How to write a C Program to Merge Two Arrays with an example?. Before going into this C Program to Merge Two Arrays example.
C Program to Merge Two Arrays Example 1
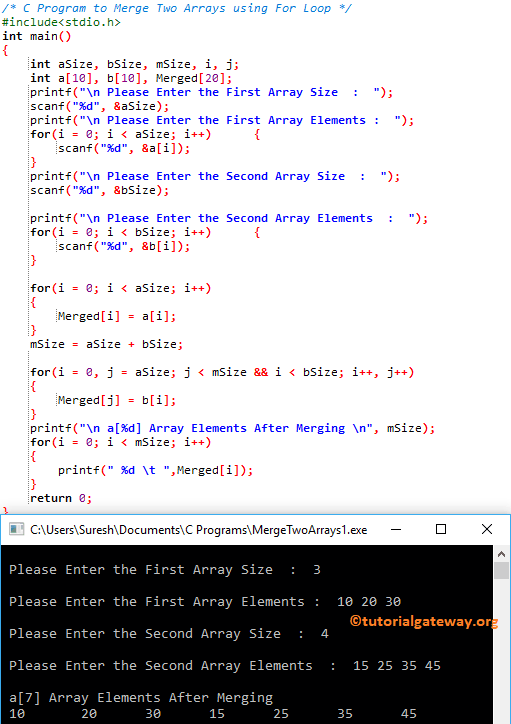
This program to merge two arrays in c allows the user to enter the Array size and elements of two different arrays. Next, it will merge two arrays one after the other using For Loop.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int aSize, bSize, mSize, i, j;
int a[10], b[10], Merged[20];
printf("\n Please Enter the First Array Size : ");
scanf("%d", &aSize);
printf("\nPlease Enter the First Array Elements : ");
for(i = 0; i < aSize; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
printf("\n Please Enter the Second Array Size : ");
scanf("%d", &bSize);
printf("\nPlease Enter the Second Array Elements : ");
for(i = 0; i < bSize; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &b[i]);
}
for(i = 0; i < aSize; i++)
{
Merged[i] = a[i];
}
mSize = aSize + bSize;
for(i = 0, j = aSize; j < mSize && i < bSize; i++, j++)
{
Merged[j] = b[i];
}
printf("\n a[%d] Array Elements After Merging \n", mSize);
for(i = 0; i < mSize; i++)
{
printf(" %d \t ",Merged[i]);
}
return 0;
}
In this example, the below For loop will help to iterate every cell present in a[3] array. Condition inside the for loops (i < Size) will ensure the compiler not to exceed the array limit. Please refer to Array in C article to understand the concept of Array size, index position, etc.
Inside the C Programming for loop, we are assigning each and every arr array element to the Merged array. It means, Merged[0] = arr[0], Merged[1] = arr[1], Merged[2] = arr[2], Merged[3] = arr[3], Merged[4] = arr[4]
for(i = 0; i < aSize; i++)
{
Merged[i] = a[i];
}
Now merged[3] = {10, 20, 30}
In the next line, We have one more for loop to insert the second array elements into the Merged array
for(i = 0, j = aSize; j < mSize && i < bSize; i++, j++)
{
Merged[j] = b[i];
}
From the above Program to Merge Two Arrays in C screenshot, you can observe that the Second array elements are b[4] = {15, 25, 35, 45}
First Iteration: for(i = 0, j = aSize; j < mSize && i < bSize; i++, j++)
for (i = 0, j = 3; 3 < 7 && 0 < 4; 0++, 3++)
The condition (3 < 7 && 0 < 4) is True.
Merged[j] = b[i]
Merged[3] = b[0]
Merged[3] = 15
Second Iteration: for (i = 1, j = 4; 4 < 7 && 1 < 4; 1++, 4++)
The condition (4 < 7 && 1 < 4) is True.
Merged[j] = b[i]
Merged[4] = b[1]
Merged[4] = 25
Third Iteration: for (i = 2, j = 5; 5 < 7 && 2 < 4; 2++, 5++)
The condition (5 < 7 && 2 < 4) is True.
Merged[j] = b[i]
Merged[5] = b[2]
Merged[5] = 35
Fourth Iteration: for (i = 3, j = 6; 6 < 7 && 3 < 4; 3++, 6++)
The condition (6 < 7 && 3 < 4) is True.
Merged[j] = b[i]
Merged[6] = b[3]
Merged[6] = 45
Fifth Iteration: for (i = 4, j = 7; 7 < 7 && 4 < 4; 4++, 7++)
The condition (7 < 7 && 4 < 4) is False. So, it will exit from the For Loop
Next, we used one more for loop to print the output. I suggest you refer to the Print Array Elements article to understand this for loop.
C Program to Merge Two Arrays Example 2
This merge two arrays program will merge two arrays. While Merging, it will check which number is the least value and then insert the least number first
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int aSize, bSize, mSize, i, j, k;
int a[10], b[10], Merged[20];
printf("\n Please Enter the First Array Size : ");
scanf("%d", &aSize);
printf("\nPlease Enter the First Array Elements : ");
for(i = 0; i < aSize; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
printf("\n Please Enter the Second Array Size : ");
scanf("%d", &bSize);
printf("\nPlease Enter the Second Array Elements : ");
for(i = 0; i < bSize; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &b[i]);
}
mSize = aSize + bSize;
i = 0;
j = 0;
for(k = 0; k < mSize; k++)
{
if(i >= aSize || j >= bSize)
{
break;
}
if(a[i] < b[j])
{
Merged[k] = a[i];
i++;
}
else
{
Merged[k] = b[j];
j++;
}
}
while(i < aSize)
{
Merged[k] = a[i];
k++;
i++;
}
while(j < bSize)
{
Merged[k] = b[j];
k++;
j++;
}
printf("\n a[%d] Array Elements After Merging \n", mSize);
for(i = 0; i < mSize; i++)
{
printf(" %d \t ",Merged[i]);
}
return 0;
}
Merge Two Arrays output
Please Enter the First Array Size : 5
Please Enter the First Array Elements : 10 20 30 40 50
Please Enter the Second Array Size : 6
Please Enter the Second Array Elements : 5 7 15 35 95 17
a[11] Array Elements After Merging
5 7 10 15 20 30 35 40 50 95 17 Program to Merge Two Arrays Example 3
This program to merge two arrays is the same as above, but we used the Functions concept to arrange the code.
#include<stdio.h>
void Merge_Array(int a[], int aSize, int b[], int bSize, int Merged[]);
int main()
{
int aSize, bSize, mSize, i, j, k;
int a[10], b[10], Merged[20];
printf("\n Please Enter the First Array Size : ");
scanf("%d", &aSize);
printf("\nPlease Enter the First Array Elements : ");
for(i = 0; i < aSize; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
printf("\n Please Enter the Second Array Size : ");
scanf("%d", &bSize);
printf("\nPlease Enter the Second Array Elements : ");
for(i = 0; i < bSize; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &b[i]);
}
Merge_Array(a, aSize, b, bSize, Merged);
mSize = aSize + bSize;
printf("\n a[%d] Array Elements After Merging \n", mSize);
for(i = 0; i < mSize; i++)
{
printf(" %d \t ",Merged[i]);
}
return 0;
}
void Merge_Array(int a[], int aSize, int b[], int bSize, int Merged[])
{
int i, j, k, mSize;
j = k = 0;
mSize = aSize + bSize;
for(i = 0; i < mSize;)
{
if(j < aSize && k < bSize)
{
if(a[j] < b[k])
{
Merged[i] = a[j];
j++;
}
else
{
Merged[i] = b[k];
k++;
}
i++;
}
else if(j == aSize)
{
while(i < mSize)
{
Merged[i] = b[k];
k++;
i++;
}
}
else
{
while(i < mSize)
{
Merged[i] = a[j];
j++;
i++;
}
}
}
}
Please Enter the First Array Size : 5
Please Enter the First Array Elements : 10 20 30 40 50
Please Enter the Second Array Size : 8
Please Enter the Second Array Elements : 25 9 35 45 85 89 75 125
a[13] Array Elements After Merging
10 20 25 9 30 35 40 45 50 85 89 75 125 