Write a Java Program to Transpose a Matrix with an example or convert rows into columns in a given multi-dimensional array. Here, Transpose means converting rows into columns and columns into rows.
Java Program to Transpose Matrix using for loop
In this example, we declared a 3 * 3 org_arr integer with random values and another to store the transposed matrix. Next, we used a for loop to iterate the org_arr items. Within the nested for loop, we assigned the org_arr rows to tras_arr columns.
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i, j;
int[][] org_arr = {{15, 25, 35}, {45, 55, 65}, {75, 85, 95}};
int[][] trans_arr = new int[3][3];
for(i = 0; i < org_arr.length ; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < org_arr[0].length; j++)
{
trans_arr[j][i] = org_arr[i][j];
}
}
System.out.println("\nOriginal Items are :");
for(i = 0; i < org_arr.length ; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < org_arr[0].length; j++)
{
System.out.format("%d \t", org_arr[i][j]);
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
System.out.println("\nAfter Transposing Items are :");
for(i = 0; i < trans_arr.length ; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < trans_arr[0].length; j++)
{
System.out.format("%d \t", trans_arr[i][j]);
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}
Original Items are :
15 25 35
45 55 65
75 85 95
After Transposing Items are :
15 45 75
25 55 85
35 65 95 This Java code is the same as the above. However, this matrix code allows users to enter the number of rows, columns, and items.
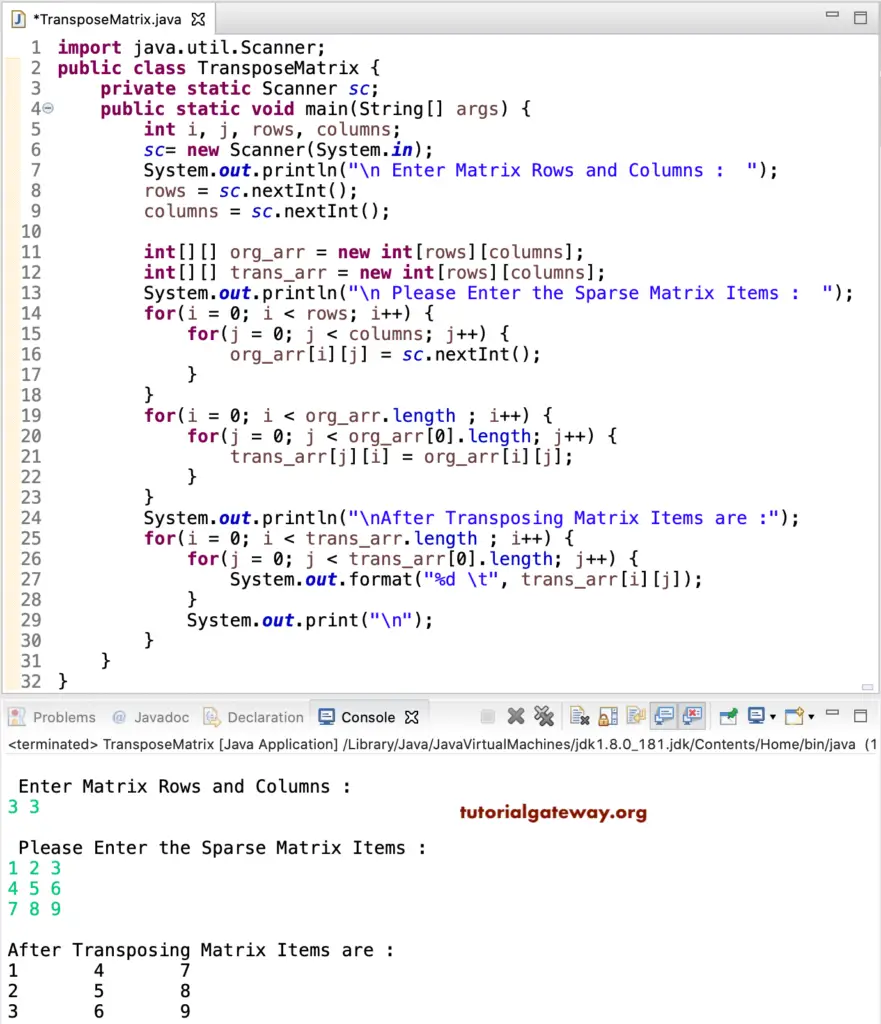
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TransposeMatrix {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i, j, rows, columns;
sc= new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("\n Enter Rows and Columns : ");
rows = sc.nextInt();
columns = sc.nextInt();
int[][] org_arr = new int[rows][columns];
int[][] trans_arr = new int[rows][columns];
System.out.println("\n Please Enter the Items : ");
for(i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < columns; j++) {
org_arr[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
for(i = 0; i < org_arr.length ; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < org_arr[0].length; j++)
{
trans_arr[j][i] = org_arr[i][j];
}
}
System.out.println("\nAfter Transposing Matrix Items are :");
for(i = 0; i < trans_arr.length ; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < trans_arr[0].length; j++)
{
System.out.format("%d \t", trans_arr[i][j]);
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}