Factorial is denoted by the exclamation mark (!). We can define it as the product of all positive integers less than or equal to that number & greater than 0. For example, the factorial of 4 (4!) means 4 x 3 x 2 x 1, which equals 24. This blog post will explore how to write a Python program to find or calculate the factorial of a number efficiently.
We begin with a basic understanding of the factorial algorithm and how to calculate it in mathematics. Next, we show you different approaches to writing Python programs to find the factorial of a number using For Loop, While Loop, Functions, and Recursion.
The math or mathematical module in this programming language has a factorial() function that directly calculates and returns the results for any positive number. You can use this function by importing the math library.
Python Program to find the factorial of a Number using math function
The Mathematical Representation of the Factorial of n is represented as n!. Where n! = n * (n-1) * (n -2) * …….* 1. For instance, consider n = 5.
- 5! = 5 * (5 – 1) * (5 – 2) * (5 – 3) * (5 – 1)
- 5! = 5 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1 = 120
It is denoted with the exclamation mark (!), and in this program code, we use the built-in math module factorial function on the number to find it.
import math
a = int(input(" Please enter any Integer : "))
ft = math.factorial(a)
print("The Result of %d = %d" %(a, ft))
In this example, we use the math prod() function that accepts the iteration value, finds the product of each value, and returns the factorial of a number.
import math
num = int(input("Enter any Number : "))
if num < 0:
print("Please Enter Positive Integer Only.")
elif num == 0:
print("The Fact of 0 = 1.")
else:
fact = math.prod(range(1, num + 1))
print(f"The Fact of {num} is {fact}.")

Python Program to find the Factorial of a Number using For Loop
This code allows the user to enter any integer. Using this given value, this program finds the Factorial of a number using For Loop. The for loop will start from 1 and multiply the current value by the next integer until it reaches the user given number.
number = int(input(" Please enter any Number : "))
fact = 1
for i in range(1, number + 1):
fact = fact * i
print("The factorial of %d = %d" %(number, fact))
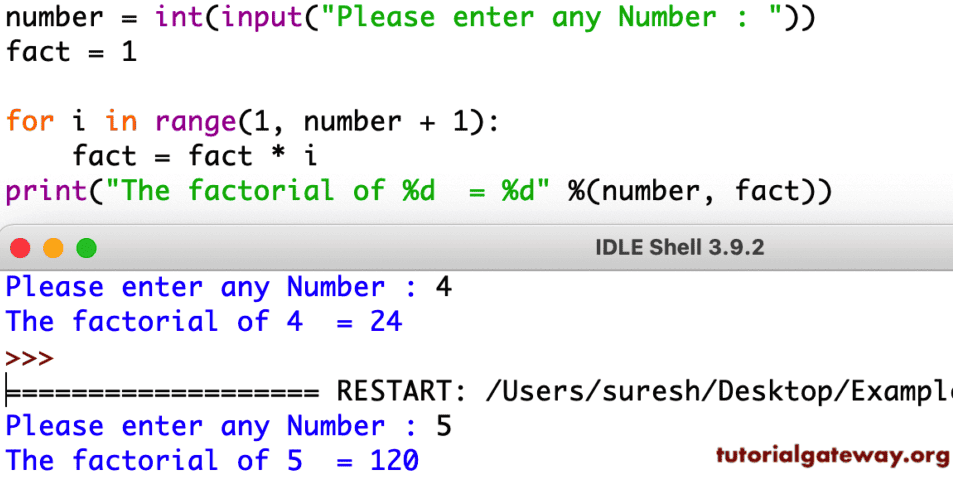
The user entered integer in the above program example is 4. Please refer to math functions, For Loop, While Loop, and Functions articles in Python.
First Iteration
i = 1, Fact = 1 and number = 5
Fact = Fact * i;
Fact = 1 * 1 = 1
2nd Iteration: i = 2, Fact = 1 and Number = 5
Fact = 1 * 2 = 2
3rd Iteration: i = 3, Fact = 2 and Number = 5
Fact = 2 * 3 = 6
4th Iteration: i = 4, Fact = 6 and Number = 5
Fact = 6 * 4 = 24
Next, i become 5. So, For loop Terminated.
The For Loop Time Complexity is O(n), and Space Complexity is O(1)
The above code for the factorial program returns 1 for the negative values. So, we need the If else statement to print a message for negative input.
num = int(input("Enter any Number : "))
fact = 1
if num < 0:
print("Please Enter Positive Integer Only.")
else:
for i in range(1, num + 1):
fact = fact * i
print("The factorial of %d = %d" %(num, fact))
Enter any Number : -9
Please Enter Positive Integer Only.
Enter any Number : 6
The factorial of 6 = 720Python Program to find the Factorial of a Number using while Loop
In this program, we just replaced the for loop with the while Loop to find the factorial of a number.
value = int(input(" Please enter any Value : "))
fact = 1
i = 1
while(i <= value):
fact = fact * i
i = i + 1
print("The Result of %d = %d" %(value, fact))

Python Program to find the Factorial of a Number using Functions
This code is the same as the first example. However, we separated the factorial logic using the Functions.
def calculating(num):
faco = 1
for i in range(1, num + 1):
faco = faco * i
return faco
val = int(input(" Please enter any Value : "))
faco = calculating(val)
print("The Result of %d = %d" %(val, faco))

Python Program for Factorial of a Number using Recursion
This code passes the user entered value to the Function. Within this recursive function, this example program finds the factorial of a number using the recursive function or recursively.
Within the user-defined function of this program, the If Else Statement checks whether the integer is Equal to 0 or 1. If the condition is TRUE, then the function returns 1. If the condition is False, the function recursively returns Num * (Num -1).
def factFind(num):
if num < 0:
print("Please Enter Positive Integer Only.")
elif num == 0:
return 1
else:
return num * factFind(num - 1)
num = int(input("Enter any Num : "))
print(f"Fact of {num} is {factFind(num)}.")

User Entered Value = 6.
Fac = num * factFind (num -1);
= 6 * factFind (5)
= 6 * 5 * factFind (4)
= 6 * 5 * 4 * factFind (3)
= 6 * 5 * 4 * 3 * factFind (2)
= 6 * 5 * 4 * 3 * 2 * factFind(1)
= 6 * 5 * 4 * 3 * 2
= 720
The Recursive function Time and Space Complexity are O(n).
Factorial using List comprehension
This Program finds the Factorial of a Number using list comprehension.
num = int(input("Enter any Number : "))
if num < 0:
print("Please Enter Positive Integer Only.")
elif num == 0:
print("The Fact of 0 = 1.")
else:
fact = 1
[fact := fact * i for i in range(1, num + 1)]
print(f"The Fact of {num} is {fact}.")
Enter any Number : 5
The Fact of 5 is 120.Factorial using the lambda reduce function
This Python Program for the Factorial of a Number example uses the lambda and reduce functions.
from functools import reduce
num = int(input("Enter any Number : "))
if num < 0:
print("Please Enter Positive Integer Only.")
elif num == 0:
print("The Fact of 0 = 1.")
else:
fact = reduce(lambda a, b: a * b, range(1, num + 1), 1)
print(f"The Fact of {num} is {fact}.")

This example is the same as the above. However, it uses the lambda recursive function.
from functools import reduce
def factorial(num):
return reduce(lambda a, b: a * b, range(1, num + 1), 1)
num = int(input("Enter any Number : "))
if num < 0:
print("Please Enter Positive Integer Only.")
elif num == 0:
print("The Fact of 0 = 1.")
else:
print(f"The Fact of {num} is {factorial(num)}.")
Enter any Number : 0
The Fact of 0 = 1.