How to write a C Program to find LCM of Two Numbers with an example? According to Mathematics, the Least Common Multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is perfectly divisible by the given integer values without the remainder.
For example, the LCM value of integers 2 and 3 is 12 because 12 is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by both 2 and 3 (the remainder is 0).
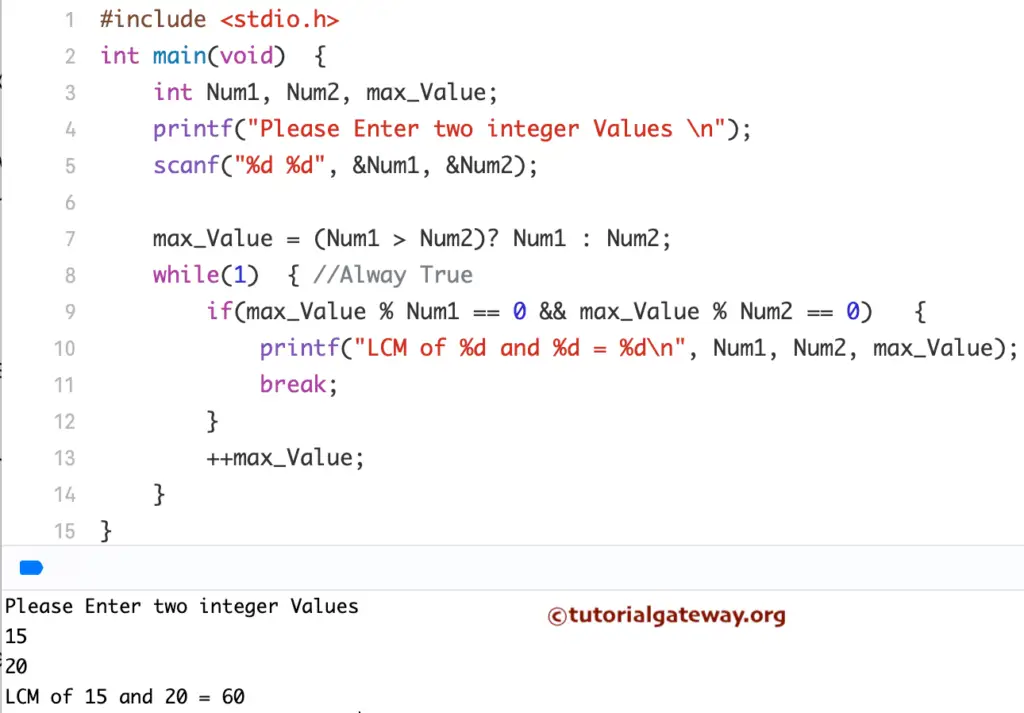
C Program to find LCM of Two Numbers using While Loop
This C program allows the user to enter two positive integer values, and we are going to find or calculate the LCM of those two numbers using the While Loop.
TIP: Some people will call the Lowest Common Multiple as LCM.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int Num1, Num2, max_Value;
printf("Please Enter two integer Values \n");
scanf("%d %d", &Num1, &Num2);
max_Value = (Num1 > Num2)? Num1 : Num2;
while(1) //Alway True
{
if(max_Value % Num1 == 0 && max_Value % Num2 == 0)
{
printf("LCM of %d and %d = %d", Num1, Num2, max_Value);
break;
}
++max_Value;
}
return 0;
}
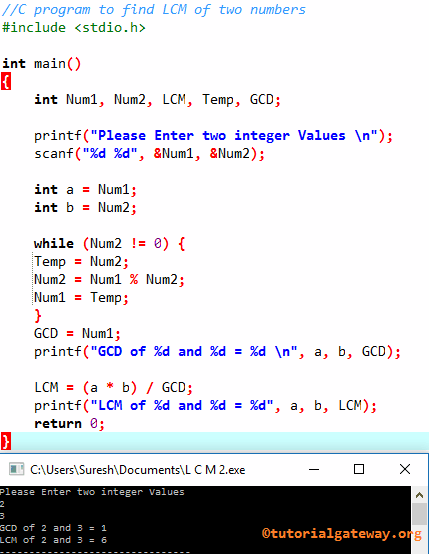
C Program to find the LCM of Two Numbers using GCD
In this LCM program, we are going to calculate the Least Common Multiple of those two values using the While Loop.
TIP: The basic formula behind the Least Common Multiple in C is LCM(a, b) = (a * b) / GCD. We already explained the GCD in our previous article. Please refer to the Find GCD of Two Numbers article in this Programming for more information.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int Num1, Num2, LCM, Temp, GCD;
printf("Please Enter two integer Values \n");
scanf("%d %d", &Num1, &Num2);
int a = Num1;
int b = Num2;
while (Num2 != 0) {
Temp = Num2;
Num2 = Num1 % Num2;
Num1 = Temp;
}
GCD = Num1;
printf("GCD of %d and %d = %d \n", a, b, GCD);
LCM = (a * b) / GCD;
printf("LCM of %d and %d = %d", a, b, LCM);
return 0;
}
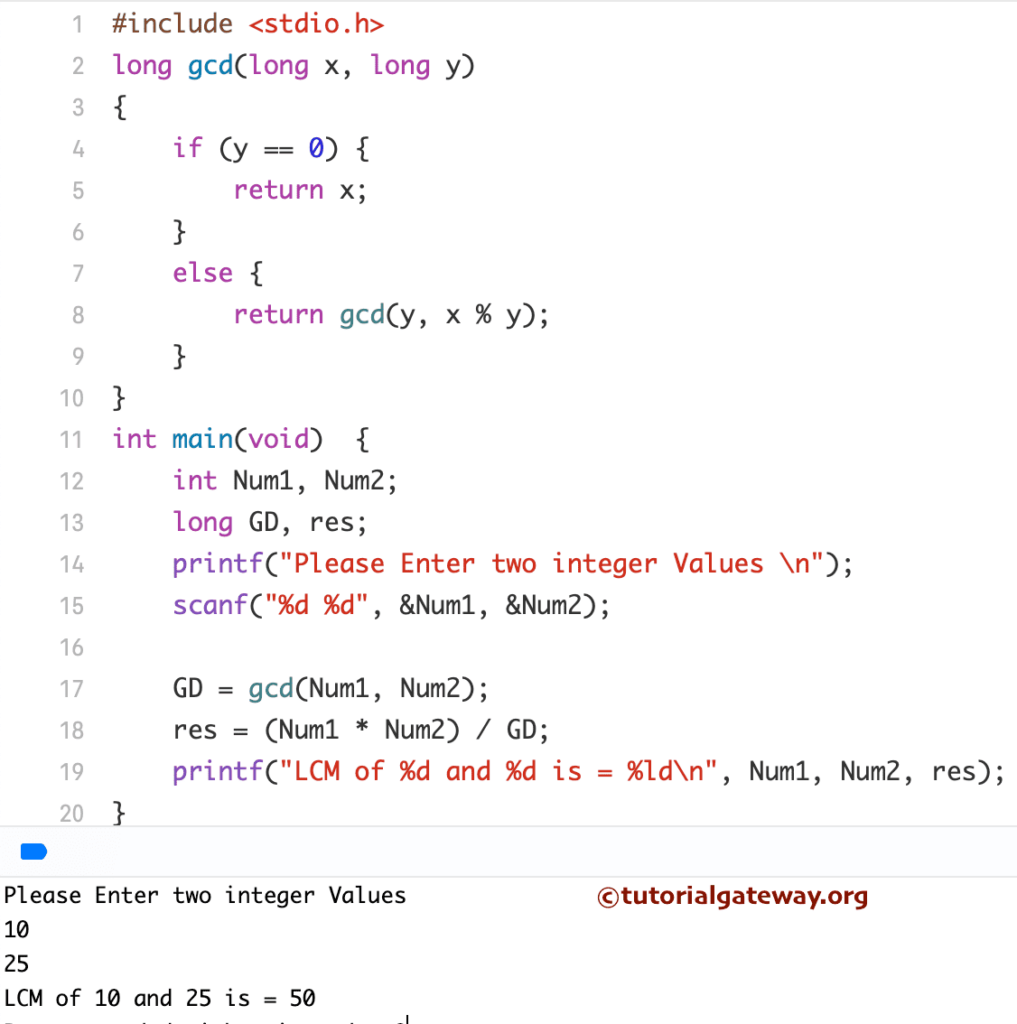
C Program to find the LCM of Two Numbers using Recursion
This program allows you to enter two positive integer values. Next, we will calculate the Lowest Common Multiple of those two values by calling the function recursively. Please refer to Recursion in C for further reference.
#include <stdio.h>
long gcd(long x, long y);
int main()
{
int Num1, Num2, GD, res;
printf("Please Enter two integer Values \n");
scanf("%d %d", &Num1, &Num2);
GD = gcd(Num1, Num2);
res = (Num1 * Num2) / GD;
printf("LCM of %d and %d is = %d", Num1, Num2, res);
return 0;
}
long gcd(long x, long y)
{
if (y == 0) {
return x;
}
else {
return gcd(y, x % y);
}
}
The following statement will find the Least Common Multiple using the traditional formula.
res = (Num1 * Num2) / GCD;
When the compiler reaches the long gcd(long x, long y) line in the main() program example, the compiler will immediately jump to the below function:
long gcd(long x, long y)
In the above-specified function, the return gcd(y, x % y) statement will help the program call the function Recursively with the updated value. If you miss this statement in the LCM of Two Numbers example, then after completing the first line, it will terminate.
Let’s see the If condition if (y == 0) will check whether the number is equal to 0 or not. For Recursive functions, placing a condition before using the function recursively is very important. Otherwise, we will end up in infinite execution (Same as Infinite Loop). Please be careful :)
