Write a Java program to reverse an array using for loop, while loop, and functions. To reverse an array, we must create an entirely new one, for loop to iterate the items from last to first and add them to the new array.
Java Program to Reverse an Array using for loop
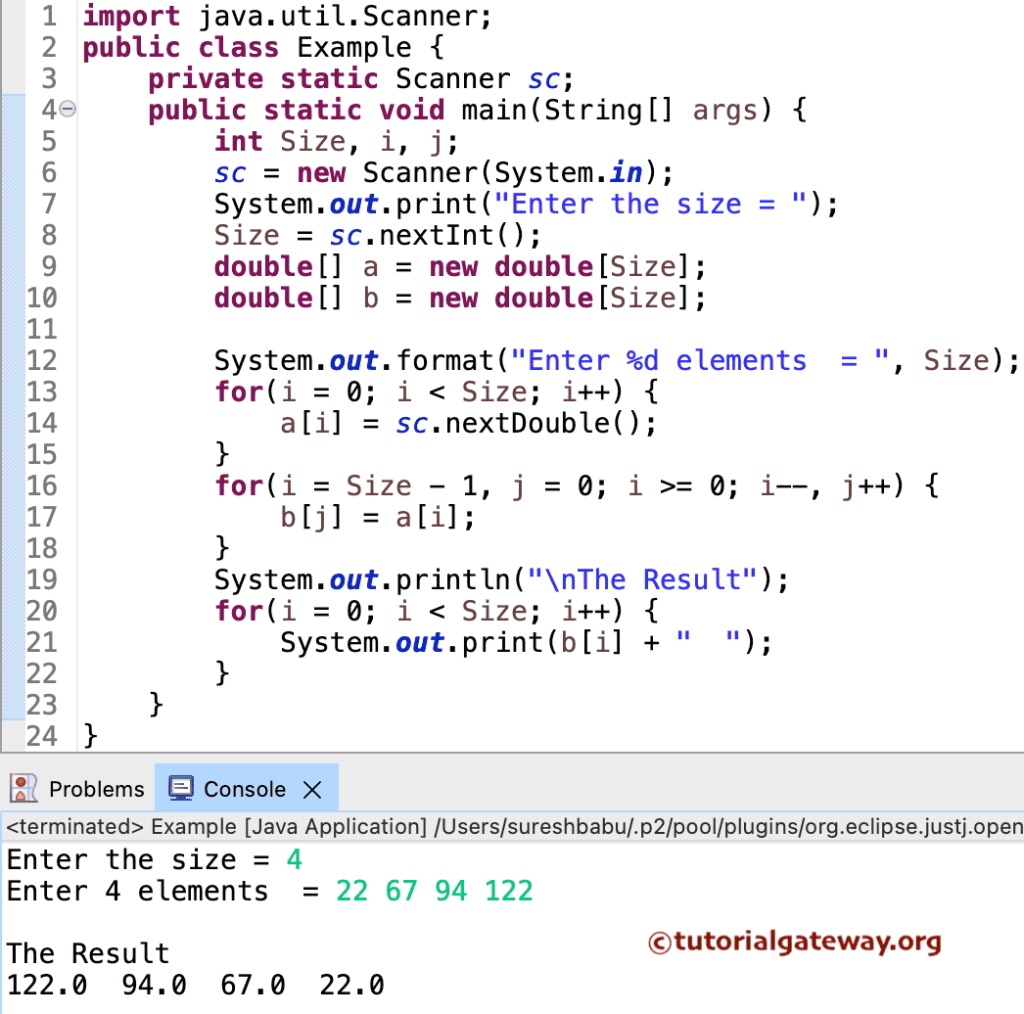
In this example, the for loop (for(i = Size – 1, j = 0; i >= 0; i–, j++)) iterates from bottom to top, assigning each value to another array. Next, we print that reverse array using another for loop.
package RemainingSimplePrograms;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Example1 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int Size, i, j;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the size = ");
Size = sc.nextInt();
double[] a = new double[Size];
double[] b = new double[Size];
System.out.format("Enter %d elements = ", Size);
for(i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
a[i] = sc.nextDouble();
}
for(i = Size - 1, j = 0; i >= 0; i--, j++)
{
b[j] = a[i];
}
System.out.println("\nThe Result");
for(i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
System.out.print(b[i] + " ");
}
}
}
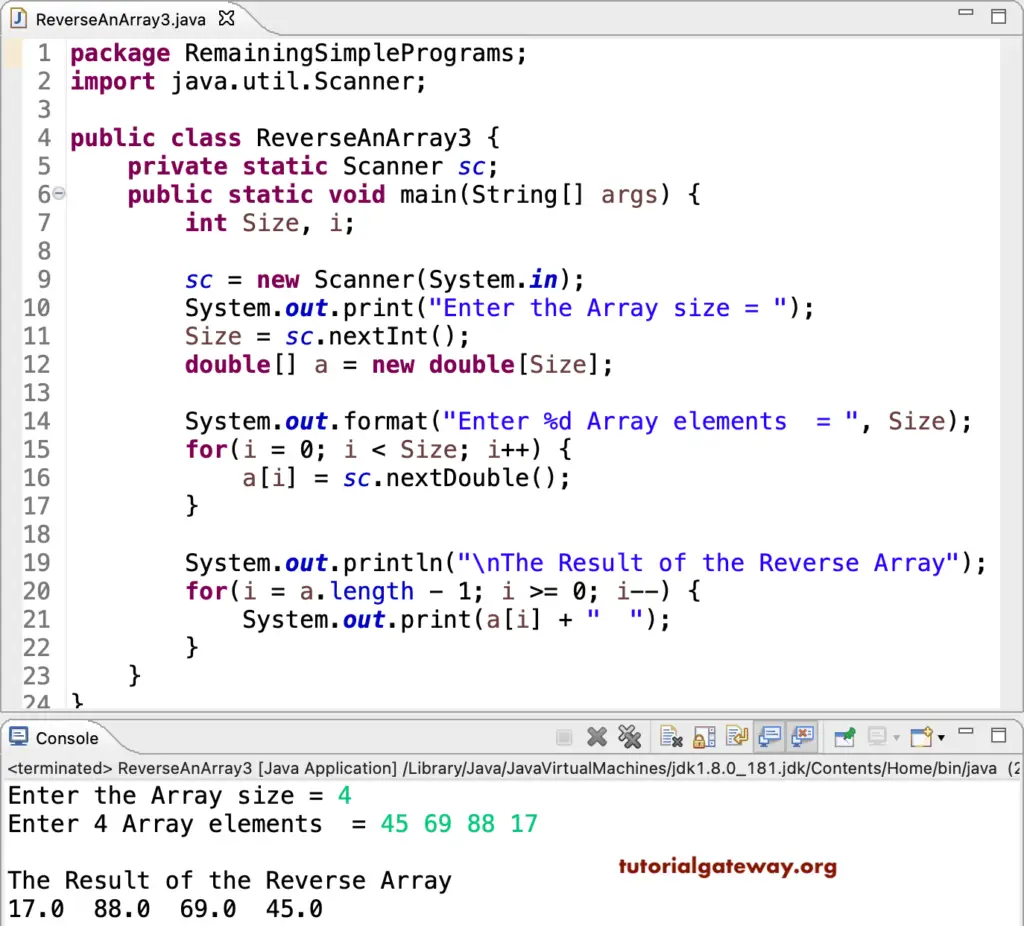
Instead of using another one in this example, we reversed and printed the array in a single for loop.
package RemainingSimplePrograms;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ReverseAnArray3 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int Size, i;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the Array size = ");
Size = sc.nextInt();
double[] a = new double[Size];
System.out.format("Enter %d Array elements = ", Size);
for(i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
a[i] = sc.nextDouble();
}
System.out.println("\nThe Result of the Reverse Array");
for(i = a.length - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
}
}
Using a while loop
This example uses the while loop and temporary variable to swap the array items and reverse them.
package RemainingSimplePrograms;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Example2 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int Size, i, j;
double temp;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the size = ");
Size = sc.nextInt();
double[] a = new double[Size];
System.out.format("Enter %d elements = ", Size);
for(i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
a[i] = sc.nextDouble();
}
j = i - 1;
i = 0;
while(i < j)
{
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
i++;
j--;
}
System.out.println("\nThe Result");
for(i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
}
}
Enter the size = 6
Enter 6 elements = 11 98.4 29.6 12.9 14.4 12.1
The Result
12.1 14.4 12.9 29.6 98.4 11.0 Java Program to Reverse an Array using recursive functions
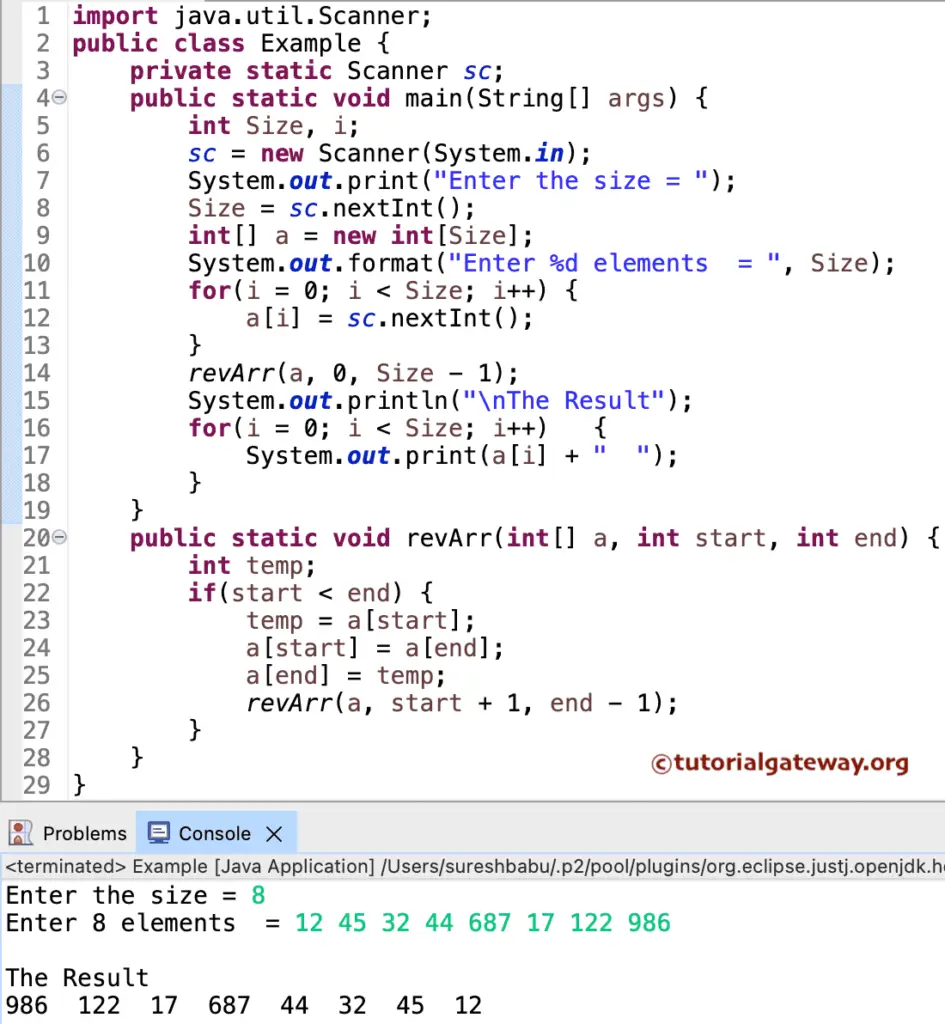
In this example, we created a revArr() function that accepts the start and end values. Within the If statement, the revArr(a, start + 1, end – 1) line calls the revArr() function recursively with an incremented start value and decreased end value.
package RemainingSimplePrograms;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Example4 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int Size, i;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the size = ");
Size = sc.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[Size];
System.out.format("Enter %d elements = ", Size);
for(i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
revArr(a, 0, Size - 1);
System.out.println("\nThe Result");
for(i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
}
public static void revArr(int[] a, int start, int end) {
int temp;
if(start < end)
{
temp = a[start];
a[start] = a[end];
a[end] = temp;
revArr(a, start + 1, end - 1);
}
}
}