The Java Arrays.copyOf Method is one of the Array Methods, which is to copy the array content into a new array of user-specified length. This article will show how to copy an Array to a new one with examples. The basic syntax of the Arrays.copyOf in Java Programming language is shown below.
Java Arrays.copyOf Method syntax
The Java Programming Language provides nine different Arrays copyof methods to copy the specified array to New. While coping:
- If the specified user length is greater than the Original Array, then the remaining elements will be filled with default values of the data type. For example, array a[5] of integer type holds five elements (1, 2, 3, 4, 5), but we specified the new length as 7 (Arrays.copyOf(b, 7), then b array will become b[7] holding elements 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 0 (Here, 0 is the default value for int type)
- The remaining elements will be truncated if the specified user length is less than the Original Array. For example, array a[7] of integer type holds five elements (10, 15, 22, 45, 65, 3, 54), but we specified the new length as 4 (Arrays.copyOf(b, 4), then b array will become b[4] holding elements 10, 15, 22, 45.
The following Java arrays copyof method will accept the Boolean Array and length as the parameters and copy that to a new one of user-specified length.
public static boolean copyOf(Boolean[] anBooleanArray, int newLength); // It will return Boolean Array //In order to use in program Arrays.copyOf(Boolean[] anBooleanArray, int newLength);
The following are the remaining Java arrays copyof methods.
public static byte copyOf(byte[] anByteArray, int newLength); // It will return Byte Array Arrays.copyOf(byte[] anByteArray, int newLength); public static short copyOf(short[] anShortArray, int newLength); // It will return short Array Arrays.copyOf(short[] anShortArray, int newLength); public static char copyOf(char[] anCharArray, int newLength); // It will return char Array Arrays.copyOf(char[] anCharArray, int newLength); public static short copyOf(int[] anIntArray, int newLength); // It will return Integer Array Arrays.copyOf(int[] anIntArray, int newLength); public static long copyOf(long[] anLongArray, int newLength); // It will return Long Array Arrays.copyOf(long[] anLongArray, int newLength); public static double copyOf(double[] anDoubleArray, int newLength); // It will return Double Array Arrays.copyOf(double[] anDoubleArray, int newLength); public static float copyOf(float[] anFloatArray, int newLength); // It will return float Array Arrays.copyOf(float[] anFloatArray, int newLength); public static <T> T[] copyOf(T[] Array, int newLength); Arrays.copyOf(T[] Array, int newLength); public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] Array, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType); Arrays.copyOf(T[] Array, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType);
- Array: This is the Original. We will use the Java copyOf method to copy this array to a new one.
- newlength: Please specify the length of the new array. Based on the length, elements truncated or extended (with default values)
- newType: Please specify the class type you want to apply for your new array.
Java Arrays.copyOf to copy Byte Array
In this program, we declared the byte array with random elements. Then we call the public static byte copyOf (byte[] anByteArray, int newLength) method to copy the Byte array to a new one of a specified length.
package ArrayMethods;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class CopyOfBytes {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte[] byteArray = {12, 24, 26};
//Copying Array
byte[] bitArray = Arrays.copyOf(byteArray, 5);
System.out.println("New Byte Array after Copying:");
arrayPrint(bitArray);
//Copying Array and assign Values
byte[] btArray = Arrays.copyOf(byteArray, 5);
btArray[3] = 5;
btArray[4] = 19;
System.out.println("New Byte Array with Vlaues:");
arrayPrint(btArray);
}
public static void arrayPrint(byte[] anByteArray) {
for (byte Number: anByteArray) {
System.out.println("Array Elelment = " + Number);
}
}
}
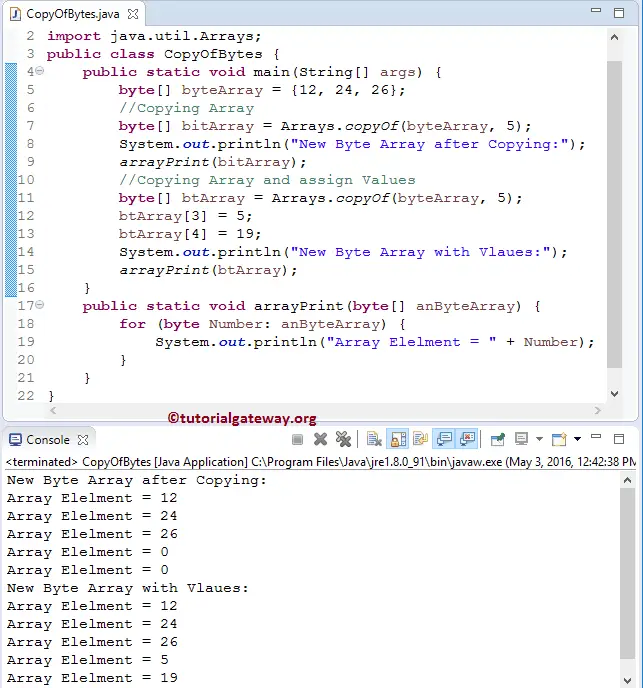
In this example, we used this function to copy the above-specified byte array to bitArray of length 5. It will copy the available elements from byteArray to bitArray and fill the remaining values with a default value.
byte[] bitArray = Arrays.copyOf(byteArray, 5);
The following Java statement is to print the Byte array elements to the output.
arrayPrint(byteArray);
Next line, we used the Java Arrays.copyOf method to copy the above-specified byte array to btArray of length 5, and we assigned the new values to index positions 3 and 4. It means these values will replace default values (zeros)
byte[] btArray = Arrays.copyOf(byteArray, 5); btArray[3] = 5; btArray[4] = 19;
The following statement is to print the Byte Array elements to the output.
arrayPrint(byteArray);
When the compiler reaches the above statement, the compiler will jump to the following function. We used the Foreach Loop from the code snippet to iterate the Byte Array. Then we print every element using the System.out.println statement.
public static void arrayPrint(byte[] anByteArray) {
for (byte Number: anByteArray) {
System.out.println("Array Elelment = " + Number);
}
}
Java copyOf to copy Boolean Array
In this program, we declare the Boolean array with random elements. Then we call the public static Boolean copyOf (boolean[] anBooleanArray, int newLength) method to copy the Boolean array to a new of a specified length.
package ArrayMethods;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class CopyOfBoolean {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean[] bool = {true, true};
boolean[] boolArray = Arrays.copyOf(bool, 4);
System.out.println("New Boolean Array after Copying:");
arrayPrint(boolArray);
boolean[] bolArray = Arrays.copyOf(bool, 4);
bolArray[2] = false;
bolArray[3] = true;
System.out.println("New Boolean Array with Vlaues:");
arrayPrint(bolArray);
}
public static void arrayPrint(boolean[] anBooleanArray) {
for (boolean bool: anBooleanArray) {
System.out.println("Array Elelment = " + bool);
}
}
}
New Boolean Array after Copying:
Array Elelment = true
Array Elelment = true
Array Elelment = false
Array Elelment = false
New Boolean Array with Vlaues:
Array Elelment = true
Array Elelment = true
Array Elelment = false
Array Elelment = trueJava Arrays.copyOf to copy Short Array
In this method program, we declared the short array with random elements. Then we call the public static Short copyOf (short[] anShortArray, int newLength) method to copy the short array to a new one of a specified length.
package ArrayMethods;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ShortCopyOf {
public static void main(String[] args) {
short[] srtArray = {2, 6, 4};
short[] ShortArray = Arrays.copyOf(srtArray, 5);
System.out.println("New Short Array after Copying:");
arrayPrint(ShortArray);
short[] ShrtArray = Arrays.copyOf(srtArray, 5);
ShrtArray[3] = 3;
ShrtArray[4] = 9;
System.out.println("New Short Array with Vlaues:");
arrayPrint(ShrtArray);
}
public static void arrayPrint(short[] anShortArray) {
for (short Number: anShortArray) {
System.out.println(Number);
}
}
}
New Short Array after Copying:
2
6
4
0
0
New Short Array with Vlaues:
2
6
4
3
9Java Arrays.copyOf to copy Integer Array
In this program, we declare the integer array with random elements. Then we call the public static IntcopyOf (int[] anIntegerArray, int newLength) method to copy the Java Int array to a new of a specified length.
package ArrayMethods;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class CopyOfIntegers {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] intArray = {25, 45};
int[] integerArray = Arrays.copyOf(intArray, 5);
System.out.println("New Integer Array after Copying:");
arrayPrint(integerArray);
int[] anIntArray = Arrays.copyOf(intArray, 5);
anIntArray[2] = 65;
anIntArray[4] = 75;
System.out.println("New Integer Array with Vlaues:");
arrayPrint(anIntArray);
}
public static void arrayPrint(int[] anIntArray) {
for (int Number: anIntArray) {
System.out.println(Number);
}
}
}
New Integer Array after Copying:
25
45
0
0
0
New Integer Array with Vlaues:
25
45
65
0
75copy Long Array
In this program, we declare the long array with random elements. Then we call the public static LongcopyOf (long[] anLongArray, int newLength) method to copy the Long array to a new one of a specified length.
package ArrayMethods;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class CopyOfLong {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long[] LngArray = {504, 405};
long[] longArray = Arrays.copyOf(LngArray, 5);
System.out.println("New Long Array after Copying:");
arrayPrint(longArray);
long[] anLongArray = Arrays.copyOf(LngArray, 5);
anLongArray[2] = 265;
anLongArray[4] = 750;
System.out.println("New Long Array with Vlaues:");
arrayPrint(anLongArray);
}
public static void arrayPrint(long[] anLongArray) {
for (long Number: anLongArray) {
System.out.println(Number);
}
}
}
New Long Array after Copying:
504
405
0
0
0
New Long Array with Vlaues:
504
405
265
0
750Java copyof Double Array
In this program, we declared the double array with random elements. Next, we call the public static Double copyOf (double[] anDoubleArray, int newLength) to copy the double array to a new.
package ArrayMethods;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class CopyOfDouble {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double[] DoubArray = {64.542, 75.983};
double[] DoubleArray = Arrays.copyOf(DoubArray, 5);
System.out.println("New Integer Array after Copying:");
arrayPrint(DoubleArray);
double[] dblArray = Arrays.copyOf(DoubArray, 4);
dblArray[2] = 465.6054;
dblArray[3] = 986.70534;
System.out.println("New Integer Array with Vlaues:");
arrayPrint(dblArray);
}
public static void arrayPrint(double[] anDoubleArray) {
for (double Number: anDoubleArray) {
System.out.println(Number);
}
}
}
New Integer Array after Copying:
64.542
75.983
0.0
0.0
0.0
New Integer Array with Vlaues:
64.542
75.983
465.6054
986.70534Java Arrays.copyOf to copy Float Array
In this Java program, we declared the floating-point array with random elements. Then we call the public static float copyOf (float[] anFloatArray, int newLength) to copy the float array to a new one of a specified length.
package ArrayMethods;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class CopyOfFloat {
public static void main(String[] args) {
float[] floatArray = {4.54f, 7.98f, 5.68f, 3.25f, 6.95f};
float[] fltArray = Arrays.copyOf(floatArray, 2);
System.out.println("New Float Array after Copying:");
arrayPrint(fltArray);
float[] ftArray = Arrays.copyOf(floatArray, 4);
ftArray[0] = 12.56f;
ftArray[3] = 22.56f;
System.out.println("New Float Array with Changed Vlaues:");
arrayPrint(ftArray);
}
public static void arrayPrint(float[] anfloatArray) {
for (float Number: anfloatArray) {
System.out.println(Number);
}
}
}
New Float Array after Copying:
4.54
7.98
New Float Array with Changed Vlaues:
12.56
7.98
5.68
22.56Java copyOf Char Array
In this program, we declared the character array with random elements. Next, we call the public static Char copyof (char[] anCharacterArray, int newLength) to copy the Char array to a new character one of a specified length.
package ArrayMethods;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class CopyOfChar {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] CharArray = {'J', 'a', 'v', 'a'};
char[] ChArray = Arrays.copyOf(CharArray, 5);
System.out.println("New Character Array after Copying:");
arrayPrint(ChArray);
char[] ChrArray = Arrays.copyOf(CharArray, 6);
ChrArray[4] = 'T';
ChrArray[5] = 'G';
System.out.println("New Character Array with Vlaues:");
arrayPrint(ChrArray);
}
public static void arrayPrint(char[] anCharacterArray) {
for (char Number: anCharacterArray) {
System.out.println(Number);
}
}
}
New Character Array after Copying:
J
a
v
a
New Character Array with Vlaues:
J
a
v
a
T
Gcopy Object Array
In this Java copyof program, we declared the String array with random elements. Next, we call the method to copy the Object array to a new one of a specified length.
package ArrayMethods;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class CopyOfObject {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] stringArray = {"India", "USA"};
String[] strArray = Arrays.copyOf(stringArray, 5);
System.out.println("New Object Array after Copying:");
arrayPrint(strArray);
String[] strngArray = Arrays.copyOf(stringArray, 4);
strngArray[2] = "Australia";
strngArray[3] = "Japan";
System.out.println("New Object Array with Values:");
arrayPrint(strngArray);
}
public static void arrayPrint(Object[] anObjectArray) {
for (Object Number: anObjectArray) {
System.out.println(Number);
}
}
}
New Object Array after Copying:
India
USA
null
null
null
New Object Array with Values:
India
USA
Australia
Japancopy array to user-specified type
In this Java program, we declare the Object array with random elements. Then we will call the public static <T, U> T[] copyOf (U[] anObjectArray, int newLength, , Class<? extends T[]> newType) to copy the Java Object array to a new specified array.
package ArrayMethods;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class CopyOfT {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object[] objectArray = {"Australia", "India"};
String[] objArray = Arrays.copyOf(objectArray, 5, String[].class);
System.out.println("New Object Array after Copying:");
arrayPrint(objArray);
}
public static void arrayPrint(Object[] anObjectArray) {
for (Object Number: anObjectArray) {
System.out.println(Number);
}
}
}
New Object Array after Copying:
Australia
India
null
null
null