The String Comparison in Java, or comparing two strings, is one of the most commonly asked questions in the interview. The Java String Comparison may twist as differences between equals(), equalsIgnoreCase() method, == Operator, compareTo.
This article will show how to Perform String Comparison (compare two) in Java Programming Language. Before we get into a practical example, let us see the major differences between equals() and ==:
- The equals Method compares the string data with user-specified Object data to check whether they both represent the same sequence of characters or not. In short, it will compare the string values. Based on the result, it will return Boolean True or False.
- == Operator compares the Object reference of one string with another and returns the result.
How to Perform String Comparison in Java?
In this Java program, we are going to perform a string comparison and we will compare two strings using both the equals method and the == operator.
package FAQs;
public class StringComparison {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "Tutorial Gateway";
String str2 = "Tutorial Gateway";
String str3 = new String("Java Programming");
String str4 = new String("Java Programming");
String str5 = new String("Tutorial Gateway");
String str6 = null;
boolean a = str1.equals(str2);
boolean b = str3.equals(str4);
boolean c = str1.equals(str5);
System.out.println("equals Method Result: str1 Equals to str2 = " + a);
System.out.println("== Result : str1 Equals to str2 = " + (str1 == str2));
System.out.println("equals Method Result: str3 Equals to str4 = " + b);
System.out.println("== Result : str3 Equals to str4 = " + (str3 == str4));
System.out.println("equals Method Result: str1 Equals to str5 = " + c);
System.out.println("== Result : str1 Equals to str5 = " + (str1 == str5));
System.out.println("== Result : Null Equals to Null = " + (null == null));
System.out.println("equals Method Result: Null Equals to Null = " + str6.equals(null));
}
}
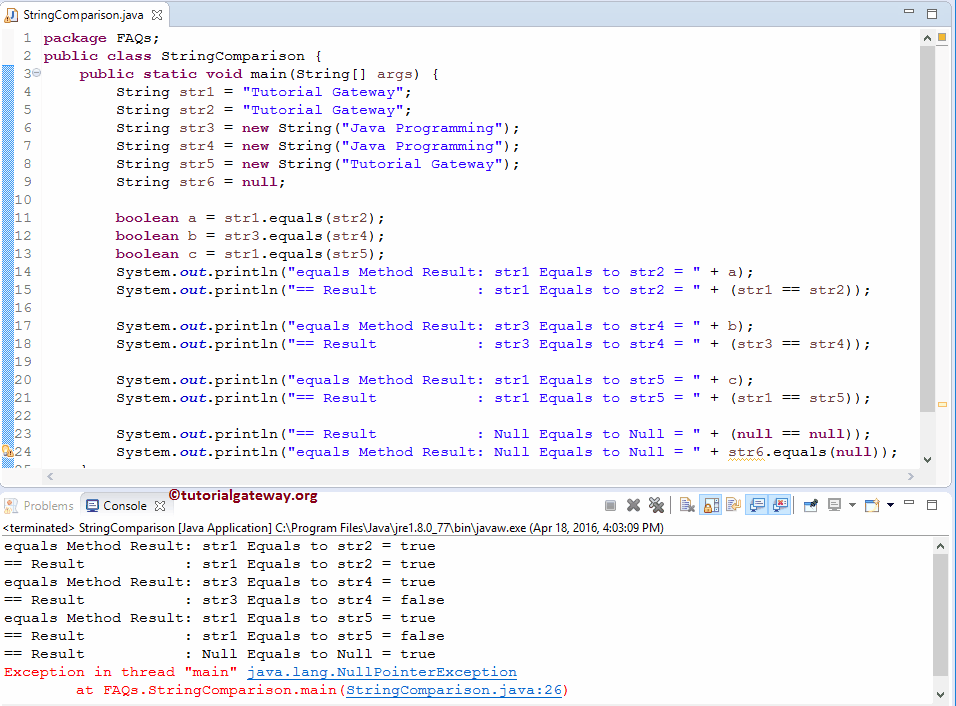
Within this Java string comparison example program, we declared three variables, str3, str4, and str5, and assigned the corresponding values using the following six statements.
The following statement will call the equals Method method to compare the str1 with str2. From the above screenshot, if you observe that it is returning True because it is an Object.
boolean a = str1.equals(str2);
This Java String example will perform a comparison of the literal str1 with str2. From the above screenshot, it is returning True because both of them refer to the same object in memory.
System.out.println("== Result : str1 Equals to str2 = " + (str1 == str2));
The following Java statements will perform a comparison of str3 with another string, str4. From the above screenshot, observe that.
- The first statement returns True because the value in both str3 and str4 is the same.
- The second statement returns False. Though the value is the same, the == operator is returning False because str3 is creating a new object in Cache, and str4 creates another new object in Cache. It means the object reference of str3 and str4 is different. So, it is returning False.
boolean b = str3.equals(str4);
System.out.println("== Result : str3 Equals to str4 = " + (str3 == str4));
The below statement in this Java String comparison example will differentiate the literal str1 from object str5.
- The first statement returns True because the value in both str1 and str5 is the same.
- The second Java statement returns False. Though the value is the same, the == operator is returning False because str1 is creating an object inside the memory, and str5 creates a new object in Cache. It means the object reference of str1 and str5 is different. So, it is returning False.
boolean b = str1.equals(str5);
System.out.println("== Result : str1 Equals to str5 = " + (str1 == str5));
In the last program line, we compare the null values using this == operator. If we use the equals method to differentiate the null values, it will throw an error.
Case-insensitive comparison
Instead of using the equals() method, you must use the equalsIgnoreCase()function to compare strings without considering the capital and small letters.
Suppose you look at the output of the below example. In that case, the equals() method returns False, whereas the equalsIgnoreCase() method returns True because it does not care about the lower and uppercase characters.
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "Radar";
String s2 = "radar";
boolean a = s1.equals(s2);
boolean b = s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2);
System.out.println("equals : s1 Equals to s2 = " + a);
System.out.println("equalsIgnoreCase: s1 Equals to s2 = " + b);
}
}
equals : s1 Equals to s2 = false
equalsIgnoreCase: s1 Equals to s2 = trueJava Lexicographic Comparison of Strings
You can also use the compareTo() method to perform the Lexicographic Comparison on two strings. However, it returns the integer values of -1, 1, and 0. So, you have to use the Else if statement to print the appropriate message.
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "Hello";
String s2 = "Hello";
int result = s1.compareTo(s2);
if (result < 0) {
System.out.println(s1 + " comes before " + s2);
} else if (result > 0) {
System.out.println(s1 + " comes after " + s2);
} else {
System.out.println(s1 + " equals " + s2);
}
}
}
Hello equals HelloTIP: For Case-insensitive Lexicographic comparison, replace the compareTo() with the compareToIgnoreCase() method.
Java Program to Compare two Strings using for loop
In this program, the first if statement checks whether the length of both strings is equal or not. Is there aren’t? There is no point in performing the comparison. Otherwise, it goes to the Else statement. Within the same, we used the for loop to iterate the characters. Next, compare each character in s1 against s2. If they are not equal, flag = 1. And in the last lines, we used the if else statement to check the flag value. If true, both strings are equal; otherwise, they are not.
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "Tutorial Gateway";
String s2 = "Tutorial Gateway";
int flag = 0;
if (s1.length() != s2.length()) {
flag = 1;
}
else {
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length(); i++) {
if (s1.charAt(i) != s2.charAt(i)) {
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
}
if (flag == 0) {
System.out.println("\n s1 is Equal to s2");
} else {
System.out.println("\n s1 Not Equal to s2");
}
}
}
s1 is Equal to s2