How to write a C Program to pass Pointers to Functions?. Or How the Pointers to Functions in C programming work with a practical example.
Pass Pointers to Functions in C Example
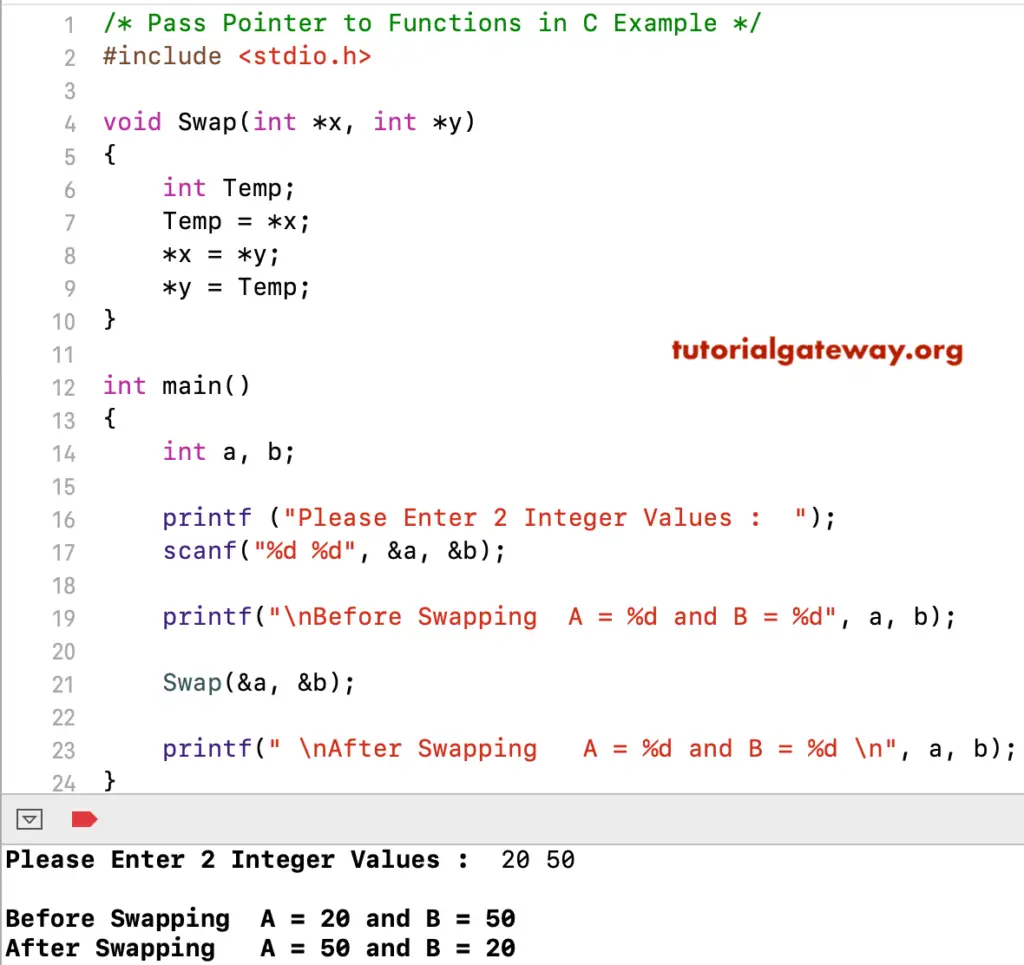
In this Pass Pointers to Functions program, we created a function that accepts two integer variables and swaps those two variables. I suggest you refer to the C Program to Swap two numbers article to understand the logic.
Like any other variable, you can pass the pointer as a function argument. I suggest you refer to Call By Value and Call by Reference and Pointers article to understand the C function arguments and pointers.
#include<stdio.h>
void Swap(int *x, int *y)
{
int Temp;
Temp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = Temp;
}
int main()
{
int a, b;
printf ("Please Enter 2 Integer Values : ");
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
printf("\nBefore Swapping A = %d and B = %d", a, b);
Swap(&a, &b);
printf(" \nAfter Swapping A = %d and B = %d \n", a, b);
}
C Pass Pointers to Functions Example 2
In this Pass Pointers to Functions program, we created a function that accepts the array pointer and its size. Please refer to the C program to find the Sum of All Elements in an Array article to know the logic. Within the main Pass Pointers to Functions program, we used for loop to iterate the array. Next, pass the user given value to an array. Next, we pass an array to a function
#include<stdio.h>
int SumofArrNumbers(int *arr, int Size)
{
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
sum = sum + arr[i];
}
return sum;
}
int main()
{
int i, Addition, Size, a[10];
printf("Please Enter the Size of an Array : ");
scanf("%d", &Size);
printf("\nPlease Enter Array Elements : ");
for(i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
Addition = SumofArrNumbers(a, Size);
printf("Sum of Elements in this Array = %d \n", Addition);
return 0;
}
Please Enter the Size of an Array : 7
Please Enter Array Elements : 10 20 200 30 500 40 50
Sum of Elements in this Array = 850 