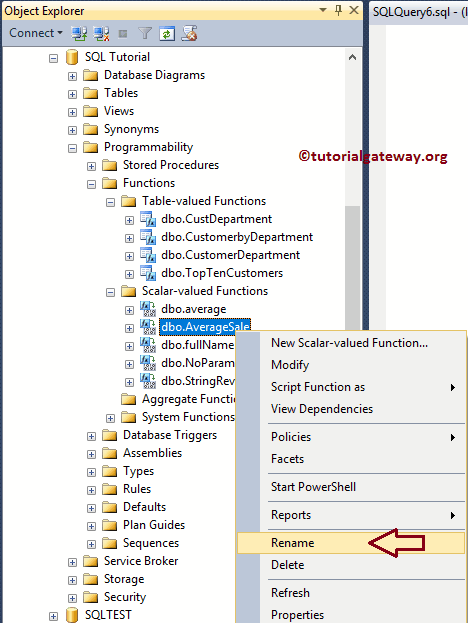
Once you click the Rename option, SSMS allows us to rename as per our requirements.
Modify User Defined Functions in SQL Server
The following examples will help you understand how to modify or alter the SQL User Defined Functions using the Management Studio (SSMS) and query.
Alter UDFs using SSMS
To modify the UDFs using the SQL Server Management Studio, right-click on the function (CustomerbyDepartmnet) that you want to change and select the Modify option.
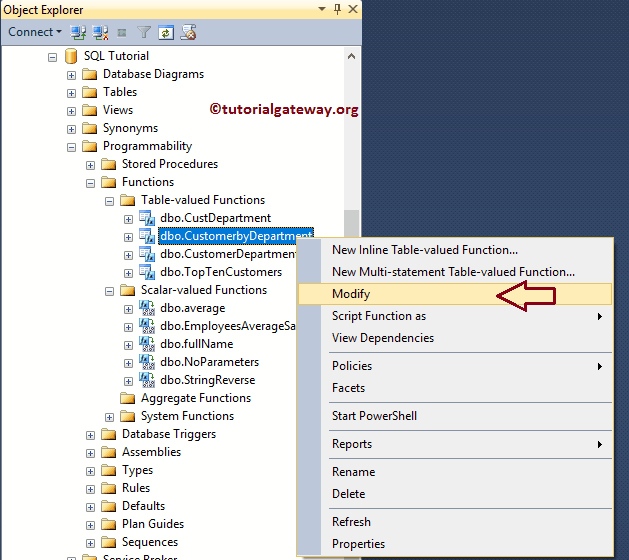
Once you choose the modify option, a new query window will open with the following query. You can edit as per your requirement.
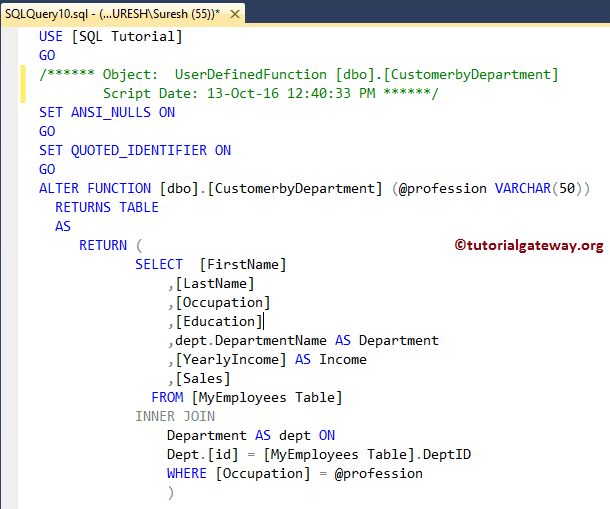
Alter SQL User Defined Functions using Query
Let me use the ALTER FUNCTION to modify the existing one. For demonstration purposes, we are concatenating the First Name and Last Name as NAME.
ALTER FUNCTION [dbo].[CustomerbyDepartment] (@profession VARCHAR(50))
RETURNS TABLE
AS
RETURN (
SELECT [FirstName] + ' ' + [LastName] AS Name
,[Occupation]
,[Education]
,dept.DepartmentName AS Department
,[YearlyIncome] AS Income
,[Sales]
FROM [MyEmployees Table]
INNER JOIN
Department AS dept ON
Dept.[id] = [MyEmployees Table].DeptID
WHERE [Occupation] = @profession
)
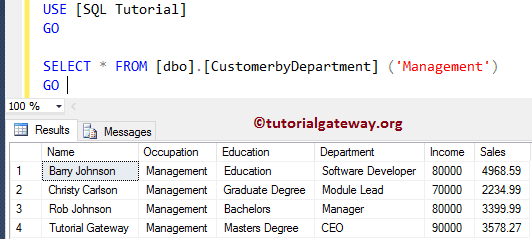
Let us see the Output.
SELECT * FROM [dbo].[CustomerbyDepartment] ('Management')
GO
The screenshot below shows that it is returning the NAME instead of First Name and Last Name.
Delete User Defined Functions in SQL Server
Delete the User Defined Functions using the Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), and transact Query. Before we get into the examples, remember the limitations:
- SQL Server will not allow you to delete the function if there are any references from it or Views to it.
- We cannot delete if there are any references from Computed Columns, CHECK, or Default Contrarians to it.
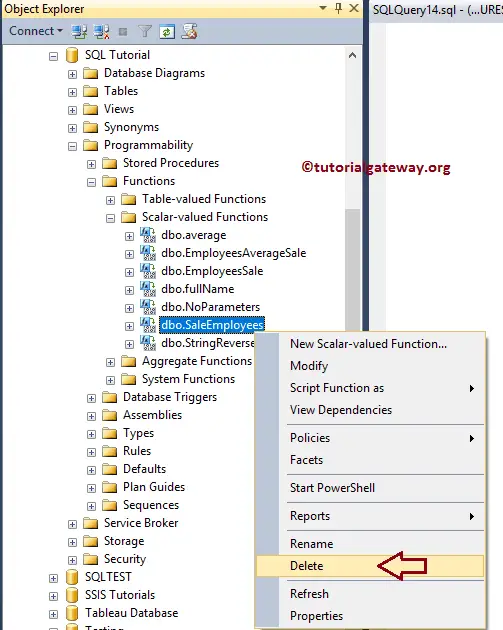
To demonstrate the delete operation, we added two more scalar functions. Our task is to delete the EmployeeSale and SaleEmployees.
Delete UDFs using SQL Server Management Studio
To delete the UDFs using the SQL Server Management Studio, right-click the function name and click the Delete option. Here, we want to delete SaleEmployees (scalar).
Choosing the delete option opens a Delete Object window. Click the Show Dependencies button to check the dependencies, then click OK to delete that.
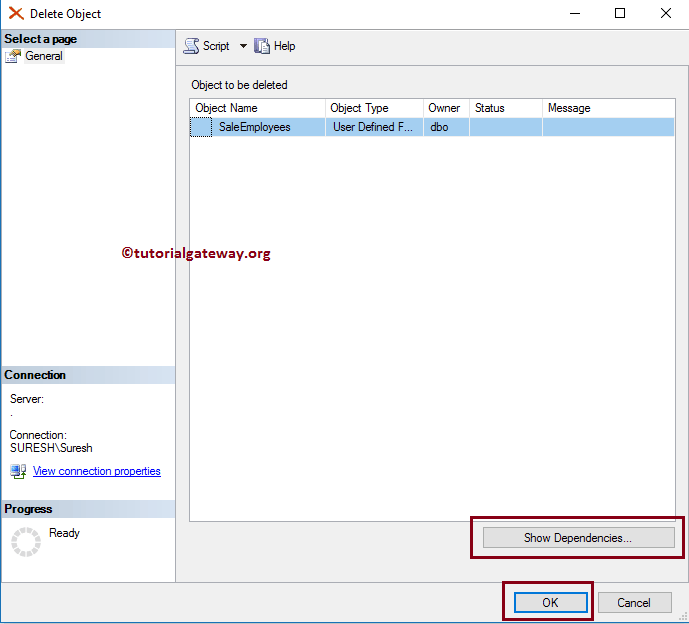
Delete Functions using SQL Query
How to use SQL Server DROP FUNCTION to delete the User Defined.
DROP FUNCTION [dbo].[EmployeesSale] GO
TIP: It is good practice to check, whether it exists in the database or not using IF OBJECT_ID (N’EmployeeSale’, N’IF’) IS NOT NULL
Let us see what happens when we call the deleted one.
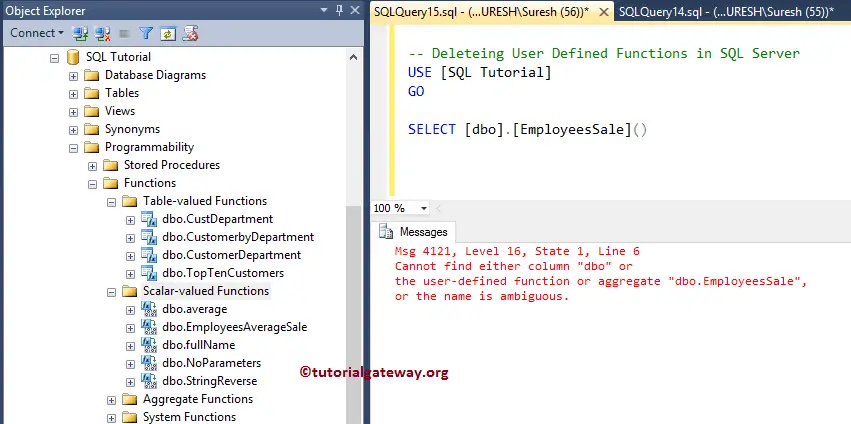
From the above screenshot, we don’t have EmployeeSale in our Object Explorer, and querying on it throws an error.
Limitations of User Defined Functions in SQL Server
The following is the list of limitations but not limited.
- We cannot use the functions shortly called UDF in SQL Server to modify the database state.
- UDF can not return multiple result sets.
- The UDF does not support error handling, such as TRY..CACHE, RAISEERROR, or @ERROR
- We cannot call a Stored Procedure from UDF, but we can call an extended Stored Procedure.
- They do not support the temporary tables, but they will allow the Table variable.
- SET statements are not allowed in UDFs
- The FOR XML Clause is not permitted inside them.

Comments are closed.