The Relational operators in Java programming are mostly used either in If Conditions or Loops. The Java Relational operators are commonly used to check the relationship between two variables. If the relation is true, then it will return Boolean True. And if the relation is false, then it will return Boolean False.
The table below shows all the Relational Operators in Java Programming with examples.
| Operators | Usage | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| > | a > b | a is greater than b | 5 > 2 returns True |
| < | a < b | a is less than b | 5 < 2 returns False |
| >= | a >= b | a is greater than or equal to b | 5 >= 2 returns True |
| <= | a <= b | a is less than or equal to b | 5 <= 2 return False |
| == | a == b | a is equal to b | 5 == 2 returns False |
| != | a != b | a is not equal to b | 5 != 2 returns True |
Relational Operators in Java Example
This example helps to understand the Relational Operators practically.
This Java program allows users to enter two integer variables, a and b. Next, we use these two variables and the operators mentioned above to perform various relational operations in Java Programming Language.
package JavaOperators;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class RelationalOperators {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a, b;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(" Please Enter two integer Value: ");
a = sc.nextInt();
b = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(" Result of a > b is = " + (a > b));
System.out.println(" Result of a >= b is = " + (a >= b));
System.out.println(" Result of a < b is = " + (a < b));
System.out.println(" Result of a <= b is = " + (a <= b));
System.out.println(" Result of a == b is = " + (a == b));
System.out.println(" Result of a != b is = " + (a != b));
}
}
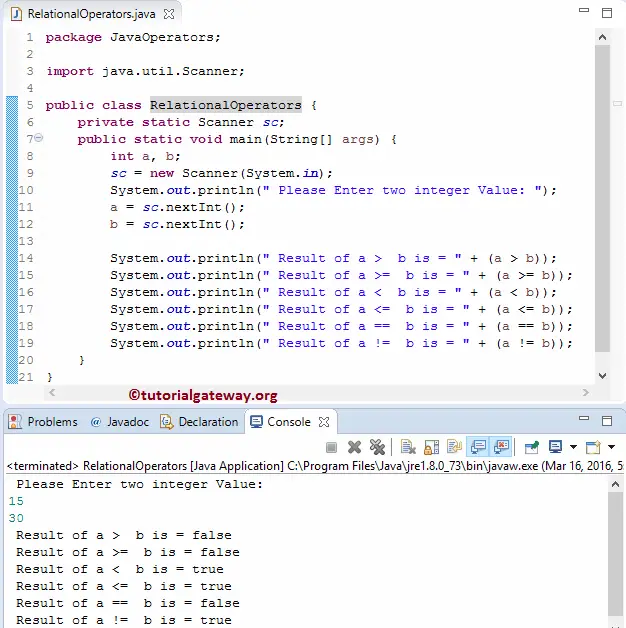
Within this Java relational operators example, the following statement will ask the user to enter integer values a, b. Next, we are going to assign the user input values to variables.
System.out.println(" Please Enter two integer Value: ");
a = sc.nextInt();
b = sc.nextInt();
In the next line, We checked those values against every relational operator we have
inside If Condition
This example will help to understand how relational operators in Java programming language are used in If Condition. For this example, we use two variables, a and b, inside the If Statement and a relational operator to perform a condition check.
package JavaOperators;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class RelationalOperatorsinIf {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a, b;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please Enter two integer Value: ");
a = sc.nextInt();
b = sc.nextInt();
if (a == b) {
System.out.println("a is equal to b");
}
else {
System.out.println("a is NOT equal to b");
}
}
}
From the Java program output, you can observe that we entered a = 22 and b = 65. It means a is not equal to b. So, the second Java statement was printed.
Please Enter two integer Value:
22
65
a is NOT equal to bLet us see what will happen when we change our values. From the screenshot below, we entered a= 12 and b= 12. It means a is equal to b. So, the First statement was printed.
Please Enter two integer Value:
12
12
a is equal to bIn this Java relational operators in if statement example, the first three statements will ask the user to enter integer values, a, and b, and they will assign the user input values to respected variables.
The Relational Operators If Condition
If x equals y, the statement inside the If condition block is executed.
System.out.println("a is equal to b");
If x is not equal to y, the statement inside the If condition block will execute.
System.out.println("a is NOT equal to b");
