In the previous post, we already explained the Structure and Union. So, please refer to those posts in C before going into the differences between union and structure.
- Both are used to group different data types to organize data structurally.
- In C Programming, Structure and Union are similar in syntax with keyword differences.
- Creating these variables to access their respective members is the same as keyword differences.
This article shows you the difference between Structure and Union in C Programming with an example. Before going into a practical example, let us see their differences.
| Structures | Union |
|---|---|
| Struct keyword is used to declare the structure | Union keyword is used to declare it |
| The structure variable will allocate memory for all the structure members separately. | The union variable will allocate common memory for all the union members. |
| Example: struct Employee{ int age; char name[50]; float salary; }; | Example: union Employee{ int age; char name[50]; float salary; }; |
| Structures will occupy more memory space. Memory_Size = addition of all the structure members sizes. Memory_Size = int + char array [50] + float Memory_Size = 2 + 50 + 4 Bytes Memory_Size = 56 Byte | The union will occupy less memory space compared to structures.Memory_Size = Size of the largest Union member. From the above example, the Largest member is the char array. So, Memory_Size = 50 Bytes |
| It allows us to access any or all the members at any time. | It allows us to access only one union member at a time. |
C Program to find the Difference between Structure and Union
In this C program, we are going to declare the structure and union with the same data type members. Then we are going to calculate the size using the sizeof function. Before these differences, I suggest you refer to Structure and Union articles in this C Programming.
#include <stdio.h>
struct Employee
{
int age;
char Name[50];
char Department[20];
float Salary;
};
union Person
{
int ag;
char Nam[50];
char Departent[20];
float Salar;
};
int main()
{
struct Employee emp1;
union Person Person1;
printf(" The Size of Employee Structure = %d\n", sizeof (emp1) );
printf(" The Size of Person Union = %d\n", sizeof (Person1));
return 0;
}
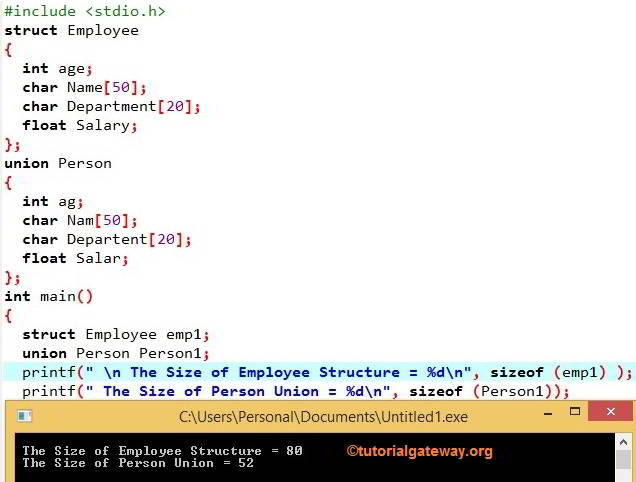
If you observe the above, both the Employee and Person hold the same data type and the same size. Within the main() function, we created the Employee structure variable emp1 using the below statement.
struct Employee emp1;
Next, We created Person Union variable Person1 using the below statement
union Person Person1;
Next, within the printf statement, we used the C sizeof operator to calculate the size of both the Employee structure and Person Union.
sizeof (emp1) = 80
int Age; - It will take 4 bytes of space in the memory char Name[50]; - It will take 50 bytes of space in the memory char Department[20]; - It will take 20 bytes of space in the memory float Salary; - It will take 4 bytes of space in the memory
Memory Size of a Structure = 4 + 50 + 20 + 4 => 78 Bytes
If you observe the output, it has given 80 Bytes. Because of the structure padding, it has taken an extra 2 Bytes. We will discuss the structure padding in the coming posts.
sizeof (Person1) = 52 Bytes
The largest member from the above is Name[50]. As we all know
Memory Size = Largest union number size = 50 Bytes
It’s again 2 extra bytes for padding

Comments are closed.