MySQL ROUND function Mathematical Function is helpful to round the specified expression to user-specified precision or length.
The basic syntax of the MySQL ROUND Function is as shown below:
SELECT ROUND(Numeric_Expression) FROM Source -- Or SELECT ROUND(Numeric_Expression, length) FROM Source
- Numeric_Expression: It can be a number or a valid numerical expression.
- Length: This is the precision to which the expression has to consider. The Length can be a number or a valid numerical expression.
- If length is a positive number, it displays the Numeric_Expression to the decimal point number specified as length.
- If length is a negative number, Expression prints the nearest number to the left side of the decimal point.
To demonstrate this MySQL ROUND Numeric function, we are going to use the below-shown data.
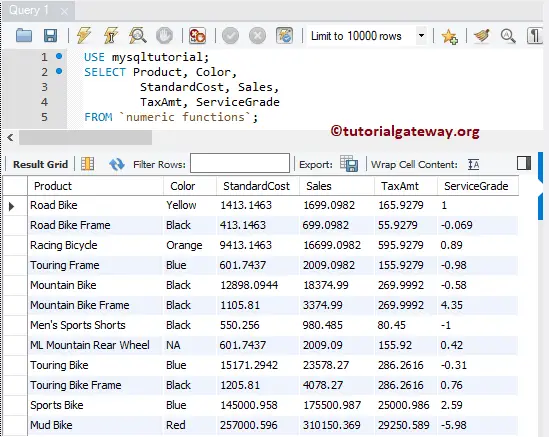
MySQL ROUND Function Example
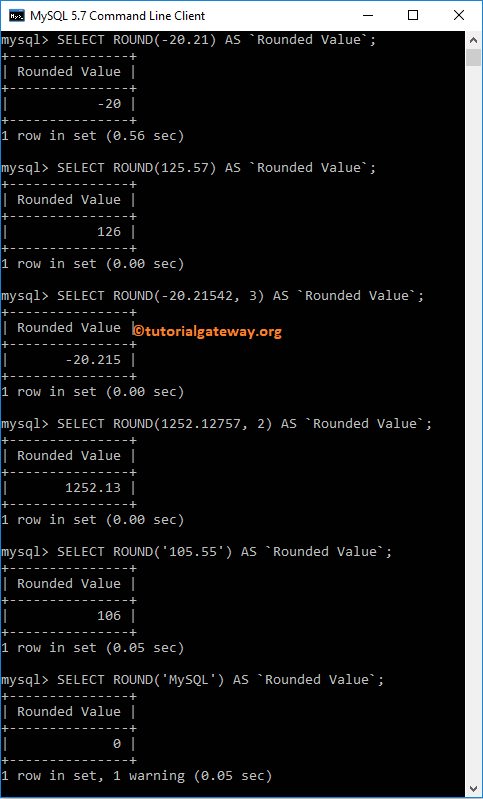
This Function returns the rounded value of the specified number. The following query shows multiple ways to use this method with positive and no lengths.
-- without length on Negative
SELECT ROUND(-20.21) AS `RoundedValue`;
-- without length on Positive Value
SELECT ROUND(125.57) AS `RoundedValue`;
-- along with length on Negative
SELECT ROUND(-20.21542, 3) AS `RoundedValue`;
-- along with length on Positive Value
SELECT ROUND(1252.12757, 2) AS `RoundedValue`;
-- on string data
SELECT ROUND('105.55') AS `RoundedValue`;
-- on String text
SELECT ROUND('MySQL') AS `RoundedValue`;
The screenshot below shows that we used it on different values.
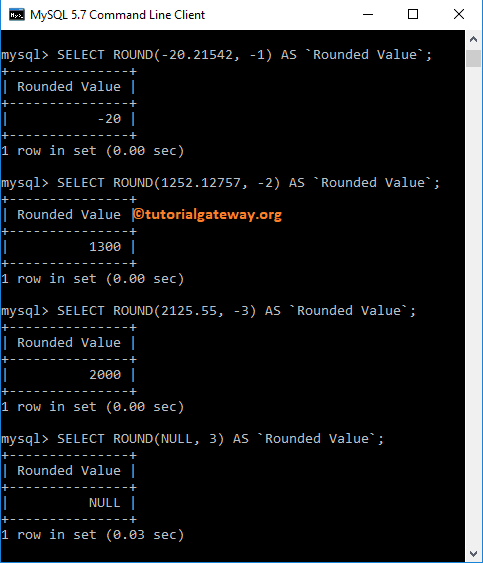
Let me try Negative Values as the MySQL length, i.e., the second argument. And also, it is used the null value is the first argument in the last statement.
-- with Negative length and Negative numbers SELECT ROUND(-20.21542, -1) AS `RoundedValue`; -- with Negative length and Positive numbers SELECT ROUND(1252.12757, -2) AS `RoundedValue`; -- with Negative length Example 3 SELECT ROUND(2125.55, -3) AS `RoundedValue`; -- with NULLS SELECT ROUND(NULL, 3) AS `RoundedValue`;
ROUND Example 2
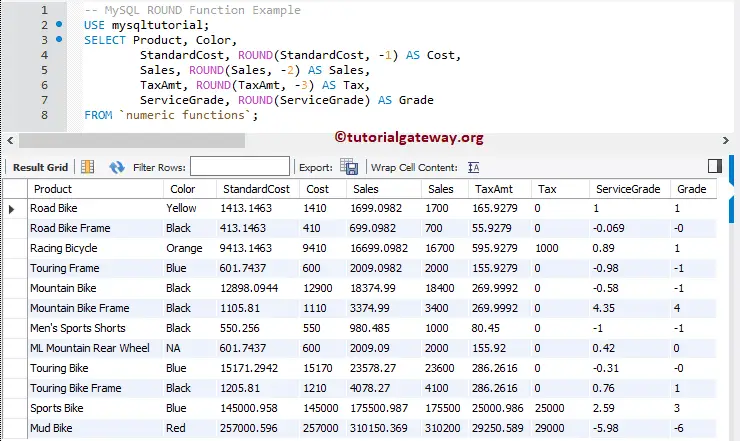
This MySQL Numeric function also allows you to find the round values for the column data. In this example, we will find the nearest values for all the records present in the Standard Cost, Sales, tax Amount, and Service Grade columns.
SELECT Product, Color,
StandardCost, ROUND(StandardCost, 3) AS Cost,
Sales, ROUND(Sales, 1) AS Sales,
TaxAmt, ROUND(TaxAmt, 2) AS Tax,
ServiceGrade, ROUND(ServiceGrade) AS Grade
FROM `numeric functions`;
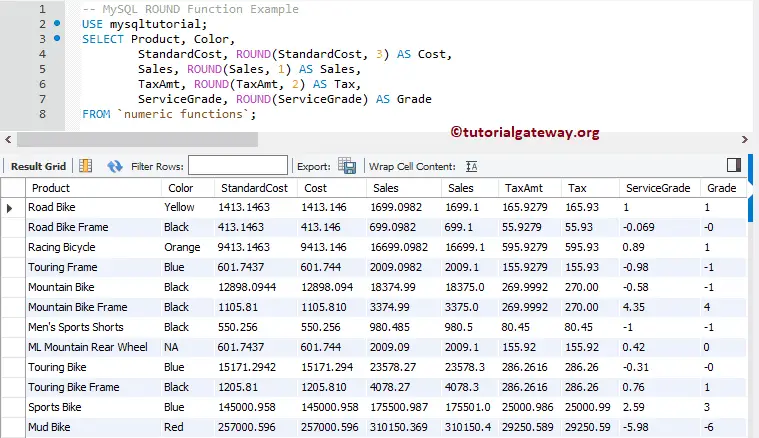
We reproduce the query we used in our previous example in this example. But, this time, we use the negative values as the second argument for the Mathematical Functions.
SELECT Product, Color,
StandardCost, ROUND(StandardCost, -1) AS Cost,
Sales, ROUND(Sales, -2) AS Sales,
TaxAmt, ROUND(TaxAmt, -3) AS Tax,
ServiceGrade, ROUND(ServiceGrade) AS Grade
FROM `numeric functions`;