How to Write a Program for Armstrong Number in C using While Loop, For Loop, Functions, and Recursion.? We will also show you the C Program for Armstrong Number between 1 and n.
If the given number is equal to the sum of the power of n for each digit present in that integer, then that can be an Armstrong Number in C programming. For example, 153 is an Armstrong Number because the total individual digits in 153 = 3
153 = 1³ + 5³ + 3³
= 1 + 125 + 27 = 153
The below steps will show you the standard approach to checking for the Armstrong Number in C programming.
- Enter any value.
- Divide the given one into individual digits (For Example, Divide 153 into 1, 5, and 3).
- Calculate the power of n for each individual and add those digits.
- Compare the original value with the Sum value.
- If they exactly matched, then it is. Otherwise, it is not.
C Program to Check Armstrong Number using While Loop
This program allows the user to enter any positive integer. Then, this C program will check whether a number is Armstrong or Not using the While Loop.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(void)
{
int Number, Temp, Reminder, Times =0, Sum = 0;
printf("Please Enter number to Check = ");
scanf("%d", &Number);
//Helps to prevent altering the original value
Temp = Number;
while (Temp != 0)
{
Times = Times + 1;
Temp = Temp / 10;
}
Temp = Number;
while( Temp > 0)
{
Reminder = Temp %10;
Sum = Sum + pow(Reminder, Times);
Temp = Temp /10;
}
printf("Sum of entered number is = %d\n", Sum);
if ( Number == Sum )
printf("%d is Armstrong Number.\n", Number);
else
printf("%d is not.\n", Number);
return 0;
}

This C Armstrong Number program allows users to enter any positive integer. Next, assign it to a variable. Next, We assign the original value to the Temp variable. It will help us to preserve our actual value and then do all the manipulation on the Temp variable.
The While loop will ensure that the given value is greater than 0. The statements inside the while loop will split the value and count the total individual digits inside the given value.
If you don’t understand this program logic, Please refer to the C Program to Count Number Of Digits article.
Second While Loop will ensure that the given integer is greater than 0. Let us see the working principle of this C Programming while loop in iteration wise.
For this Armstrong number in C demonstration, User Entered value: Number = 1634 and Sum = 0
Temp = Number
Temp = 1634
First Iteration
Reminder = Temp %10
Reminder = 1634 % 10 = 4
Sum = Sum + pow (Reminder, Times)
For this example, Times = 3 because the digits in 1634 = 4. So, the pow() function in this C Armstrong number will multiply the Reminder 4 times.
Sum = Sum + (Reminder * Reminder * Reminder * Reminder)
Sum= 0 + (4 * 4 * 4 * 4) => 0 + 256
Sum = 256
Temp = Temp /10 = 1634 /10
Temp = 163
NOTE: If the digits count is 5, the Reminder will be multiplied by 5 times.
Second Iteration: From the first iteration, the values of both the Temp and Sum have changed as Temp = 163 and Sum = 256
Reminder = 163 % 10 = 3
Sum = 256 + (3 * 3 * 3 * 3)
Sum = 256 + 81 => 337
Temp = 163 /10 = 16
C Armstrong Number Program Third Iteration: Temp = 16 and Sum = 337
Reminder = 16 % 10 = 6
Sum = 337 + (6 * 6 * 6 *6) => 337 + 1296
Sum = 1633
Temp = 16 /10 = 1
Fourth Iteration of the C Armstrong number program: Temp = 1 and Sum = 1633
Reminder = 1 % 10 = 0
Sum = 1633 + (1 * 1 * 1 * 1)
Sum = 1633 + 1 => 1634
Temp = 1/10 = 0
Here, temp = 0. So, the while loop condition in this C Armstrong Number program will fail.
if (Number== Sum ) – Condition will check whether the user entered value is exactly equal to Sum or not. This condition is True, and it is, else it is not.
if(1634 == 1634) –TRUE.
NOTE: If finding the number below 1000, remove the while loop to count the digits. Next, replace the below code.
Sum = Sum + pow(Reminder, Times); With Sum = Sum + (Reminder * Reminder * Reminder)
C Program for Armstrong Number using For Loop
This program allows the user to enter any positive integer. Then, this C program will check whether a number is Armstrong or Not using For Loop.
// using For Loop
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(void)
{
int Num, Temp, Reminder, Times =0, Sum = 0;
printf("\nPlease Enter any num \n");
scanf("%d", &Num);
for(Temp = Num; Temp != 0;Temp = Temp / 10)
{
Times = Times + 1;
}
for(Temp = Num; Temp > 0; Temp = Temp /10 )
{
Reminder = Temp % 10;
Sum = Sum + pow(Reminder, Times);
}
printf("Sum = %d\n", Sum);
if ( Num == Sum )
printf("\n%d is Armstrong.\n", Num);
else
printf("%d is not.\n", Num);
return 0;
}
We replaced the While loop in the above example with the For loop. Please refer to For Loop in C Programming to understand this program.
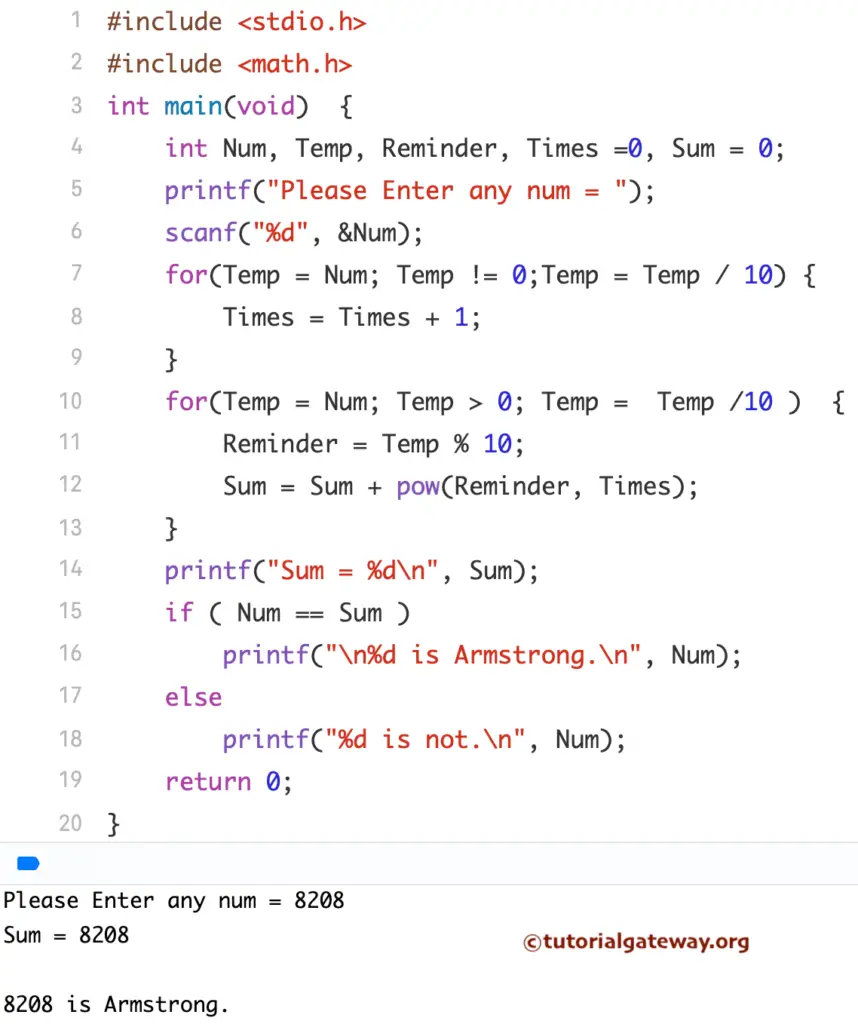
C Program for Armstrong Number using Functions
This program allows the user to enter any positive integer. Next, this C program checks whether the number is Armstrong or Not using Functions.
// using Functions
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int Check_Arm(int);
int main()
{
int num, Sum = 0;
printf("\nPlease Enter any value \n");
scanf("%d", &num);
Sum = Check_Arm (num);
printf("Sum = %d\n", Sum);
if ( num == Sum )
printf("\n%d is Armstrong.\n", num);
else
printf("%d is not.\n", num);
return 0;
}
int Check_Arm (int num)
{
int Temp, Reminder, Times =0, Sum = 0;
Temp = num;
while (Temp != 0)
{
Times = Times + 1;
Temp = Temp / 10;
}
for(Temp = num; Temp > 0; Temp = Temp /10 )
{
Reminder = Temp %10;
Sum = Sum + pow(Reminder, Times);
}
return Sum;
}
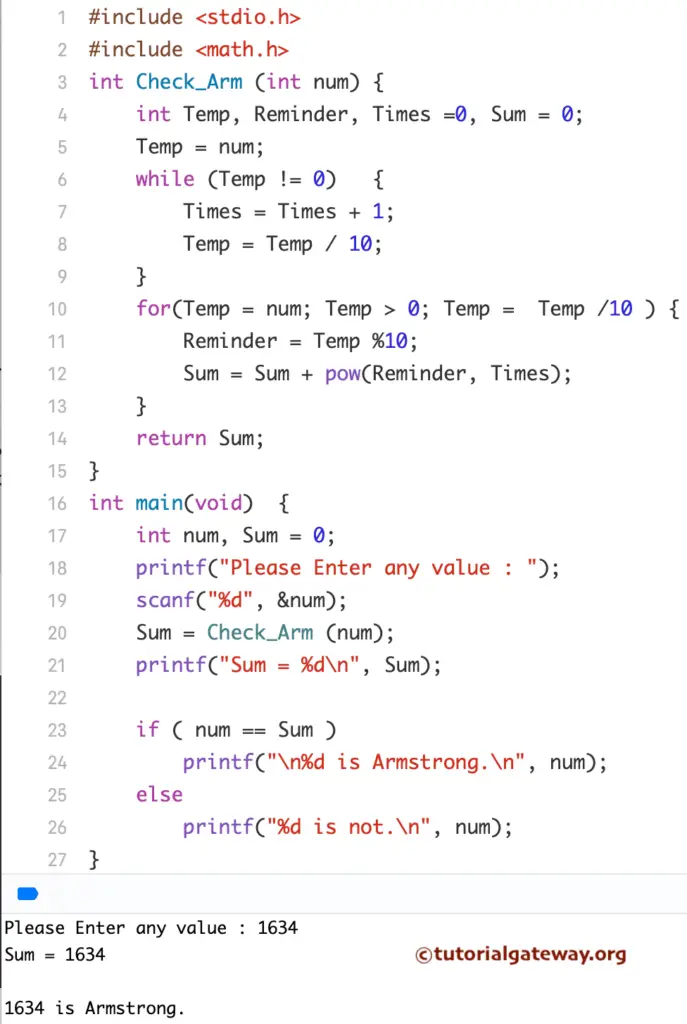
Within this program, when the compiler reaches Sum = Check_Arm(num); line in the main() program, then the compiler will immediately jump to the below Function:
int Check_Arm (int Number)
We already explained the LOGIC of this one in the above example.
NOTE: If we create a function with Void, there is no need to return any value. However, if we declare a function with any data type (int, float, etc.), we have to return something from the function.
C Program to find Armstrong Number using Recursion
This program allows you to enter any positive integer. Next, using the Recursion concept, this C program will check whether a number is Armstrong or Not.
This program used the Check_Arm (Number/10) statement inside a function. This statement will help to call the function Recursively with the updated value. If you miss this statement after completing the first line, it will terminate. For example, Num = 153, then the output will be 27
Let’s see the If condition of this program.
if (Num > 0) will check whether the num is greater than 0 or not. For Recursive functions, placing a condition before using the function recursively is very important. Otherwise, we will end up in infinite execution (Like Infinite Loop).
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int Check_Arm (int, int);
int main(void)
{
int Number, Sum = 0, Times =0,Temp;
printf("Please Enter num = ");
scanf("%d", &Number);
for(Temp = Number; Temp != 0; Temp = Temp / 10)
{
Times = Times + 1;
}
Sum = Check_Arm (Number, Times);
printf("Sum of entered is = %d\n", Sum);
if ( Number == Sum )
printf("%d is Armstrong.\n", Number);
else
printf("%d is not.\n", Number);
return 0;
}
int Check_Arm (int Number, int Times)
{
static int Reminder, Sum = 0;
if (Number > 0)
{
Reminder = Number %10;
Sum = Sum + pow(Reminder, Times);
Check_Arm (Number /10, Times);
return Sum;
}
else
return 0;
}

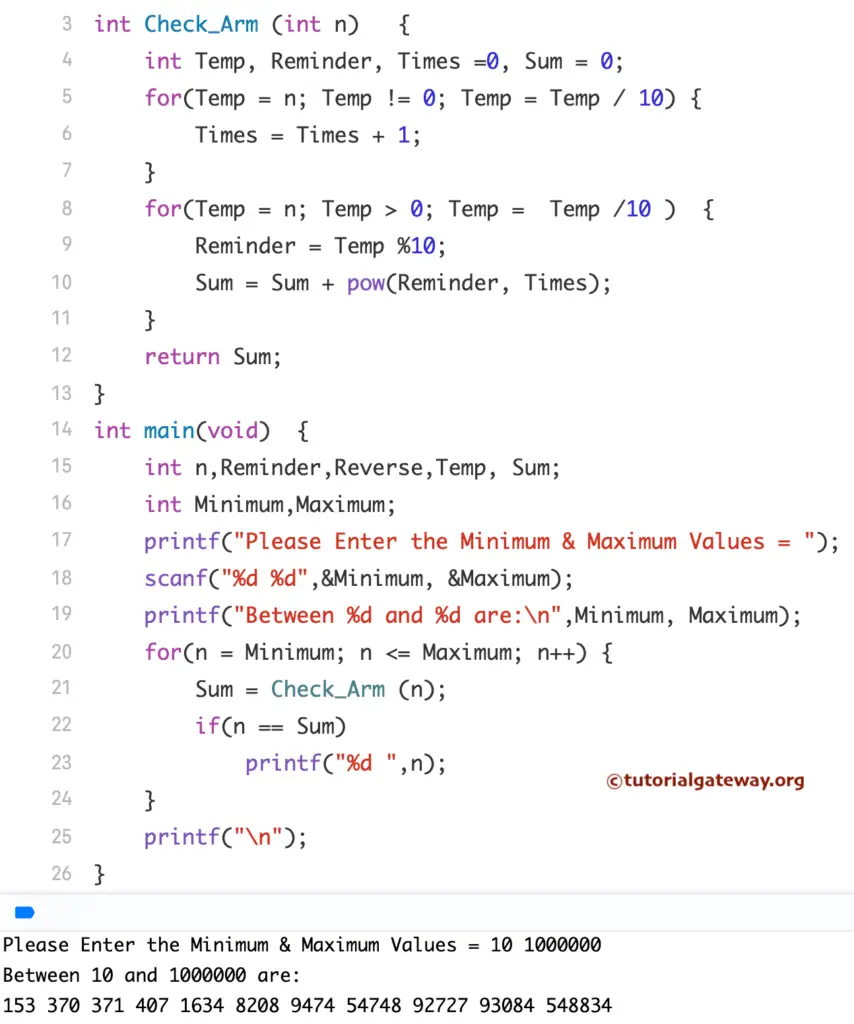
C Program to Print Armstrong Numbers between 1 to 1000 (or n)
This program allows you to enter minimum and maximum values. This C program finds and prints Armstrong Numbers between the Minimum and Maximum values.
The For Loop helps the compiler iterate between Minimum and Maximum Variables. Iteration starts at the Minimum, and then it will not exceed the Maximum variable.
if(n==Sum) -– condition will check whether the iteration is precisely equal to the Reverse of it or not. And, if this condition is True, then it is Armstrong. Otherwise, it is not. So, if this condition is True, the print statement will print.
// between 1 to N or 1000
#include<stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int Check_Arm (int);
int main(void)
{
int n,Reminder,Reverse,Temp, Sum;
int Minimum,Maximum;
printf("\nPlease Enter the Minimum & Maximum Values\n");
scanf("%d %d",&Minimum, &Maximum);
printf("Between %d and %d are:\n",Minimum, Maximum);
for(n = Minimum; n <= Maximum; n++)
{
Sum = Check_Arm (n);
if(n == Sum)
printf("%d ",n);
}
printf("\n");
}
int Check_Arm (int n)
{
int Temp, Reminder, Times =0, Sum = 0;
for(Temp = n; Temp != 0; Temp = Temp / 10) {
Times = Times + 1;
}
for(Temp = n; Temp > 0; Temp = Temp /10 )
{
Reminder = Temp %10;
Sum = Sum + pow(Reminder, Times);
}
return Sum;
}