How to Write a Program to Print Fibonacci Series in C programming using While Loop, For Loop, Functions, and Recursion? The C Fibonacci Series numbers are displayed in the following sequence: 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34,…
If you observe the above C Fibonacci Series pattern, the First Value is 0, the Second Value is 1, and the following number results from the sum of the previous two numbers. For example, the Third value is (0 + 1), the Fourth value is (1 + 1), and so on.
Fibonacci series program in C using While Loop
This program allows the user to enter any positive integer. And then display the Fibonacci series of numbers from 0 to user-specified numbers using the While Loop in C programming.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int Number, i = 0, Next, First_Value = 0, Second_Value = 1;
printf("\n Please Enter the Range Number: ");
scanf("%d",&Number);
while(i < Number)
{
if(i <= 1)
{
Next = i;
}
else
{
Next = First_Value + Second_Value;
First_Value = Second_Value;
Second_Value = Next;
}
printf("%d \t", Next);
i++;
}
return 0;
}
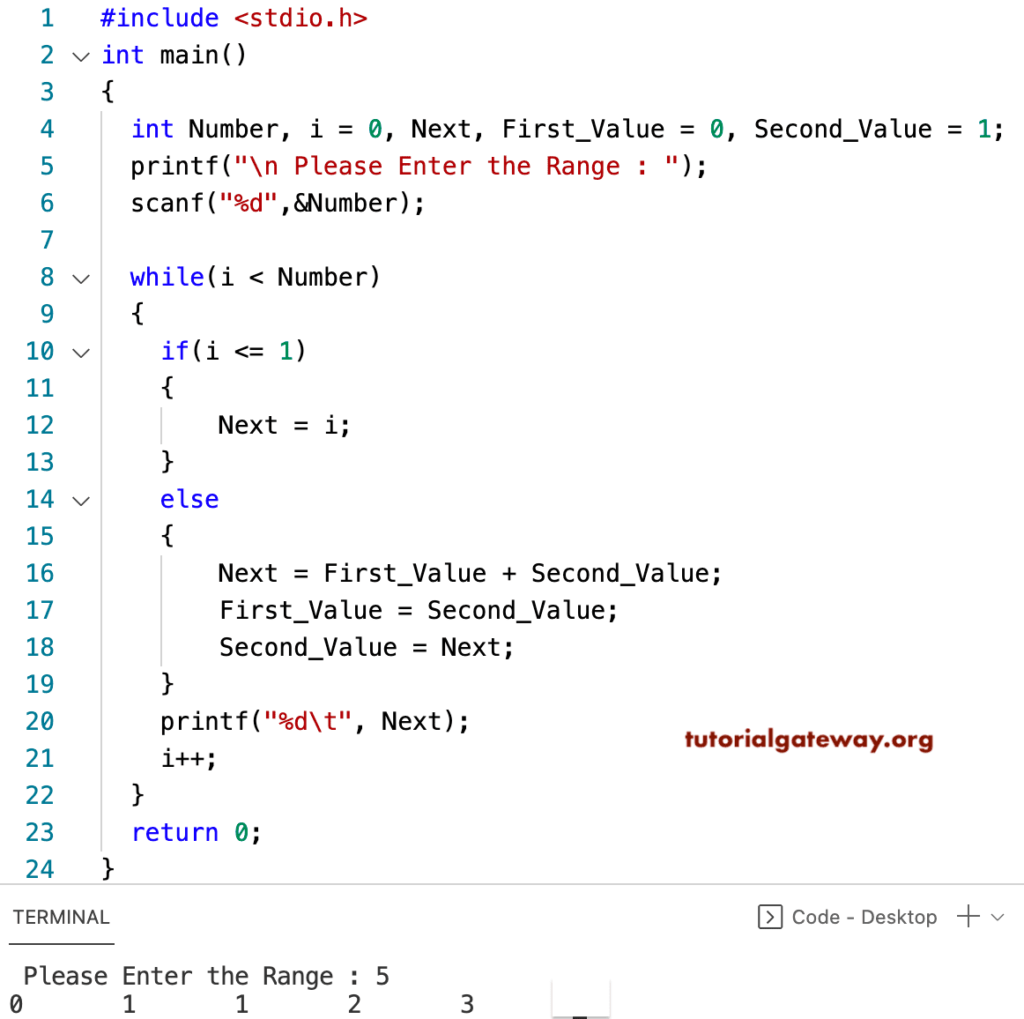
In this program, first, We declared four integer variables Number, i, First_Value, Second_Value, and assigned values as we showed above. Then, the first printf and scanf statements ask the user to enter any positive integer, which assigns to a Number variable.
The While loop in this c Fibonacci series program will ensure that the Loop will start from 0, which is less than the user-specified number. Within the While Loop, we used the If Else statement.
- If i value is less than or equal to 1, i value will be assigned to Next.
- If i value is greater than 1, perform calculations inside the Else block.
Let us see the working principle of this while loop iteration-wise. From the above C programming screenshot, you can observe that the user entered values are Number= 5, i = 0, First_Value = 0, Second_Value = 1
First Iteration
The condition inside the While (0 < 5) returns TRUE. So, the Fibonacci series program will start executing the statements inside the while loop.
We have the If Else statement within the while loop, and the condition if (0 <= 1) returns TRUE. So, Next = 0, and the compiler will exit from the if statement block.
Print statement printf(“%d”, Next) will print 0.
Lastly, i will increment to 1. Please refer to the Increment and Decrement Operators article to understand the ++ notation.
C Fibonacci Series program Second Iteration
- The condition While (1 < 5) returns TRUE
- If condition if (1 <= 1) returns TRUE. So, Next = 1, and the compiler will exit from the if statement block
- printf(“%d”, Next) will print the value 1
- Lastly, i will increment to 1
Third Iteration
- While (2 < 5) returns TRUE
- if (2 <= 1) returns FALSE. So, statements inside the else block will start executing
- Next = First_Value + Second_Value ==> 0 + 1 = 1
- First_Value = Second_Value = 1
- Second_Value = Next = 1
- Next, Print statement printf(“%d”, Next) will print the value 1.
- i = 3
C Fibonacci series program Fourth Iteration
- While (3 < 5) returns TRUE
- if (3 <= 1) returns FALSE. So, the compiler executes else block
- Next = First_Value + Second_Value ==> 1 + 1 = 2
- First_Value and Second_Value = 1
- Second_Value = Next = 2
- It prints 2. Next, i will be 4
Fifth Iteration: while(4 < 5) = True
- If condition if (4 <= 1) returns FALSE
- Next = 1 + 2 => 3
- First_Value = Second_Value = 2
- Second_Value = Next = 3
- i becomes 5
Sixth Iteration: While (5 < 5) returns FALSE. So, the compiler exits from the while loop.
From the above, Our final output of the program Next values are: 0 1 1 2 3
C Fibonacci Series Program using For Loop
This program allows the user to enter any positive integer. And then, this C program will print the Fibonacci series of numbers from 0 to n using For Loop.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int Number, Next, i, First_Value = 0, Second_Value = 1;
printf("\n Please Enter the Range Number: ");
scanf("%d",&Number);
/* Find & Displaying */
for(i = 0; i <= Number; i++)
{
if(i <= 1)
{
Next = i;
}
else
{
Next = First_Value + Second_Value;
First_Value = Second_Value;
Second_Value = Next;
}
printf("%d \t", Next);
}
return 0;
}
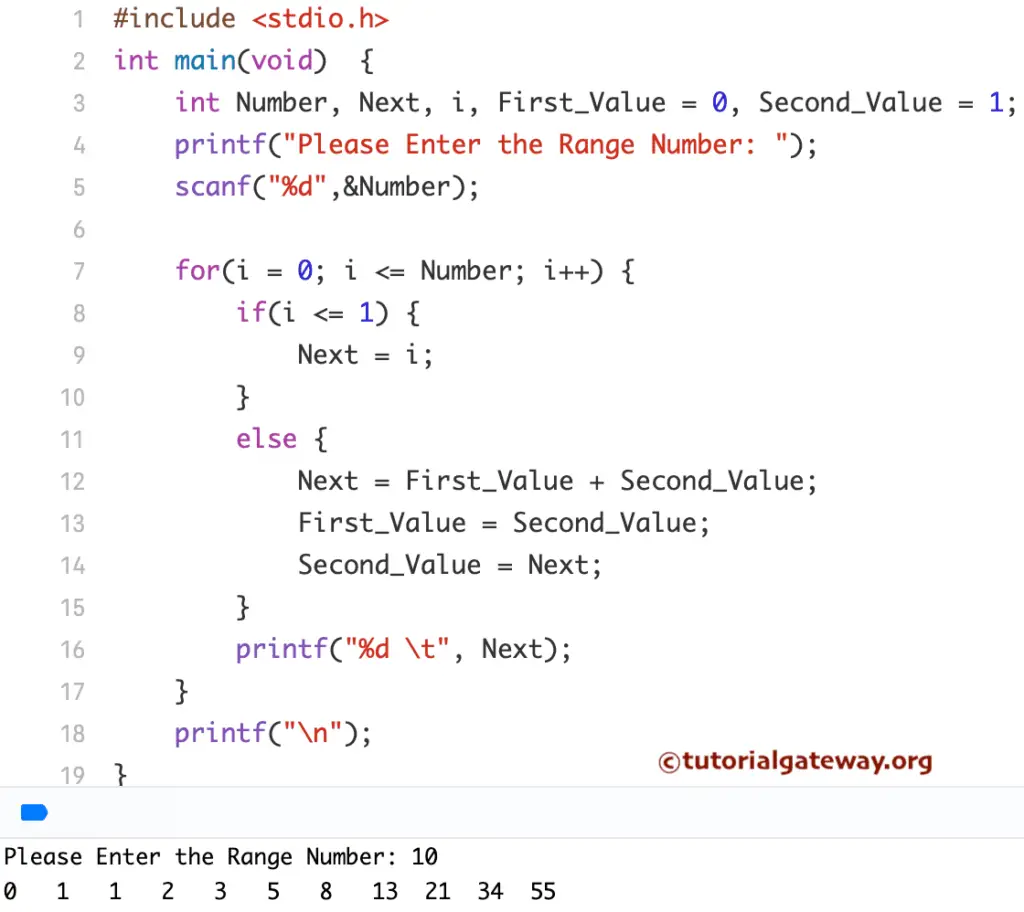
We just replaced the While loop in the above example with the For loop. Please refer to the For Loop article.
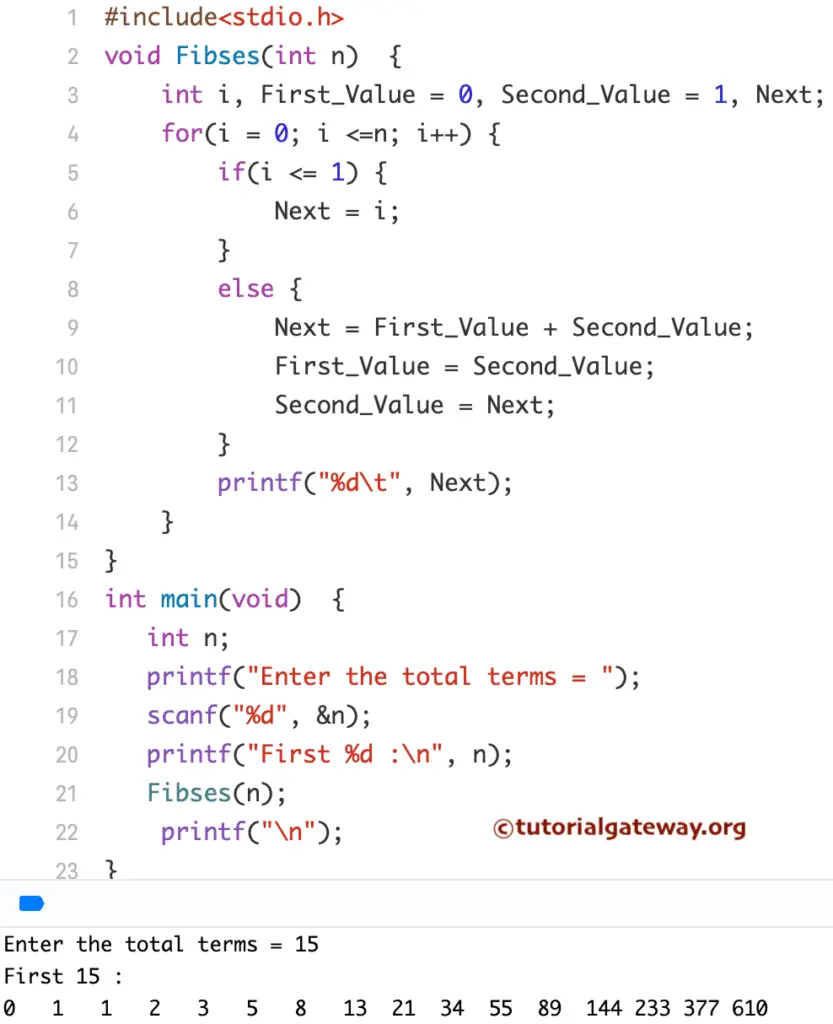
C Program to Print Fibonacci Series of Numbers using Functions
This C program prints the Fibonacci series of numbers from 0 to 100 using Functions. When the compiler reaches the FibSes(Number); line, the compiler will immediately jump to the below function void FibSes.
#include<stdio.h>
void Fibses(int n) ;
int main()
{
int n;
printf("Enter the total terms\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("First %d :\n", n);
Fibses(n) ;
return 0;
}
void Fibses(int n)
{
int i, First_Value = 0, Second_Value = 1, Next;
for(i = 0; i <=n; i++)
{
if(i <= 1)
{
Next = i;
}
else
{
Next = First_Value + Second_Value;
First_Value = Second_Value;
Second_Value = Next;
}
printf("%d\t", Next);
}
}
C Program to Print Fibonacci Series of Numbers using Recursion
The below Program prints the Fibonacci series numbers from 0 to a user-specified value using the Recursion.
#include<stdio.h>
int FibSeries(int);
int main()
{
int Num, i = 0, j;
printf("\n Please Enter upto which you want too print: ");
scanf("%d", &Num);
printf("Fib series\n");
for ( j = 0 ; j <= Num ; j++ )
{
printf("%d\t", FibSeries(j));
}
return 0;
}
int FibSeries(int Num)
{
if ( Num == 0 )
return 0;
else if ( Num == 1 )
return 1;
else
return ( FibSeries(Num - 1) + FibSeries(Num - 2) );
}
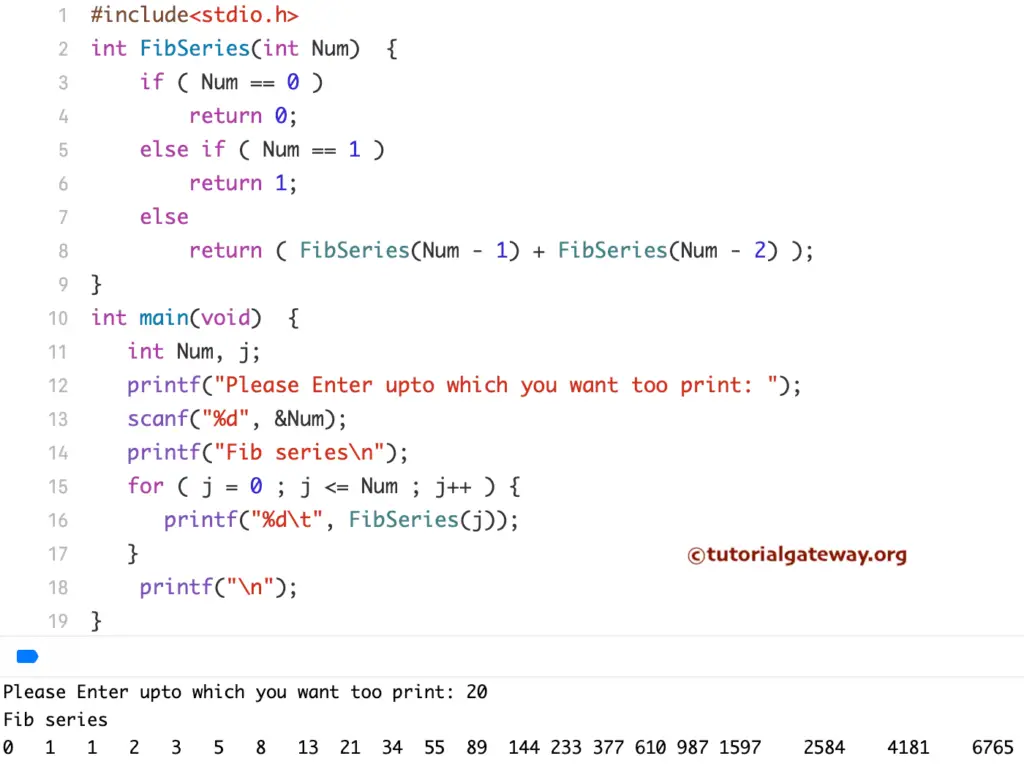
Recursion Class Analysis:
The following function will accept an integer as a parameter value and return an integer.
int FibSeries(int Num)
Let’s see the Else If statement inside the above-specified recursion functions
- if (Num == 0) checks whether the given number is 0 or not. When it is TRUE, the function will return Zero.
- if (Num == 1) checks whether the number is equal to 1 or not. If it’s TRUE, the function returns One.
- And if it is greater than 1, the compiler executes the statements in the else block.
Within the Else block of this C Fibonacci series using the Recursion program, we are calling the FibSeries function recursively to display the numbers.
return ( FibSeries(Num - 1) + FibSeries(Num - 2) );
For example, Num = 2
(FibSeries(Num – 2) + FibSeries(Num – 1))
(FibSeries(2 – 2) + FibSeries(2 – 1)), It means
(FibSeries (0)+ FibSeries(1))
return (0 + 1) = return 1
NOTE: For the recursive function, it is essential to place a condition before using the function recursively. Otherwise, this program will end up in infinite recursive execution (Same as an infinite Loop).
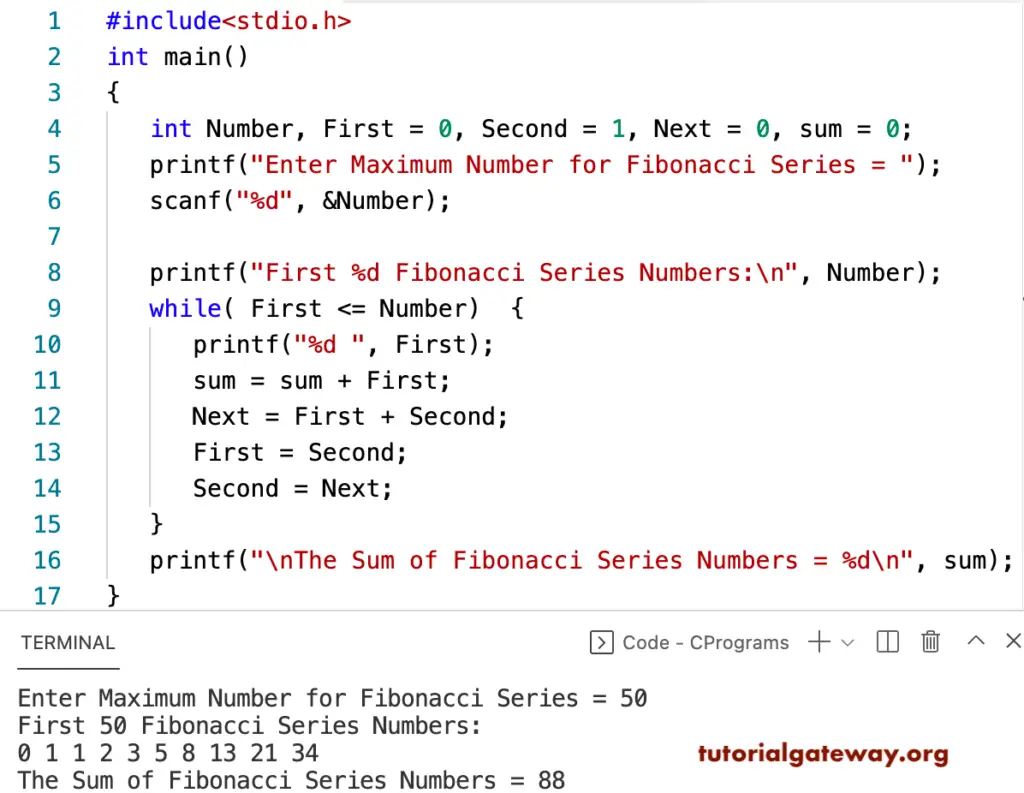
C program to find the Sum of the Fibonacci Series Numbers
This section shows how to write a C program to find the sum of Fibonacci series numbers using a while loop. In this example, the whole loop iterates numbers from 0 to n to print Fibonacci numbers and find the sum of those values.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int Number, First = 0, Second = 1, Next = 0, sum = 0;
printf("Enter Maximum Number for Fibonacci Series = ");
scanf("%d", &Number);
printf("First %d Fibonacci Series Numbers:\n", Number);
while( First <= Number)
{
printf("%d ", First);
sum = sum + First;
Next = First + Second;
First = Second;
Second = Next;
}
printf("\nThe Sum of Fibonacci Series Numbers = %d\n", sum);
}
C program to find the Sum of the Fibonacci Series using the for loop
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int Number, Next, Second = 1, sum = 0;
printf("\n Please Enter the Range Number: ");
scanf("%d",&Number);
for(int First = 0; First <= Number;)
{
printf("%d ", First);
sum = sum + First;
Next = First + Second;
First = Second;
Second = Next;
}
printf("\nThe Sum = %d\n", sum);
}
Please Enter the Range Number: 25
0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21
The Sum = 54In this example, the fibonacciSeries recursive function calculates the sum of Fibonacci series numbers by calling it recursively.
#include<stdio.h>
int fibonacciSeries(int Number)
{
if ( Number == 0 )
return 0;
else if ( Number == 1 )
return 1;
else
return ( fibonacciSeries(Number - 1) + fibonacciSeries(Number - 2) );
}
int main()
{
int Number, i = 0, j, sum = 0;
printf("\nEnter Maximum Number = ");
scanf("%d", &Number);
printf("Fibonacci Series Numbers up to %d:\n", Number);
for ( j = 0 ; j < Number; j++ )
{
printf("%d ", fibonacciSeries(j));
sum = sum + fibonacciSeries(j);
}
printf("\nThe Sum = %d\n", sum);
}
Enter Maximum Number = 20
Fibonacci Series Numbers up to 20:
0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55 89 144 233 377 610 987 1597 2584 4181
The Sum = 10945C Program to Find Nth Fibonacci Number using Recursion
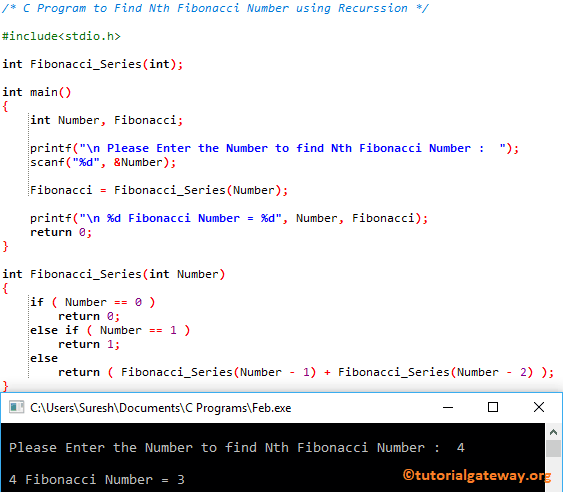
How to Write a C Program to Find Nth Fibonacci Number with example. For this, we are going to use the Recursion concept.
This program allows the user to enter any positive integer and display the Fibonacci number at that position using Recursion.
#include<stdio.h>
int Fibonacci_Series(int);
int main()
{
int Number, Fibonacci;
printf("\n Please Enter the Number to find Nth Fibonacci Number : ");
scanf("%d", &Number);
Fibonacci = Fibonacci_Series(Number);
printf("\n %d Fibonacci Number = %d", Number, Fibonacci);
return 0;
}
int Fibonacci_Series(int Number)
{
if ( Number == 0 )
return 0;
else if ( Number == 1 )
return 1;
else
return ( Fibonacci_Series(Number - 1) + Fibonacci_Series(Number - 2) );
}
Let’s see the Else If statement inside the above specified C Programming functions
- if (Number == 0) – check whether the given number is 0 or not. If the condition result is TRUE, the function will return Zero.
- if (Number == 1) – check whether the specified number equals 1. If it is TRUE, the function will return One.
- If the number is greater than 1, the Program compiler will execute the statements inside the else block.
Within the Else block, we call the Fibonacci_Series function Recursively to display the Fibonacci numbers.
For example, Number = 2
(Fibonacci_series(Number- 2) + Fibonacci_series(Number – 1))
(Fibonacci_series(2 – 2) + Fibonacci_series(2 – 1))
It means, (Fibonacci_series (0)+ Fibonacci_series(1))
return (0 + 1) = return 1
