How to write a C Program to Perform Arithmetic Operations on Arrays with a practical example?.
C Program to Perform Arithmetic Operations on Arrays Example
This C program allows the user to enter the number of rows and columns of 2 One Dimensional Arrays and then we are going to perform the Arithmetic Operations such as Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, and Division on One Dimensional Array
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int Size, i, a[10], b[10];
int Addition[10], Subtraction[10], Multiplication[10], Module[10];
float Division[10];
printf("\n Please Enter the Size of the Array\n");
scanf("%d", &Size);
printf("\nPlease Enter the First Array Elements\n");
for(i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
printf("\n Please Enter the Second Array Elements\n");
for(i = 0; i < Size; i ++)
{
scanf("%d", &b[i]);
}
for(i = 0; i < Size; i ++)
{
Addition [i]= a[i] + b[i];
Subtraction [i]= a[i] - b[i];
Multiplication [i]= a[i] * b[i];
Division [i] = a[i] / b[i];
Module [i] = a[i] % b[i];
}
printf("\n Add\t Sub\t Multi\t Div\t Mod");
for(i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
printf("\n%d \t ", Addition[i]);
printf("%d \t ", Subtraction[i]);
printf("%d \t ", Multiplication[i]);
printf("%.2f \t ", Division[i]);
printf("%d \t ", Module[i]);
}
return 0;
}
In this C Program to Perform Arithmetic Operations on arrays, We declared 2 arrays or One Dimensional Arrays a, b with the size of 10. We also declared 4 more arrays Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, and Module of integer type. And one array Division with the float data type Because the division of 2 integer numbers may give float results in most of the time.
Below printf statement asks the User to enter the arrays a, b size (Number of elements. For instance 4 elements = a[3])
printf("\n Please Enter the Size of the Array \n");
The Below C Programming scanf statement will assign the user entered values to Size variable.
scanf("%d", &Size);
Below For Loop in C Programming will help to iterate every cell present in a[3] array. Condition inside the for loops (i < Size)) will ensure the compiler, not to exceed the array size. Otherwise, the array will overflow
scanf statement inside the for loop will store the user entered values in every individual array element such as a[0], a[1], a[2]
for(i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
Below for loop will help to iterate each cell present in the b[2][3] matrix.
for(i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
In the next line of this C program, We have one more for loop to perform the Arithmetic Operations.
for(i = 0; i < Size; i ++)
{
Addition [i] = a[i] + b[i];
Subtraction [i] = a[i] - b[i];
Multiplication [i] = a[i] * b[i];
Division [i] = a[i] / b[i];
Module [i] = a[i] % b[i];
}
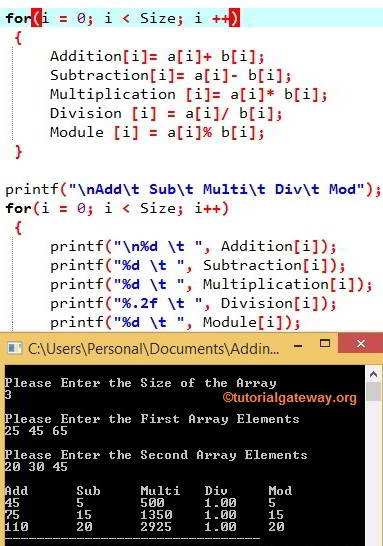
Above For loop is used to calculate the Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division, and Module of 2 arrays. From the above screenshot
User inserted values in this C Program to Perform Arithmetic Operations on arrays example are
a[3] = {25, 45, 65}} and
b[3] = {20, 30, 45}}
First Iteration
The value of i will be 0, and the condition (i < 3) is True. So, it will start executing the statements inside the loop until the condition fails.
Addition [i] = a[i] + b[i];
Addition [0] = a[0] + b[0];
Addition [0] = 25 + 20 = 45
Subtraction [0]= a[0] – b[0];
Subtraction [0] = 25 – 20 = 5
Multiplication [0] = a[0] * b[0];
Multiplication [0] = 25 * 20 = 500
Division [0] = a[0] / b[0];
Division [0] = 25 / 20 = 1
Module [0] = a[0] % b[0];
Module [0] = 25 % 20 = 5
Second Iteration
The value of i will be 1, and the condition (i < 3) is True.
Addition [1] = a[1] + b[1];
Addition [1] = 45 + 30 = 75
Subtraction [1] = 45 – 30 = 15
Multiplication [1] = 45 * 30 = 1350
Division [1] = 45 / 30 = 1
Module [1] = 45 % 30 = 15
Third Iteration
i = 2 and the condition (i < 3) is True.
Addition [2] = a[2] + b[2];
Addition [2] = 65 + 45 = 110
Subtraction [2] = 65 – 45 = 20
Multiplication [2] = 65 * 45 = 2925
Division [2] = 65 / 45 = 1
Module [2] = 65 % 45 = 20
After the increment, the value of columns will be 3, and the condition (i < 3) will fail. So it will exit from the loop.
Next for loop of this C Program to Perform Arithmetic Operations on arrays,
for(i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
printf("\n%d \t ", Addition[i]);
printf("%d \t ", Subtraction[i]);
printf("%d \t ", Multiplication[i]);
printf("%.2f \t ", Division[i]);
printf("%d \t ", Module[i]);
}
Will traverse as we explained above, but instead of addition and subtraction, it will display the values one by one using the printf statements inside them.
The final output of the Addition Array is:
Addition [3] = {45, 75, 110};
The final output of the Subtraction Array is:
Subtraction [3] = {5, 15, 20};
Final output of the Multiplication Array is:
Multiplication [3] = {500, 1350, 2925};
The final output of the Division array is:
Division [3] = {1.00, 1.00, 1.00};
The final output of the Module Array is:
Module [2][3] = { {5, 15, 20};
