Write a Java Program to Count the Number of Digits in a Number using For Loop, While Loop, Functions, and Recursion. To count the digits, we must break the number into individual items.
Java Program to Count Number of Digits in a Number using While Loop
This Java program allows the user to enter any positive integer, and then it will divide the given number into individual digits and count them using While Loop.
package SimplerPrograms;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class NumberofDigitsUsingWhile {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int Number, Count=0;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("\n Please Enter any Number: ");
Number = sc.nextInt();
while(Number > 0) {
Number = Number / 10;
Count = Count + 1;
}
System.out.format("\n Number of Digits in a Given Number = %d", Count);
}
}
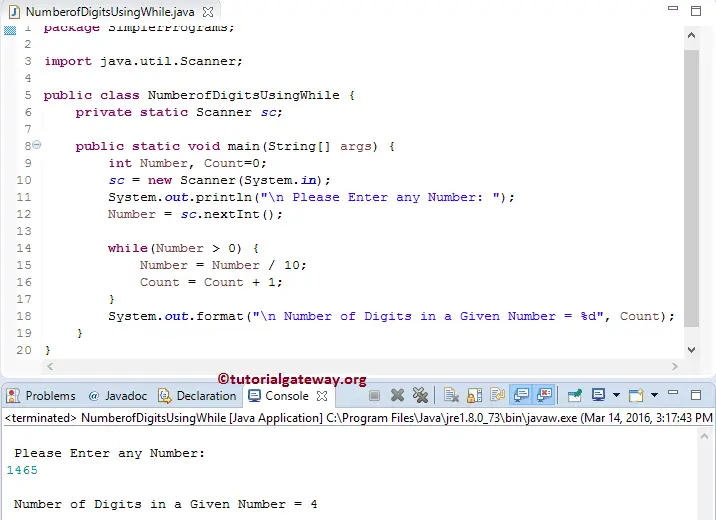
Within the following statements, the System.out.println statement will print the statement inside the double Quotes. Next, we assign the user entered value to an integer variable (Number)
System.out.println("\n Please Enter any Number: ");
Number = sc.nextInt();
Next line, we used the While Loop, and the Condition inside the While loop will make sure that the given number is greater than 0 (Means Positive integer)
while(Number > 0) {
Number = Number / 10;
Count = Count + 1;
}
In this Java Program to Count Number of Digits example, the User Entered value: Number = 1465, and we initialized the Count = 0
First Iteration
Number = Number / 10 = 1465 / 10
Number = 146
Count = Count + 1 = 0 + 1
Count = 1
Second Iteration: Within the first Iteration, Number = 146 and Count = 1
Number = 146 / 10 = 14
Count = 1 + 1 = 2
Third Iteration: Within the Second Iteration, the Number and Count’s values changed as Number = 14 and Count = 2.
Number = 14 / 10 = 1
Count = 2 + 1 = 3
Fourth Iteration: Within the third Iteration, the Number and Count’s values changed as Number = 1 and Count = 3.
Number = 1 / 10 = 0
Count = 3 + 1 = 4
Here, Number = 0. So, the condition present in the Java while loop will fail
The last System.out.format statement prints the number of digits in that number.
System.out.format("\n Number of Digits in a Given Number = %d", Count);
The output of the given variable 1465 is 4.
Java Program to Count Number of Digits in a Number using For Loop
This Java program allows the user to enter any positive integer. Then, the Java program will divide the given number into individual digits and then count those individual digits using For Loop.
package SimplerPrograms;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class NumberofDigitsUsingFor {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int Number, Count=0;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("\n Please Enter any Number: ");
Number = sc.nextInt();
for (Count = 0; Number > 0; Number = Number/10) {
Count = Count + 1;
}
System.out.format("\n Total = %d", Count);
}
}
We just replaced the While loop in the above example with the For loop. The output of the total digits in a number using for loop
Please Enter any Number:
123456789
Total = 9Java Program to Count Number of Digits in a Number Using Functions
In this program, we use the same steps that we followed in our second example, but we separated the logic and placed it in a separate method.
package SimplerPrograms;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class NumberofDigitsUsingFunctions {
private static Scanner sc;
private static int Count = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int Number;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("\n Please Enter any Number: ");
Number = sc.nextInt();
Count = NumberofDigits(Number);
System.out.format("\n Total = %d", Count);
}
public static int NumberofDigits(int Number) {
for (Count = 0; Number > 0; Number = Number/10) {
Count = Count + 1;
}
return Count;
}
}
Please Enter any Number:
904060
Total = 6If you observe the following statement, we call the NumberOfDigits (Number) method and assign the return value to the integer variable Count.
Count = NumberofDigits(Number);
When the compiler reaches the NumberOfDigits (Number) line in the main() program, the Javac immediately jumps to the below function:
public static int NumberofDigits(int Number) {
Java Program to Count Number of Digits in a Number Using Recursion
This program allows the user to enter any positive integer, then divides the given number into individual digits and counts them using the Recursion concept.
In this Java program example, we are dividing the code using OOPS. To do this, First, we will create a class that holds a method to count the number of digits in a number recursively.
package SimplerPrograms;
public class NumberofDigits {
int Count = 0;
public int DigitsCount(int Number) {
if(Number > 0) {
Count = Count + 1;
DigitsCount(Number / 10);
}
return Count;
}
}
Within the Main Program, we will create an instance of the above-specified class and call the methods.
package SimplerPrograms;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class NumberofDigitsUsingRecursion {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int Number, Count=0;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("\n Please Enter any Number: ");
Number = sc.nextInt();
NumberofDigits nd = new NumberofDigits();
Count = nd.DigitsCount(Number);
System.out.format("\n Total = %d", Count);
}
}
Please Enter any Number:
9876321
Total = 7NumberOfDigits Class Analysis:
In this Java Program to Count the Number of Digits in a Number, we declared an integer function DigitsCount, with one argument. We used the If statement within the function to check whether the given number is greater than Zero or Not. If it is true, statements inside the If block will execute. It means:
- The count will be incremented by 1 using Count = Count + 1
- DigitsCount (Number / 10) statement calls the function Recursively with the updated value. If you miss this line, the compiler terminates after completing the first line.
TIP: If you declare a method with a void keyword, we can’t return any value. If you want to return any value, replace the void with the data type and add the return keyword.
Main Class Analysis:
First, we created an instance or Object of the NumberOfDigits Class
NumberofDigits nd = new NumberofDigits();
Next, call the DigitsCount method.
Count = nd.DigitsCount(Number);
Lastly, System.out.println statement to print the output (987654321 = 9).
