Write Java Leap Year Program using an If Statement, Nested If Statement, and Else If Statement with an example. Before we get into the Java Leap Year program example, Let us see its logic and definition.
The normal year contains 365 days, but the Java leap year contains 366 days. This extra day is added to February, so we get February 29. As per Mathematics, except century years, Years perfectly divisible by four are called Leap years. Century years mean they end with 00, such as 1200, 1300, 2400, 2500, etc. (Obviously, they are divisible by 100). We must calculate further for these century years to check the Java Leap year.
- If the century year is divisible by 400, then that year is a Leap year.
- If the century year is not divisible by 400, then it is not.
Java Program to Check Leap Year using If Statement
This program allows the user to enter any year. Then, this Java program will check whether the user entered is Leap year or not using the If Else statement.
package DatePrograms;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class LeapYearUsingIf {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int year;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("\n Please Enter any year you wish: ");
year = sc.nextInt();
if (( year%400 == 0)|| (( year%4 == 0 ) &&( year%100 != 0))) {
System.out.format("\n %d is a Leap Year. \n", year);
}
else {
System.out.format("\n %d is NOT a Leap Year. \n", year);
}
}
}
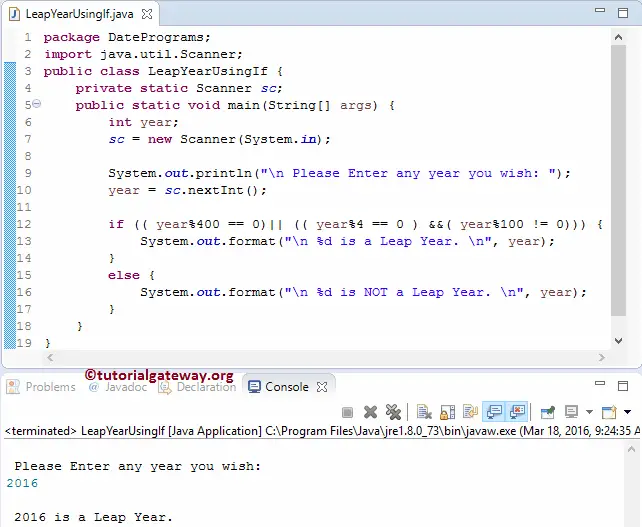
Let us check for a normal year.
Please Enter any year you wish:
2015
2015 is NOT.In this Java leap year program, Since we have to check multiple conditions within one If Statement, we used Logical AND and Logical OR operators. Let us divide the expression to understand it better
1: ( year % 400 == 0)||
2: ( year % 4 == 0 ) &&
3: ( year % 100 != 0))
The first condition (year%400 == 0) will check whether the (year%400) reminder is precisely equal to 0. As per the program algorithm, any number divisible by 400 is a Leap year.
Or the second Java If Else statement condition holds two statements, so they both have to be TRUE.
- The first condition (year%4 == 0) in this Java Leap Year Program will check whether the remainder of the (year % 4) is exactly equal to 0 or not. If the condition is False, it will exit because there is no point in checking the other condition. It is not the Leap Year. AND
- The second condition will check (year % 100) reminder is not equal to 0. If it is TRUE, the given number is not a century number.
- Any number that is divisible by four but not by 100, then that number is Leap Year.
TIP: Please refer to Logical Operators to understand the Logical And and Logical Or in Java.
Java Leap Year Program using Else If Statement
This program allows the user to enter any year. Then, the Java program will check whether the user entered is Leap year or not using the Else If statement.
package DatePrograms;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class LeapYearUsingElseIf {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int year;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("\n Please Enter any year you wish: ");
year = sc.nextInt();
if ( year % 400 == 0) {
System.out.format("\n %d is a Leap Year. \n", year);
}
else if (year%100 == 0) {
System.out.format("\n %d is NOT. \n", year);
}
else if(year%4 == 0) {
System.out.format("\n %d is a Leap Year. \n", year);
}
else {
System.out.format("\n %d is NOT. \n", year);
}
}
}
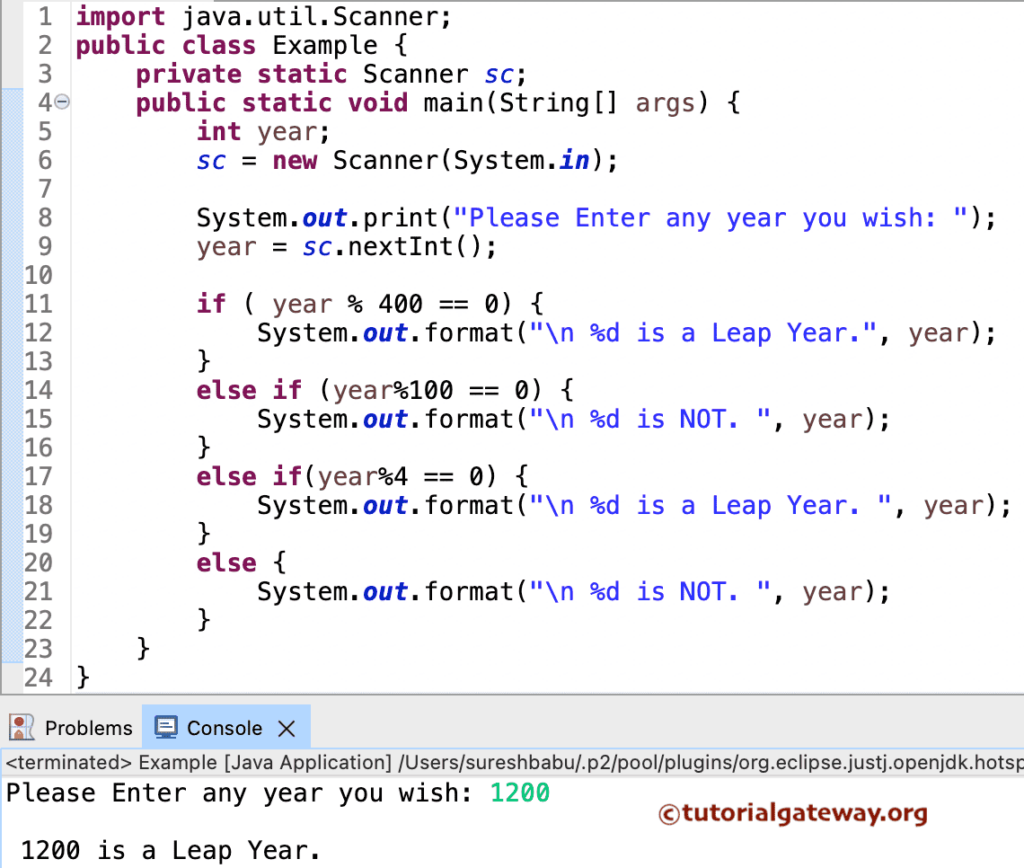
In this Java program, the first two statements ask the user to enter any year to check whether that year is a Leap year or Not. Next, we will assign the user-entered value to the year variable.
- The first If condition will check whether the (year % 400) reminder is exactly equal to 0. As per the algorithm, any number divisible by 400 is a Leap year. If this condition Fails, then it will go to the next one.
- The second If condition in the Java Leap Year Program will check whether the (year % 100) reminder is exactly equal to 0 or not. As per the algorithm, any number not divisible by 400 but by 100 is Not a Leap year (Century Year). We checked (year % 400) in the First If statement. Because it failed, so it came to the second condition. If the first and second conditions fail, it will go to the third one.
- The third condition will check whether year mod 4 is equal to 0. If this condition is True, then the given one is a Leap year because we already checked for the century years in the previous condition. If all the statements Fail, it will go to the Else statement at the end.
- If the above statements fail, it is not a Leap year.
Java Program to Check Leap Year using Nested If Statement
This program helps the user to enter any year. Then, the Java program will check whether the user entered is Leap year or not using the Nested If.
package DatePrograms;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class LeapYearUsingNestedIf {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int year;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("\n Please Enter any year you wish: ");
year = sc.nextInt();
if ( year % 4 == 0) {
if (year%100 == 0) {
if(year%400 == 0) {
System.out.format("\n %d is a Leap Year. \n", year);
}
else {
System.out.format("\n %d is NOT. \n", year);
}
}
else {
System.out.format("\n %d is a Leap Year. \n", year);
}
}
else {
System.out.format("\n %d is NOT. \n", year);
}
}
}
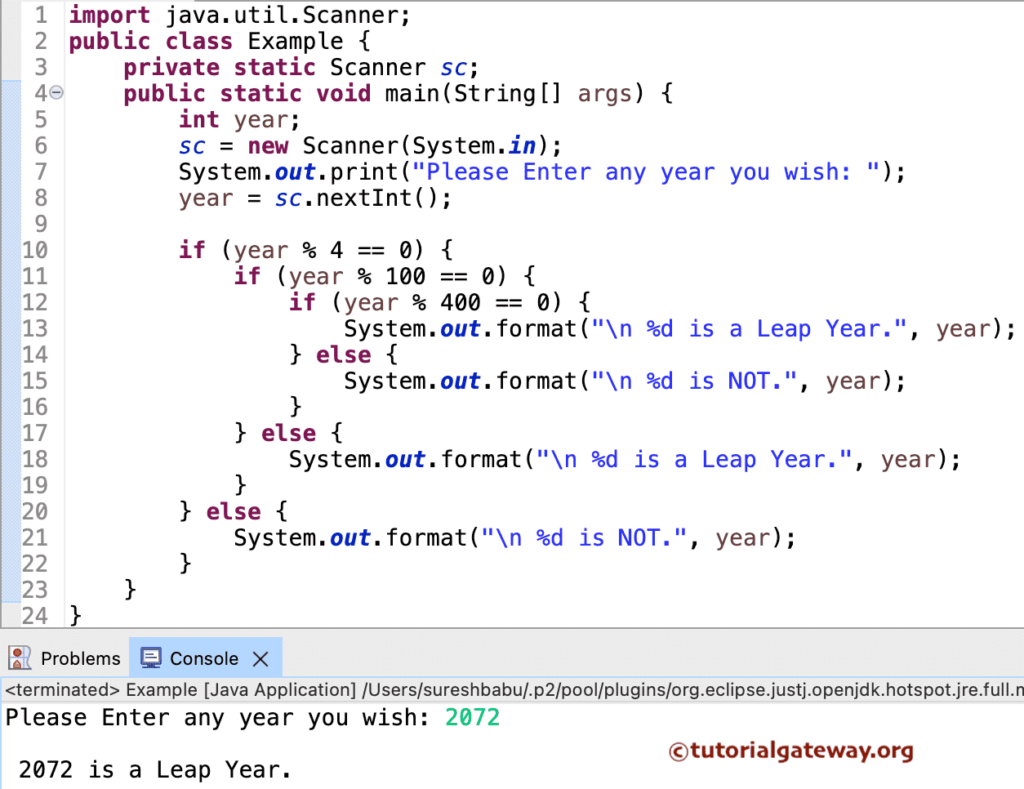
In this Java program, the User will enter any year to check whether that year is Leap Year or Not. The first If condition will check whether the remainder of the (year%4) is precisely equal to 0.
- If the expression is evaluated as False, then the given number is not.
- If the condition is True, we must check further for the century year. So, the Javac compiler will go to the Nested If condition.
The second If condition of the Java Leap Year Program will check whether the (year%100) reminder is exactly equal to 0 or Not.
- If this expression result is False, then the year is not a century year. So, the given number is a Leap year.
- If the condition is True, we must check whether the number is divisible by 400. So, the Javac compiler will go to another Nested If condition.
In this condition, the Javac will check whether the remainder of the (year%400) is exactly equal to 0.
- If the condition is False, then the given number is not.
- If the expression is evaluated to True, then the given number is Leap Year.
Java Leap Year Program using Oops
This program allows entering any positive integer (year). Then, the Java program checks whether the given year is a leap year or not. In this example, we are dividing the code using Object-Oriented Programming.
To do this, first, we will create a class that holds a method to reverse an integer recursively.
package DatePrograms;
public class LeapYear {
public int CheckLeapYear(int year) {
if (( year%400 == 0)|| (( year%4 == 0 ) && ( year%100 != 0))) {
return year;
}
else {
return 0;
}
}
}
Within the Main program of the Java leap year program, we will create an instance of the above-specified class and call the methods.
package DatePrograms;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class LeapYearUsingClass {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int year, leap;
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(" Please Enter any year you wish: ");
year = sc.nextInt();
LeapYear ly = new LeapYear();
leap = ly.CheckLeapYear(year);
if(leap != 0) {
System.out.format("\n %d is a Leap Year. \n", year);
}
else {
System.out.format("\n %d is NOT. \n", year);
}
}
}
Please Enter any year you wish:
2032
2032 is a Leap Year.LeapYear Class Analysis:
In this Java leap year program, first, we declared an integer function CheckLeapYear with one argument. Within the function, we used the If statement to check whether the given year is a leap year or not, and if it is true, it will return the year. Otherwise, it returns zero. We already explained the Logic in the above example.
Main Class Analysis:
First, we created an instance / created an Object of the LeapYear Class
LeapYear ly = new LeapYear();
Next, we are calling the CheckLeapYear method.
leap = ly.CheckLeapYear(year);
Lastly, the System.out.println statement will print the output.

Comments are closed.