The Java Ternary Operator is also called a Conditional Operator. The Ternary operator is mostly used in the decision-making process to return true or false. And it returns the statement depending upon the given expression result. The basic syntax of a Conditional or Ternary Operator in Java Programming is as shown below:
Test_expression ? statement1: statement2
If the given test condition or boolean expression evaluates to true, the conditional operator will return statement1. If the condition evaluates to false, then statement 2 is returned.
Java Ternary Operator Example
In this Java Program, we will use the Ternary or Conditional Operator to determine whether the person is eligible to vote.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Example {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int age;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(" Please Enter Your Age: ");
age = sc.nextInt();
String Message = (age >= 18)? " You are eligible to Vote " :
" You are Not eligible to Vote ";
System.out.println(Message);
/** REPLACE THE ABOVE CODE WITH FOLLOWING CODE
* System.out.println((age >= 18)?
* " You are eligible to Vote":
* "You are Not eligible to Vote");
*/
}
}
This Java Ternary Conditional Operator program allows the user to enter the age and assign the user entered integer value to the age variable. If the user enters a value is 18 or above, it will assign the first statement after the ? symbol to String variable Message. ” You are eligible to Vote.”
If the user enters below 18, the second statement (after the : symbol) will be assigned to the String variable Message. ” You are not eligible to Vote.”
Finally, we use the System.out.println statement to print the string data inside the Message variable.
Please Enter Your Age:
15
You are Not eligible to Vote Let us try with a different value
Please Enter Your Age:
29
You are eligible to VoteJava Nested Ternary or Conditional Operator Example
In this Program, we are going to use the Nested Ternary to find whether the person is eligible to work or not.
- In this Java ternary operator example, We declared a string variable called Message, and we assigned this variable to the conditional functionality.
- The first condition checks whether the age is less than 18. If this condition is True, will it return the first value after the ? symbol, which is You are too Young to Work
- When the first condition fails, it will execute the variable after : symbol. By using the Nested conditional operator, we check one more condition here (age >= 18 && age <= 60). If this condition is True, it will return the first value after the ? symbol, which is You are eligible to Work
- If the Nested condition of a conditional fails, the ternary operator will execute the variable after : symbol, which is You are too Old to Work.
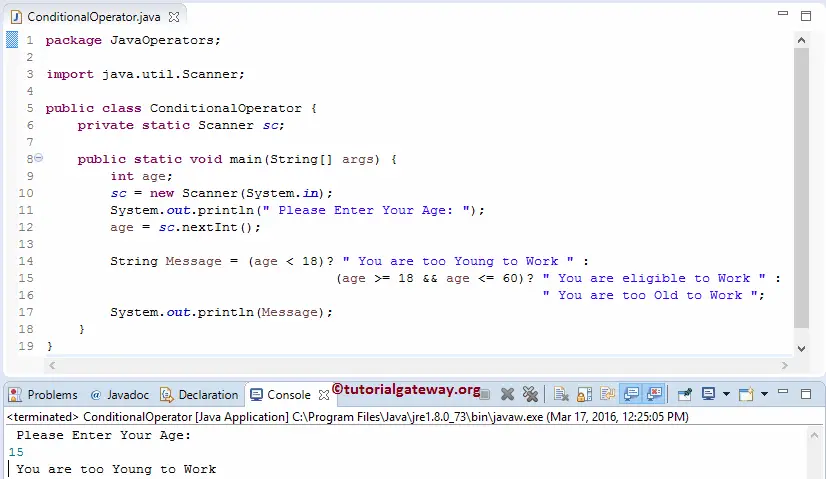
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ConditionalOperator {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int age;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(" Please Enter Your Age: ");
age = sc.nextInt();
String Message = (age < 18)? " You are too Young to Work " :
(age >= 18 && age <= 60)? " You are eligible to Work ":
" You are too Old to Work ";
System.out.println(Message);
}
}
Java Output 2
Please Enter Your Age:
28
You are eligible to Work Please Enter Your Age:
65
You are too Old to Work 