MySQL provides various aggregate functions to perform or calculate the aggregated value, such as finding minimum value, maximum value, sum, etc. Generally, we use Aggregate Functions along with Group By Clause to find the aggregated value of each group. However, you can use them without Group By clause.
MySQL Aggregate Functions
The following are the list of MySQL Aggregate functions that are available to work.
| MySQL Aggregate Functions | Description |
|---|---|
| AVG() | It finds or returns the Average value. |
| BIT_AND() | Returns bitwise AND |
| BIT_OR() | It returns the bitwise OR value. |
| BIT_XOR() | Returns the Bitwise XOR value |
| COUNT() | Counts the number of rows returned. |
| COUNT(DISTINCT) | It counts the number of distinct or different values. |
| GROUP_CONCAT() | Returns the concatenated string |
| MAX() | Finds the Maximum value |
| MIN() | Use this MySQL Aggregate function to find the Minimum value. |
| STD() | The population standard deviation |
| STDDEV() | Use this MySQL method to get the population standard deviation |
| STDDEV_POP() | This returns the population standard deviation |
| STDDEV_SAMP() | Returns the sample standard deviation |
| SUM() | Use this to return or find the sum. |
| VAR_POP() | This method returns the population standard variance. |
| VAR_SAMP() | It returns the sample variance. |
| VARIANCE() | This method returns the population standard variance. |
MySQL Aggregate Functions Example
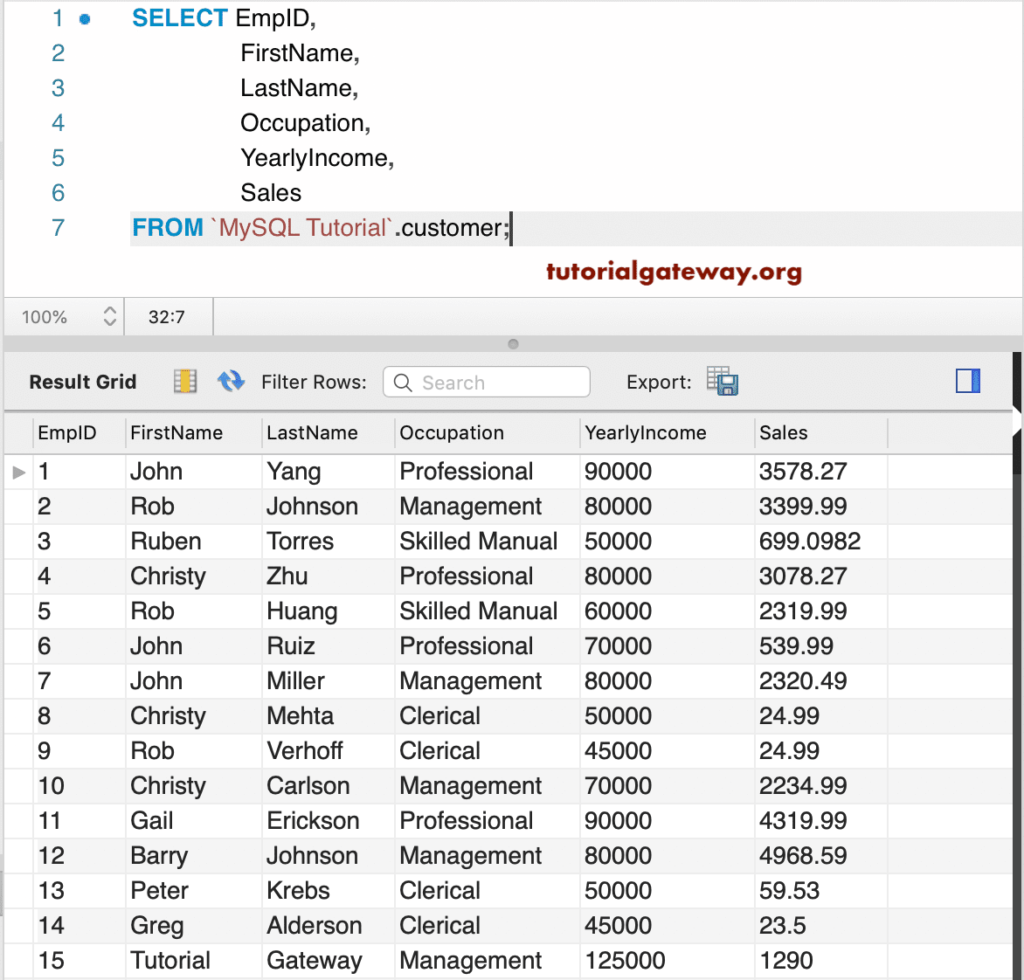
To demonstrate these Aggregate functions, we are going to use the below-shown data, which has 15 records.
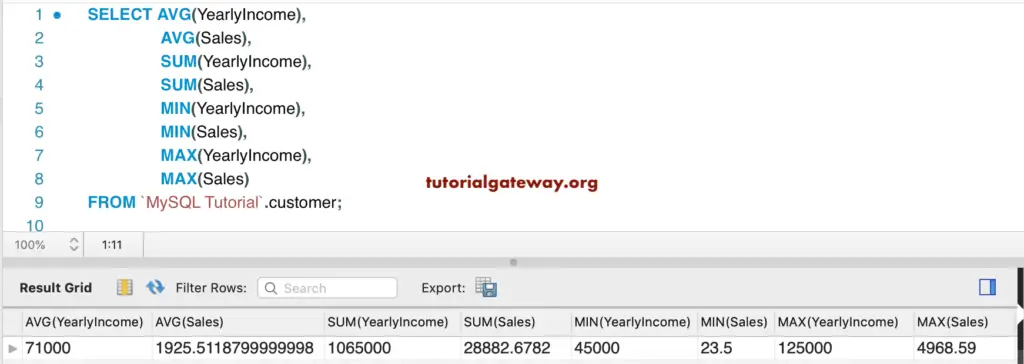
In this MySQL example, we are going to use the aggregate AVG, SUM, MIN, and MAX functions on the Yearly Income and Sales column. The following Aggregate query calculates the Sum, Average, Minimum, and Maximum of the Yearly_Income column and Sales column in a customer table.
SELECT AVG(YearlyIncome),
AVG(Sales),
SUM(YearlyIncome),
SUM(Sales),
MIN(YearlyIncome),
MIN(Sales),
MAX(YearlyIncome),
MAX(Sales)
FROM customer;
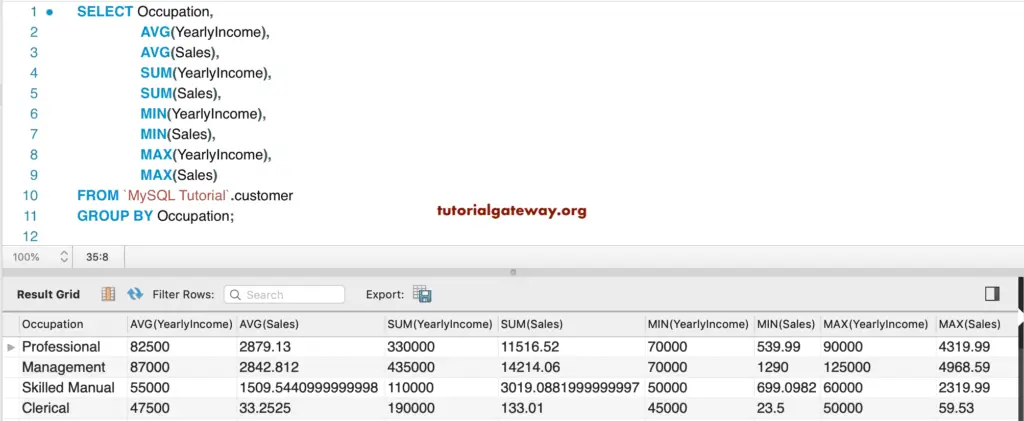
Generally, we use these MySQL Aggregate functions along with Group By Clause to group the items by category. Let us see the Example to understand better.
SELECT Occupation,
AVG(YearlyIncome),
AVG(Sales),
SUM(YearlyIncome),
SUM(Sales),
MIN(YearlyIncome),
MIN(Sales),
MAX(YearlyIncome),
MAX(Sales)
FROM customer
GROUP BY Occupation;
MySQL Aggregate Functions Standard Deviation Example
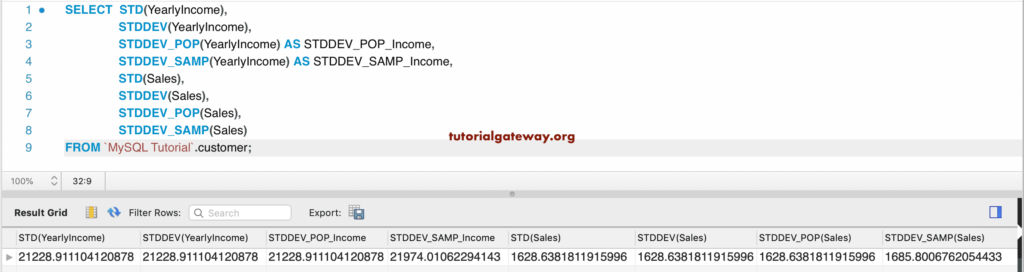
In this example, we are going to use the STD, STDDEV, STDDEV_POP, and STDDEV_SAMP on the Yearly Income and Sales column to find the standard deviation of both these columns.
SELECT STD(YearlyIncome),
STDDEV(YearlyIncome),
STDDEV_POP(YearlyIncome) AS STDDEV_POP_Income,
STDDEV_SAMP(YearlyIncome) AS STDDEV_SAMP_Income,
STD(Sales),
STDDEV(Sales),
STDDEV_POP(Sales),
STDDEV_SAMP(Sales)
FROM customer;
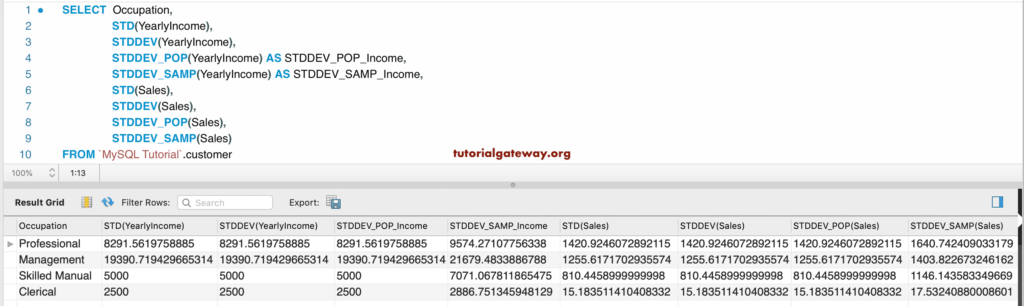
This example is the same as above — however, this time, we used the Occupation column to group the customers. Next, we used the methods mentioned above to find the standard deviation.
SELECT Occupation,
STD(YearlyIncome),
STDDEV(YearlyIncome),
STDDEV_POP(YearlyIncome) AS STDDEV_POP_Income,
STDDEV_SAMP(YearlyIncome) AS STDDEV_SAMP_Income,
STD(Sales),
STDDEV(Sales),
STDDEV_POP(Sales),
STDDEV_SAMP(Sales)
FROM customer
GROUP BY Occupation;
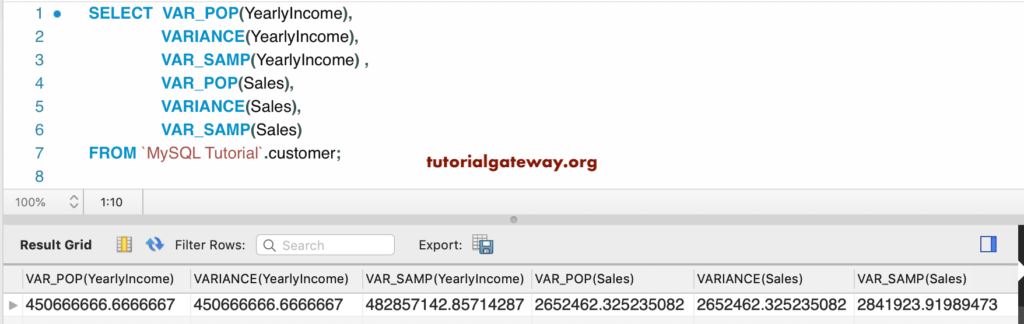
MySQL Variance, var_pop, var_samp Examples
In this example, we are going to use the MySQL aggregate functions like VARIANCE, VAR_POP, and VAR_SAMP on the Yearly Income and Sales column. They find the standard variance of both these columns.
SELECT VAR_POP(YearlyIncome),
VARIANCE(YearlyIncome),
VAR_SAMP(YearlyIncome) ,
VAR_POP(Sales),
VARIANCE(Sales),
VAR_SAMP(Sales)
FROM customer;
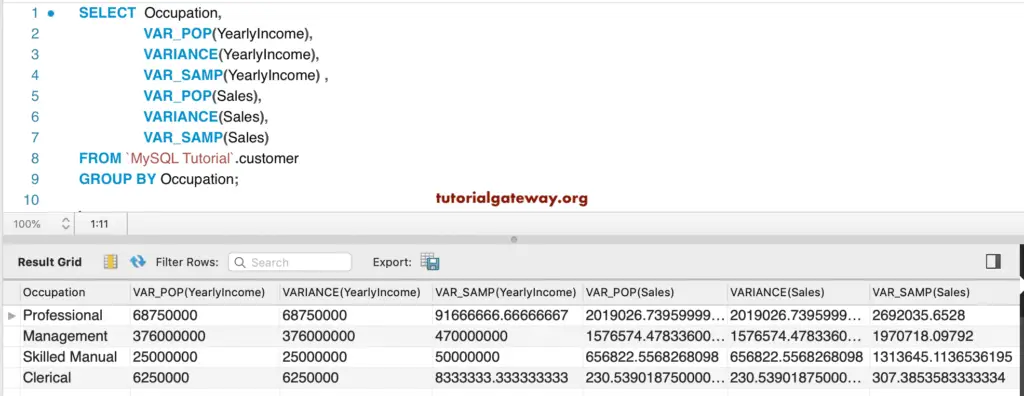
Used the Occupation column to group the customers. Next, we used the VARIANCE as mentioned earlier functions to find the standard variance of each group.
SELECT Occupation,
VAR_POP(YearlyIncome),
VARIANCE(YearlyIncome),
VAR_SAMP(YearlyIncome) ,
VAR_POP(Sales),
VARIANCE(Sales),
VAR_SAMP(Sales)
FROM customer
GROUP BY Occupation;
Bitwise AND, OR, and XOR Example
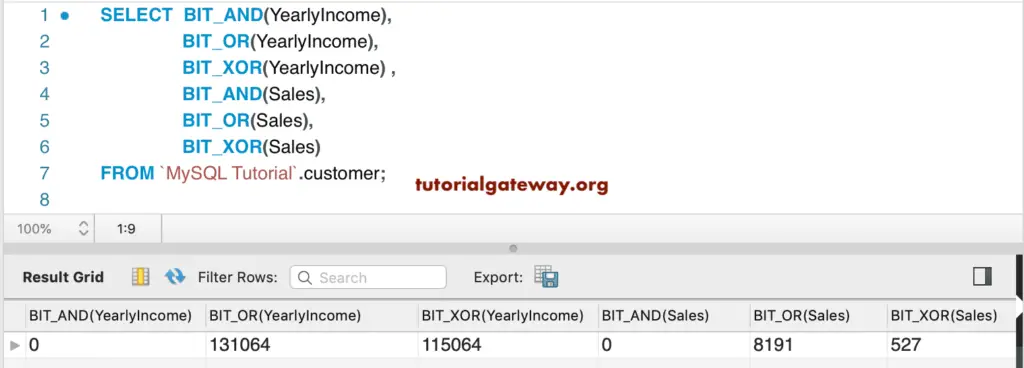
We use the BIT_AND, BIT_OR, and BIT_XOR on the Yearly Income & Sales columns.
SELECT BIT_AND(YearlyIncome),
BIT_OR(YearlyIncome),
BIT_XOR(YearlyIncome) ,
BIT_AND(Sales),
BIT_OR(Sales),
BIT_XOR(Sales)
FROM customer;
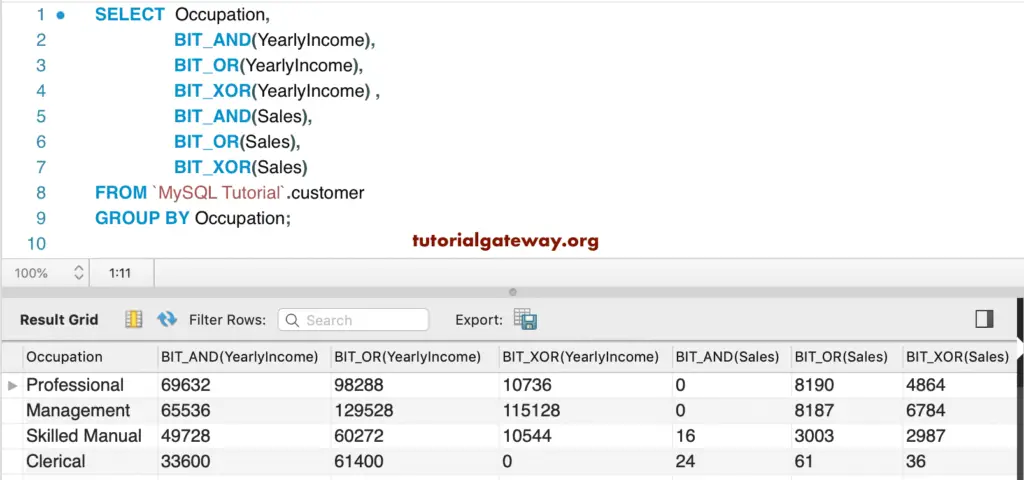
Here, we used the Group By clause to group the Occupation column in the customers table. Next, we used the above-mentioned Aggregate functions.
SELECT Occupation,
BIT_AND(YearlyIncome),
BIT_OR(YearlyIncome),
BIT_XOR(YearlyIncome) ,
BIT_AND(Sales),
BIT_OR(Sales),
BIT_XOR(Sales)
FROM customer
GROUP BY Occupation;
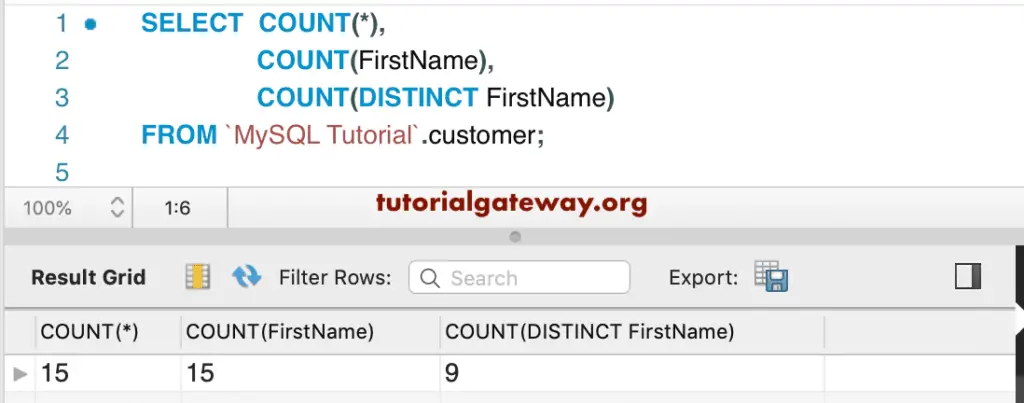
This example shows you the MySQL COUNT and COUNT(DISTINCT) Functions example. Here, we used both these methods on the First name column. As you can see, COUNT(DISTINCT) Function returns the count of distinct or unique records in this column.
SELECT COUNT(*),
COUNT(FirstName),
COUNT(DISTINCT FirstName)
FROM customer