Write a Java program to find the Roots of a Quadratic Equation with an example. The mathematical representation of a Quadratic Equation is ax²+bx+c = 0. A Quadratic Equation has two roots, and they depend entirely upon the discriminant. If discriminant > 0, then two Distinct Real Roots exist for this equation.
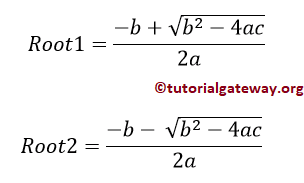
If discriminant < 0, then Two Distinct Complex Roots exist.
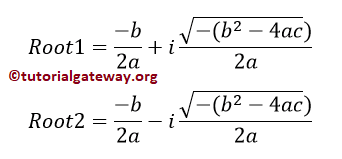
And If discriminant = 0, then Two Equal and Real Roots exist.
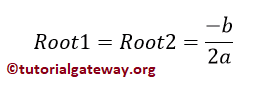
Java Program to find Roots of a Quadratic Equation using Else If
This Java program allows users to enter three values for a, b, and c. Next, this program returns the roots of a quadratic equation using the Else If Statement.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Example {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double a, b, c;
double r1, r2, i, d;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(" Please Enter the Values of a, b, c of Quadratic Equation : ");
a = sc.nextDouble();
b = sc.nextDouble();
c = sc.nextDouble();
d = (b * b) - (4 * a *c);
if(d > 0)
{
r1 = (-b + Math.sqrt(d) / (2 * a));
r2 = (-b - Math.sqrt(d) / (2 * a));
System.out.println("\n Two Distinct Real Roots Exists: r1 = " + r1 + " and r2 = " + r2);
}
else if(d == 0)
{
r1 = r2 = -b / (2 * a);
System.out.println("\n Two Equal and Real Roots Exists: r1 = " + r1 + " and r2 = " + r2);
}
else if(d < 0)
{
r1 = r2 = -b / (2 * a);
i = Math.sqrt(-d) / (2 * a);
System.out.println("\n Two Distinct Complex Roots Exists: r1 = " +
r1 + " + " + i + " and r2 = " + r2 +" - " +i);
}
}
}
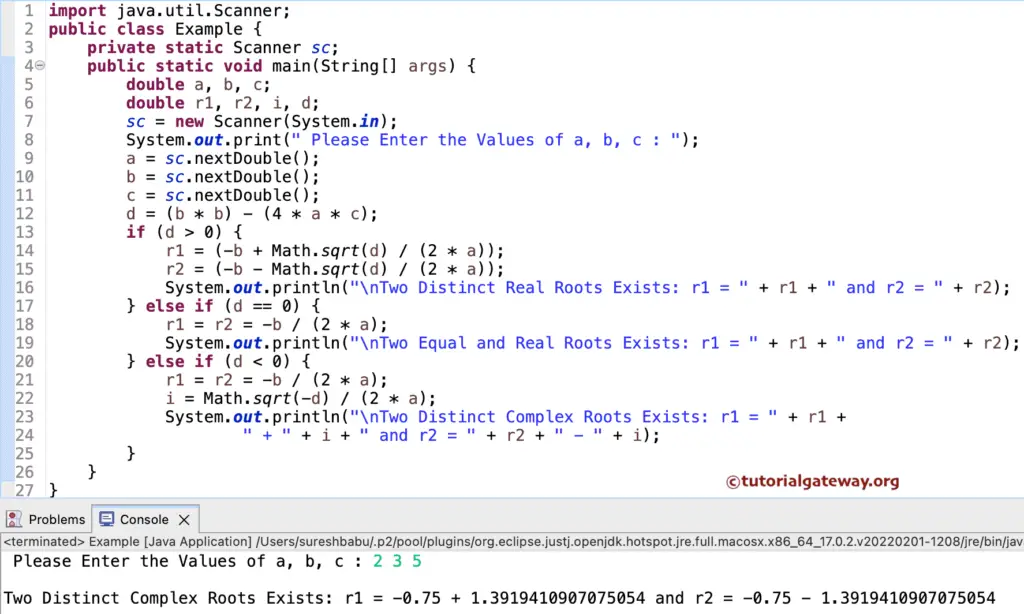
The user entered values in this Java Program to find the Roots of a Quadratic Equation values are 2, 3, and 5. It means a = 2, b = 3, c = 5 and the equation is 2x²+3x+5 = 0
d = (b * b) – (4 * a *c) => (3 * 3) – (4 * 2 * 5)
d = (9) – (40) = -31
It means d < 0 so
r1 = r2 = -b / (2 * a) => -3 / (2 * 2)
r1 = r2 = -0.75
i = sqrt(-d) / (2 * a)
= sqrt(- -31) / (2 * 2) => 5.567 / 4
i = 1.3919
r1= r1 + i = -0.75 + 1.3919
r2= r2 – i = -0.75 – 1.3919
Java Program to find Roots of a Quadratic Equation using Switch Case
This program to display the roots of a quadratic equation is the same as above, but this time, we are using the Switch case.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class QuadraticEquation2 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double a, b, c;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(" Please Enter the Values of a, b, c of Quadratic Equation : ");
a = sc.nextDouble();
b = sc.nextDouble();
c = sc.nextDouble();
QuadraticEquation(a, b, c);
}
public static void QuadraticEquation(double a, double b, double c)
{
double root1, root2, imaginary, discriminant;
discriminant = (b * b) - (4 * a *c);
if(discriminant > 0)
{
root1 = (-b + Math.sqrt(discriminant) / (2 * a));
root2 = (-b - Math.sqrt(discriminant) / (2 * a));
System.out.println("\n Two Distinct Real Roots Exists: root1 = " + root1 + " and root2 = " + root2);
}
else if(discriminant == 0)
{
root1 = root2 = -b / (2 * a);
System.out.println("\n Two Equal and Real Roots Exists: root1 = " + root1 + " and root2 = " + root2);
}
else if(discriminant < 0)
{
root1 = root2 = -b / (2 * a);
imaginary = Math.sqrt(-discriminant) / (2 * a);
System.out.println("\n Two Distinct Complex Roots Exists: root1 = " + root1 +
" + " + imaginary + " and root2 = " + root2 +" - " +imaginary);
}
}
}
Please Enter the Values of a, b, c of Quadratic Equation : 10 15 -25
Two Distinct Real Roots Exists: root1 = -13.25 and root2 = -16.75The User enters Values 10, 15, and -25 in this Java Program. It means a = 10, b = 15, c = -25 and the Quadratic equation is 10x²+15x-25 = 0
discriminant = (b * b) – (4 * a *c) => (15 * 15) – (4 * 10 *(-25))
= 225 + 1000 = 1225
It means discriminant > 0, so
root1 = (-b + sqrt(discriminant) / (2 * a))
= (-15 + sqrt(1225) / (2 * 10)) => (-15 + 35 / (20))
= -15 + 1.75 = -13.25
root2 = (-b – sqrt(discriminant) / (2 * a))
= (-15 – sqrt(1225) / (2 * 10)) => (-15 – 35 / (20))
= -15 – 1.75 = -16.75
