Write a Program to Print Array Elements. Alternatively, write a Java program to Print Elements in an Array using For Loop, While Loop, and Functions with n example of each.
Java Program to Print Array Elements using For Loop
This program allows the user to enter the Size and items of an Array. Next, we are using For Loop to iterate each element in this array and print those array elements.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PrintArray1 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int i, Number;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(" Please Enter Number of elements in an array : ");
Number = sc.nextInt();
int [] Array = new int[Number];
System.out.print(" Please Enter " + Number + " elements of an Array : ");
for (i = 0; i < Number; i++)
{
Array[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("\n **** Elements in this Array are **** ");
for (i = 0; i < Number; i++)
{
System.out.print(Array[i] + "\t");
}
}
}
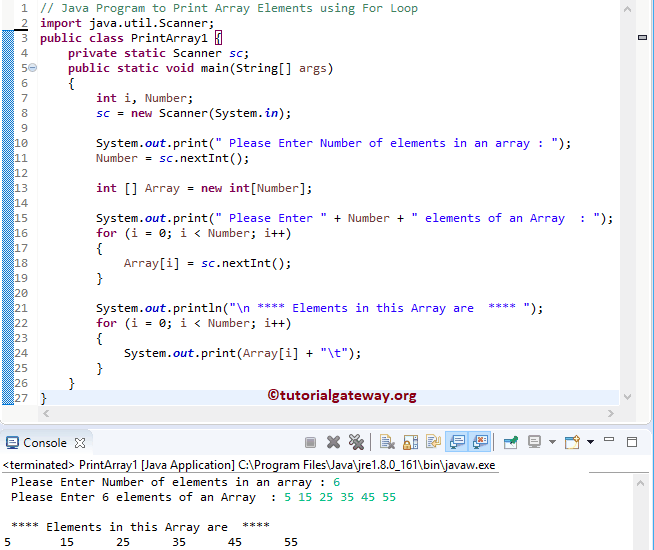
Here, Java For Loop makes sure that the number is between 0 and the maximum size value. In this example, it is from 0 to 7.
for(i = 0; i < Size; i ++)
First Iteration: for (i = 0; 0 < 6; 0++)
Condition is True. So, the compiler prints the first element(6) in this Array.
Second Iteration: for (i = 1; 1 < 6; 1++)
Condition is True – compiler prints the second element (15)
For Loop Third Iteration: for (i = 2; 2 < 6; 2++)
Condition is True. So, the Java compiler prints the third-second value (25)
Fourth Iteration: for (i = 3; 3 < 6; 3++)
Condition is True. So, it prints the fourth value (35)
Fifth Iteration: for (i = 4; 4 < 6; 4++)
Condition is True. So, the Java compiler prints the fourth value (45)
Sixth Iteration: for (i = 5; 5 < 6; 5++)
Condition is True. So, it prints the fourth value (55)
Seventh Iteration: for (i = 6; 6 < 6; 6++)
Condition is False. So, the compiler exits from the for loop
Java Program to Print Array Elements using While Loop
This program is the same as above, but this time we used the While Loop to print array items
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PrintArray2 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int i = 0, j = 0, Number;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(" Please Enter Number of elements in an array : ");
Number = sc.nextInt();
int [] Array = new int[Number];
System.out.print(" Please Enter " + Number + " elements of an Array : ");
while (i < Number)
{
Array[i] = sc.nextInt();
i++;
}
System.out.println("\n **** Elements in this Array are **** ");
while (j < Number)
{
System.out.print(Array[j] + "\t");
j++;
}
}
}
Please Enter Number of elements in an array : 10
Please Enter 10 elements of an Array : 10 20 30 540 60 876 11 44 89 13
**** Elements in this Array are ****
10 20 30 540 60 876 11 44 89 13 Using Functions
This program to display array elements is the same as the first example. However, we used a separate method to place the logic for displaying array items.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PrintArray3 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int i, Number;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(" Please Enter Total Numbers : ");
Number = sc.nextInt();
int [] Array = new int[Number];
System.out.print(" Please Enter " + Number + " Items : ");
for (i = 0; i < Number; i++)
{
Array[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
printAttay(Number, Array);
}
public static void printAttay(int Number, int[] Array)
{
int i;
System.out.println("\n **** Items are **** ");
for (i = 0; i < Number; i++)
{
System.out.println(" Element at Array["+ i +"] = " + Array[i]);
}
}
}
Please Enter Total Numbers : 5
Please Enter 5 Items : 12 24 54 65 78
**** Items are ****
Item at Array[0] = 12
Item at Array[1] = 24
Item at Array[2] = 54
Item at Array[3] = 65
Item at Array[4] = 78Java Program to Print Array Elements Using Recursive Functions
This Java program is the same as the above. But this time, we call the Print Array elements method Recursively with updated values.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PrintArray4 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int i, Number;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(" Please Enter Size : ");
Number = sc.nextInt();
int [] Array = new int[Number];
System.out.print(" Please Enter " + Number + " Items : ");
for (i = 0; i < Number; i++)
{
Array[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
printAttay(Array, 0, Number);
}
public static void printAttay(int[] Array, int Start, int Size)
{
if(Start >= Size)
{
return;
}
System.out.println(" Element at Arr["+ Start +"] = " + Array[Start]);
printAttay(Array, Start + 1, Size);
}
}
Please Enter Size : 6
Please Enter 6 Items : 3 6 9 12 15 18
Element at Arr[0] = 3
Element at Arr[1] = 6
Element at Arr[2] = 9
Element at Arr[3] = 12
Element at Arr[4] = 15
Element at Arr[5] = 18