How to declare a Java array, create it, initialize, and access elements? An Array in Java is a container object that holds a collection of similar types of elements (type may be an integer, float, long, etc.). It means we cannot store multiple data type values.
Java Array Scenario: In our previous articles, we saw the variable declaration and initialization, and they are pretty good for initializing a few variables. What if we want to store 100 employee salaries? Is it worth creating 100 variables and assigning those values? What happens if it is 150 employees?
To handle this type of situation, Java Programming language introduced the concept of arrays.
Java Array Introduction
For example, an integer array in Java will store all the integer elements. If you try inserting a float or char value, it will throw an error.
The length of it is decided when we are creating it. Once it is created, the length is fixed. We have 3 types of arrays in Java Programming.
- One Dimensional
- Two Dimensional
- MultiDimensional
- Three Dimensional
- Four Dimensional etc
Java array declaration or Syntax
The following Java code snippet will show you the most basic way of an array declaration:
Data_Type[] Array_Name;
- Data_type: It will decide the type of elements the array will accept. For example, If we want to store integer values, the Data Type will be declared as an int. To store Float values, the Data Type is a float
- Array_Name: This is the name you want to give. For example, students, age, marks, emp.
Similarly, you can declare the remaining type of one-dimensional arrays in Java as follows:
int [] anIntegerArray; byte[] anByteArray; short[] anShortArray; long[] anLongArray; float[] anFloatArray; double[] anDoubleArray; boolean[] anBooleanArray; char[] anCharArray; String[] anStringArray;
Create a Java Array
To create an array, we have to use the Java New operator
Data_Type[] Array_Name = new Array_Name[Array_Size];
Array_Size: Number of elements it can hold or store. For example, if Array_Size =10, it will hold 10 values.
If you have already initialized an array, then
int [] anIntegerArray; // Declaration // Crating it anIntegerArray = new int[10];
For Example, int[] Student_Marks = new int[10];
- We used int as the data type to declare a Java array. So, the above one will accept only integers. If we try to add float values, then it will throw an error.
- Student_Age is the name.
- The size of it is ten. It means Student_Marks will only accept ten integer values.
- If we try to store more than ten, it throws an error.
- We can store less than 10. For Example, If we store three integer values, the remaining two will be initialized to the default value (0).
Java Array Initialization
There are multiple ways to initialize the Java array.
First Approach
Declaring and Creating an Array in Java Programming.
int[] Student_Marks = new int[3];
Initializing elements in the more traditional way
Student_Marks[0] = 15; // Initializing First elements at position 0 Student_Marks[1] = 45; // Initializing elements at position 1 Student_Marks[2] = 65; // First elements at position 2
Second Approach to create
In this approach, We initialize the Java array at the declaration time only.
int[] anIntegerArray = {15, 25, 35, 45, 55}
Here, We did not mention the size. However, the Javac is intelligent enough to determine the size by checking the number of elements.
Third Approach
Although this approach works without any error, this is not the preferred way to initialize in Java Programming.
int Employees[ ] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
Fourth Approach of Java array initialization
The above 3 methods are good for storing a small number of items in an array. What if we want to store 50, 100, or more values? It will be torture to add all of them using any of the above-mentioned approaches. To resolve this, we can use the loop concept to store data:
int i, Employees[100];
for (i =0; i < 100 ; i++)
{
Employees[i] = i * 2;
}
TIP: To store the elements, We can use For loop, While Loop, and Do While Loop
Fifth Approach to create an array in Java
int[] anIntegerArray = new int[5];
anIntegerArray[0] = 10;
anIntegerArray[1] = 20;
anIntegerArray[2] = 30;
Here we declared an anIntegerArray array of size 5, but we only assigned three values to it. In this condition, the remaining values are assigned to default values (0 in this case).
The above one will be:
anIntegerArray[0] = 10
anIntegerArray[1] = 20
anIntegerArray[2] = 30
anIntegerArray[3] = 0
anIntegerArray[4] = 0
Accessing Java Array Elements
We use the index position to access the Java array element. We can access or alter/change the item using an index inside square brackets. The index value starts at 0 and ends at n-1, where n is the size or length.
For example, if it stores ten elements, the array indices start at 0 and end at 9. To access or modify the first value, use Array_Name[0] and to access or alter the 10th value, use Array_Name[10]. Let us see the example for better knowledge of accessing Java array elements:
package ArrDefinitions;
public class ArrTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] anIntegerArray = {15, 25, 35, 45, 55, 65};
System.out.println(anIntegerArray[0]);
System.out.println(anIntegerArray[1]);
System.out.println(anIntegerArray[2]);
System.out.println(anIntegerArray[3]);
System.out.println(anIntegerArray[4]);
System.out.println(anIntegerArray[5]);
}
}
15
25
35
45
55
65Java Array example
We will declare an integer array of size ten. Then we will sum those ten values and displays the output.
package ArrayDefinitions;
public class JavaArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i, Sum =0;
int [] anIntegerArray = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100};
for(i = 0; i < anIntegerArray.length; i++) {
Sum = Sum + anIntegerArray[i];
System.out.format("Addition of %d to Sum = %d \n", anIntegerArray[i], Sum);
}
System.out.format("Sum of the elemts in anIntegerArray = %d \n", Sum);
}
}
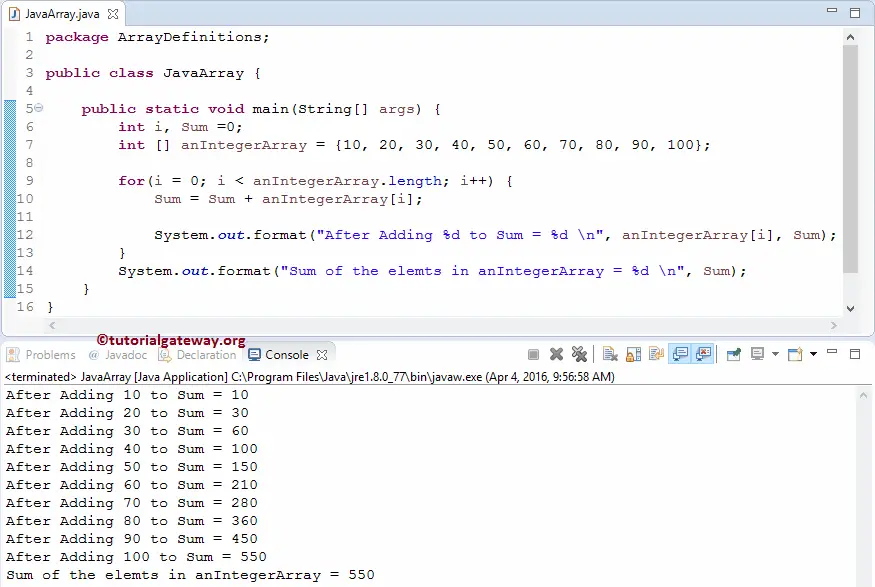
In this Java array example Program, We declared 1 One Dimensional anIntegerArray[] with 10 elements and also declared i to iterate and access elements,
int [] anIntegerArray = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100};
The For loop iterate every array element in the anIntegerArray[4] array. The condition inside the for loops (i < anIntegerArray.length) will ensure the Javac does not exceed the array limit.
- Sum = Sum + anIntegerArray[i]; statement is used to add each and individual element present in the anIntegerArray to Sum variable.
- System.out.format statement displays the Sum value after every iteration.
- anIntegerArray.length finds the length of it
Analysis
Java Array First Iteration: The value of i will be 0, and the condition (i < 10) is True. So, it will start executing the statements inside the loop.
Sum = Sum + anIntegerArray[i]
=> Sum + anIntegerArray[0]
Sum = 0 + 10 = 10
The value of i will be incremented by 1
Second Iteration: The value of i is 1, and the condition (1 < 10) is True.
Sum = Sum + anIntegerArray[1]
Sum = 10 + 20 = 30
Third Iteration: After the increment, the i = 2, and the condition (2 < 10) is True.
Sum += anIntegerArray[2]
=> 30 + 30 = 60
Fourth Iteration: The value of i is 3, and the condition (3 < 5) is True.
Sum = 60 + 40 = 100
Fifth Iteration: i = 4, and the condition (4 < 10) is True.
Sum = 100 + 50 = 150
Java Array Sixth Iteration: i is 5, and the condition (5 < 10) is True.
Sum = 150 + 60 = 210
Seventh Iteration: After increment, i = 6, and the condition (6 < 10) is True.
Sum = 210 + 70 = 280
Eighth Iteration: i = 7, and the condition (7 < 10) is True.
Sum = 280 + anIntegerArray[7] => 280 + 80 = 360
9th Iteration: i is 8, and the condition (8 < 10) is True.
Sum = 360 + anIntegerArray[8] => 360 + 90 = 450
10th Iteration: i is 9, and the condition (9 < 10) is True.
Sum = Sum + anIntegerArray[9]
Sum = 450 + 100 = 550
11th Iteration: The value of i is 10, and the condition (10 < 10) is False. So, it will exit from the for loop and goes to the last statement.
Lastly, we used System.out.format statement to display the Sum.
