The MySQL Insert statement is to load or add new records into a table. We use the tables we created in our previous post to demonstrate the Insert Query.
The basic syntax of the Insert statement is as shown below:
INSERT INTO Destination Table
(Column1, Column2,..., ColumnN)
VALUES (Column1_Value, Column2_Value,..., ColumnN_Value)
- DestinationTable: Provide a fully qualified name in which you want to load records
- Column1…ColumnN: It allows us to choose the number of columns from the table. It may be one or more.
- Column1_Value…ColumnN_Value: Please specify the values that you want to insert. For instance, Column1_Value to load in Column1. If you omit the field names, you must specify the values (i.e., filed values) in the order defined by the destination table structure.
If you are loading values for all the columns in the destination, remove (Column1, Column2,…, ColumnN) from the above syntax.
MySQL INSERT Workbench Example
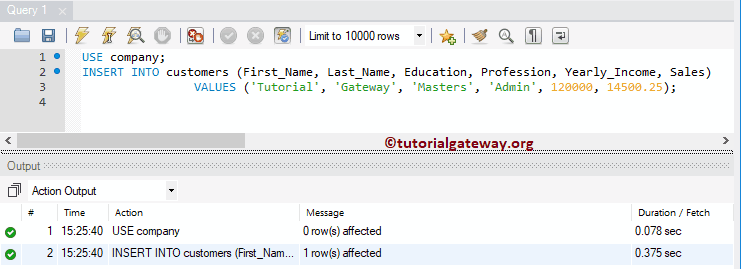
In this Insert Statement example, we will load a new record into the customers.
USE company;
INSERT INTO customers
(First_Name, Last_Name, Education, Profession, Yearly_Income, Sales)
VALUES ('Tutorial', 'Gateway', 'Masters', 'Admin', 120000, 14500.25);
NOTE: Here, we haven’t loaded the CustID value. Because it is an auto-increment column, and it updates automatically. Please refer to Create Table article.
As we said above, If you are loading data for all the existing columns, then ignore the column names (Syntax 2). It means the above MySQL statement can also write as:
TIP: It is not a good habit to ignore the column names in this statement. So, always provide the column names.
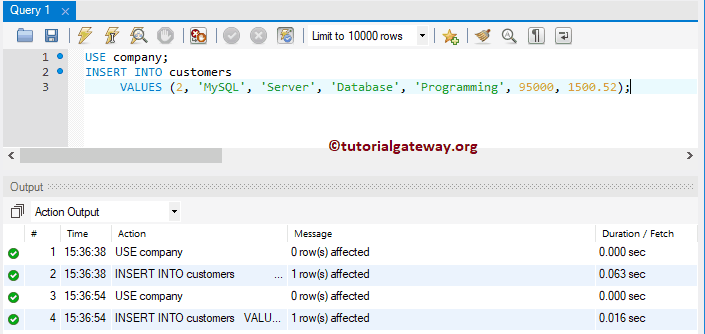
The above Insert queries put data into First_Name, Last_Name, Education, Occupation, Yearly_Income, and Sales columns. Whenever you omit the field names, you must specify the column_values in the order determined by the destination table structure.
MySQL Insert Multiple Rows
In this example, we add multiple rows to the customer more traditionally.
USE company; INSERT INTO customers VALUES (3, 'James', 'Smith', 'Degree', 'Developer', 85000, 38313.56); INSERT INTO customers VALUES (4, 'Michael', 'Smith', 'BTech', 'Developer', 80000, 34810.62);
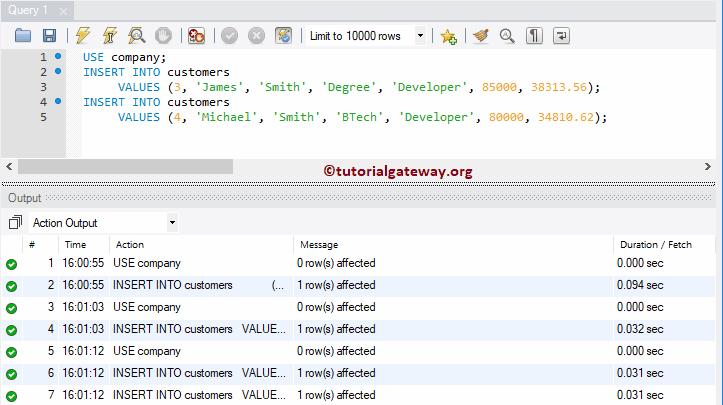
Here, we use UNION ALL (or UNION) to load multiple records into the company.
USE company;
INSERT INTO customers
SELECT 5, 'Maria', 'Garcia', 'Hig School', 'Developer', 55000, 32013.12
UNION ALL
SELECT 6, 'Maria', 'Rodriguez', 'Post Graduate', 'Senior Developer', 980000, 30510.62;
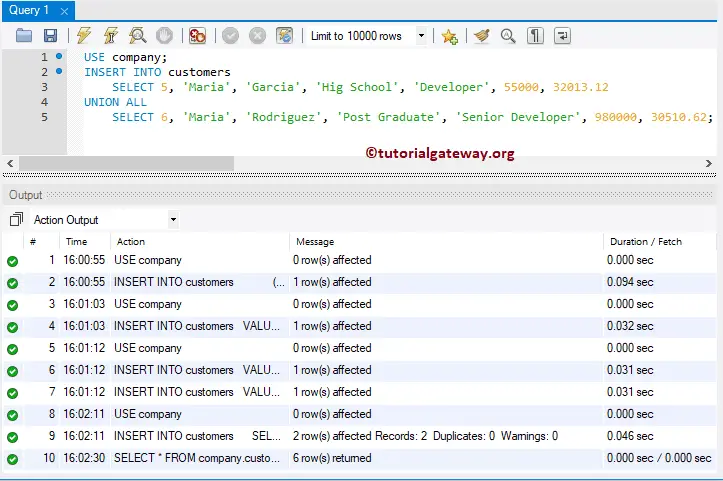
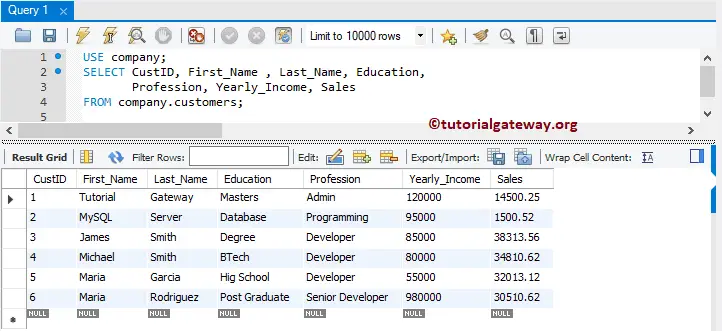
Let us see the output.
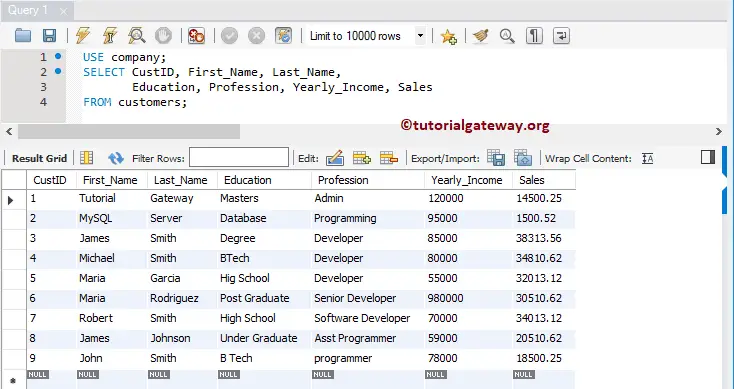
The following MySQL Insert query is the most popular way to load multiple records into a table.
USE company;
INSERT INTO customers
(First_Name, Last_Name, Education, Profession, Yearly_Income, Sales)
VALUES ('Robert', 'Smith', 'High School', 'Software Developer', 70000, 34013.12),
('James', 'Johnson', 'Under Graduate', 'Asst Programmer', 59000, 20510.62),
('John', 'Smith', 'B Tech', 'programmer', 78000, 18500.25);
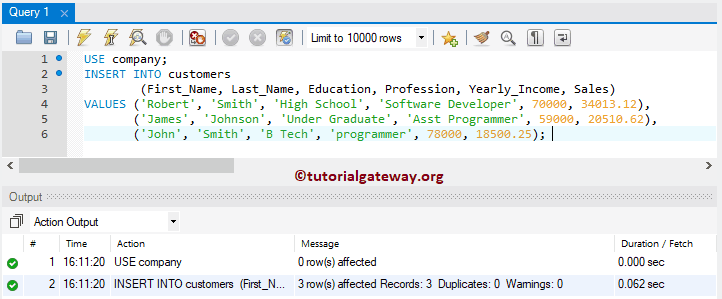
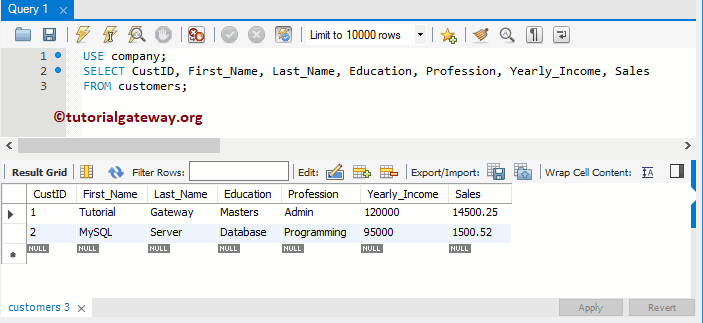
Let us the records present in the customer.
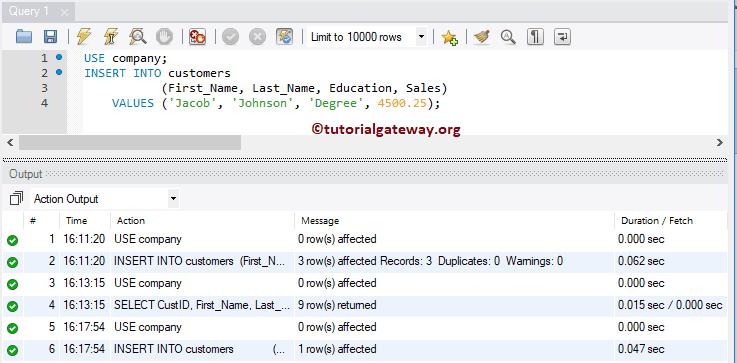
It is not mandatory to put all the column values in one go. You can omit a few columns while loading and update them later. In this insert statement example, we put a few column values into the company.
USE company;
INSERT INTO customers
(First_Name, Last_Name, Education, Sales)
VALUES ('Jacob', 'Johnson', 'Degree', 4500.25);
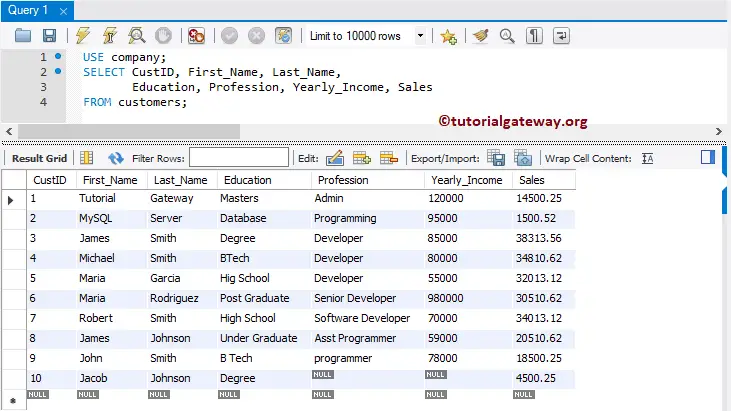
The above query loads data into First_Name, Last name, Education, and Sales columns. Here, NULL values are added for the remaining columns.
TIP: When putting a few records into the table, you must define the column names.
MySQL Insert Into Example
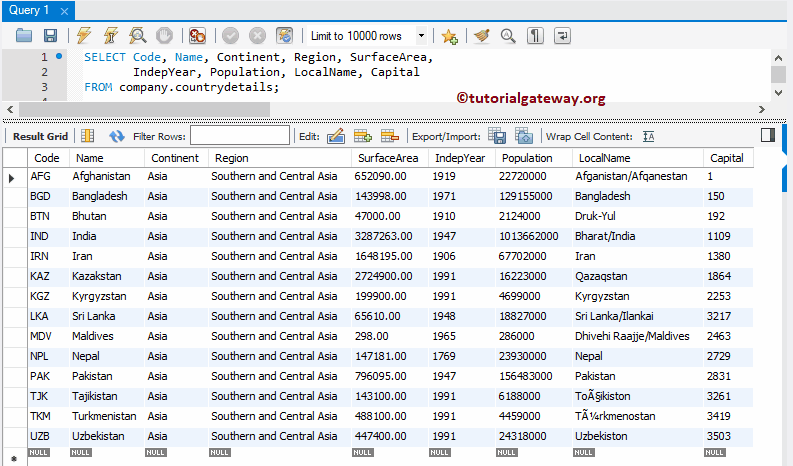
Instead of hard coding all the values, you can use INSERT INTO SELECT Statement to put rows from one table to another. In this example, we select rows from the country and load them into the countrydetails. Here, we are going to restrict the rows using the WHERE Clause.
INSERT INTO company.countrydetails
(Code, Name, Continent, Region, SurfaceArea, IndepYear, Population, LocalName, Capital)
SELECT Code, Name, Continent, Region, SurfaceArea, IndepYear, Population, LocalName, Capital
FROM world.country
WHERE Continent = 'Asia' AND Region = 'Southern and Central Asia';
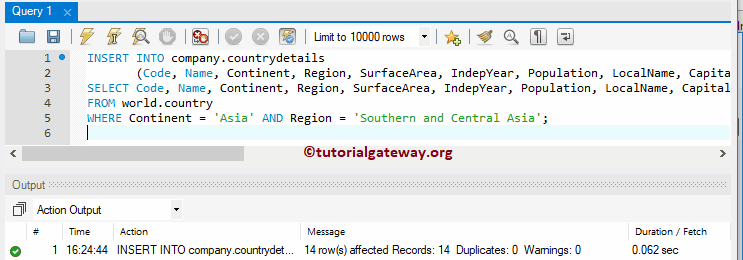
We are not going to explain the code implementation at this point. Let us see whether the query added the selected data into the destination table or not.
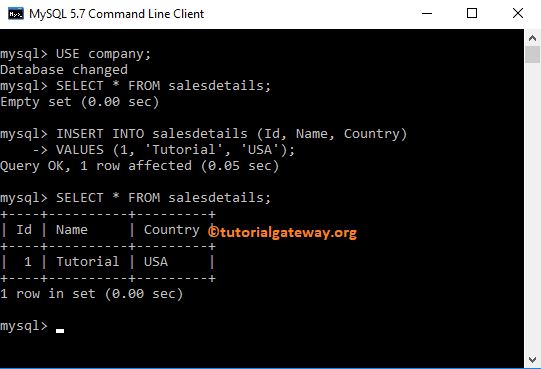
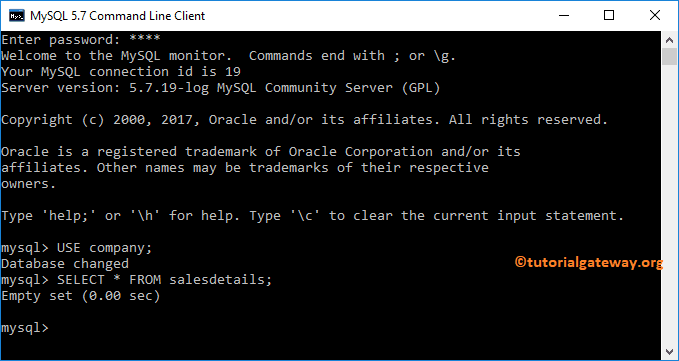
Command Prompt Example
In this Insert example, we add one record to the sales details using the command prompt. Before we get into the query, the data inside our table is
CODE and the Output.