How to write a C Program to find Sum of Upper Triangle Matrix with example?. We already explained about Upper triangle in our previous article.
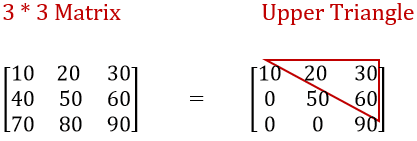
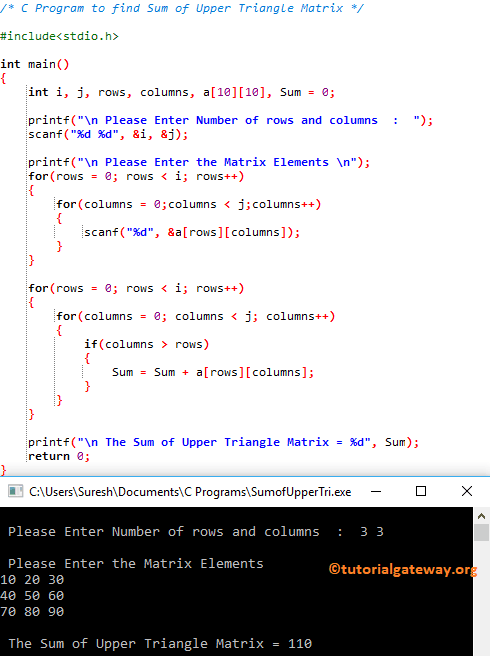
C Program to find Sum of Upper Triangle Matrix Example
This program allows the user to enter the number of rows and columns of a Matrix. Next, we are going to find the sum of the. Upper triangle of this matrix using For Loop.
/* C Program to find Sum of Upper Triangle Matrix */
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i, j, rows, columns, a[10][10], Sum = 0;
printf("\n Please Enter Number of rows and columns : ");
scanf("%d %d", &i, &j);
printf("\n Please Enter the Matrix Elements \n");
for(rows = 0; rows < i; rows++)
{
for(columns = 0;columns < j;columns++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[rows][columns]);
}
}
for(rows = 0; rows < i; rows++)
{
for(columns = 0; columns < j; columns++)
{
if(columns > rows)
{
Sum = Sum + a[rows][columns];
}
}
}
printf("\n The Sum of Upper Triangle Matrix = %d", Sum);
return 0;
}
In this C Program to find Sum of Upper Triangle Matrix, We declared single Two dimensional arrays Multiplication of size of 10 * 10. I suggest you refer to the C Program to find the Upper Triangle Matrix article.
Below C Programming statements asks the User to enter the Matrix size (Number of rows and columns. For instance 2 Rows, 2 Columns = a[2][2] )
printf("\n Please Enter Number of rows and columns : ");
scanf("%d %d", &i, &j);
Next, we used for loop to iterate each cell present in a[2][2] matrix. Conditions inside the for loops ((rows < i) and (columns < j)) will ensure the compiler, not to exceed the matrix limit. Otherwise, the matrix will overflow
scanf statement inside the for loop will store the user entered values in every individual array element such as a[0][0], a[0][1], …..
for(rows = 0; rows < i; rows++).
{
for(columns = 0; columns < j; columns++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[rows][columns]);
}
}
In the next line of this program, We have one more for loop to find the sum of Upper Triangle of a Matrix
for(rows = 0; rows < i; rows++)
{
for(columns = 0; columns < j; columns++)
{
if(columns > rows)
{
Sum = Sum + a[rows][columns];
}
}
}
User inserted values for this C Program to find Sum of Upper Triangle Matrix are: a[3][3] = {{10, 20, 30}, { 40, 50, 60},{70, 80, 90}}
Row First Iteration: for(rows = 0; rows < 3; 0++)
The condition (0 < 3) is True.
Column First Iteration: for(columns = 0; 0 < 3; 0++)
The condition (columns < 3) is True. So, it will start executing the statements inside the loop
if(columns > rows) => if(0 > 0) – This condition is False. So, it will exit from If statement
Column Second Iteration: for(columns = 1; 1 < 3; 1++)
The condition (columns < 3) is True.
if(columns > rows) => if(1 > 0) – This condition is True.
Sum = Sum + a[rows][columns] => 0 + 20
Sum = 20
Column Third Iteration: for(columns = 2; 2 < 3; 2++)
if(columns > rows) => if(2 > 0) – This condition is True.
Sum = Sum + a[rows][columns] => 20 + 30
Sum = 50
Column Fourth Iteration: for(columns = 3; 3 < 3; 3++)
The condition (columns < 3) is False. So it will exit from the loop.
Next, rows value incremented to 1.
Row Second Iteration: for(rows = 1; rows < 3; 1++)
The condition (1 < 3) is True.
Column First Iteration: for(columns = 0; 0 < 3; 0++)
The condition (columns < 3) is True. So, it will start executing the statements inside the loop
if(columns > rows) => if(0 > 1) – This condition is False.
Column Second Iteration: for(columns = 1; 1 < 3; 1++)
The condition (columns < 3) is True.
if(columns > rows) => if(1 > 1) – This condition is False.
Column Third Iteration: for(columns = 2; 2 < 3; 2++)
if(columns > rows) => if(2 > 1) – This condition is True.
Sum = Sum + a[rows][columns] => 50 + 60
Sum = 110
Column Fourth Iteration: for(columns = 3; 3 < 3; 3++)
The condition (columns < 3) is False. So it will exit from the loop.
Next, rows value will increment to 2.
Row Third Iteration: for(rows = 2; rows < 3; 2++)
The condition (2 < 3) is True.
Column First Iteration: for(columns = 0; 0 < 3; 0++)
The condition (columns < 3) is True. So, it will start executing the statements inside the loop
if(columns > rows) => if(0 > 2) – This condition is False.
Column Second Iteration: for(columns = 1; 1 < 3; 1++)
The condition (columns < 3) is True.
if(columns > rows) => if(1 > 2) – This condition is false
Column Third Iteration: for(columns = 2; 2 < 3; 2++)
if(columns > rows) => if(2 > 2) – This condition is False.
Column Fourth Iteration: for(columns = 3; 3 < 3; 3++)
The condition (columns < 3) is False. So it will exit from the loop.
Next, rows value will increment to 3. After the increment, the condition inside the first for loop (rows < 3) will fail. So it will exit from the loop.
