The Python numpy logspace function generate evenly spaced numbers on a log scale within a range. The syntax of the numpy logspace is
numpy.logspace(start, stop, num = 50, endpoint = True, base = 10.0, dtype=None, axis = 0)
The arguments of the Python numpy logspace array function are
- start – Starting value, i.e., base ** start
- start – End value, i.e., base ** stop
- num – Total samples to generate.
- endpoint – If you set it to True, it includes the last sample; otherwise, it is not.
- base – Provide the base value of the log spaces.
- dtype – The data type of an output array.
- axis – If start and stop values are arrays, it is helpful.
Python numpy logspace
It is a simple example of having the start and stop arguments.
import numpy as np a = np.logspace(1, 2) print(a)
[ 10. 10.48113134 10.98541142 11.51395399 12.06792641
12.64855217 13.25711366 13.89495494 14.56348478 15.26417967
15.9985872 16.76832937 17.57510625 18.42069969 19.30697729
20.23589648 21.20950888 22.22996483 23.29951811 24.42053095
25.59547923 26.82695795 28.11768698 29.47051703 30.88843596
32.37457543 33.93221772 35.56480306 37.2759372 39.06939937
40.94915062 42.9193426 44.98432669 47.14866363 49.41713361
51.79474679 54.28675439 56.89866029 59.63623317 62.50551925
65.51285569 68.6648845 71.9685673 75.43120063 79.06043211
82.86427729 86.85113738 91.0298178 95.40954763 100. ]Example 2
np.logspace(1, 3, num = 5) will generate five samples start from 1 and stops at 3. So, the first value will be base ** 1, and the base value is the default 10. So, the first one = 10 ** 1 and last one = 10 ** 3
b = (1.0, 5.0, num = 5, base = 2). Start value = 2 ** 1 and stop = 2 ** 5
In the third line, we used endpoint = False so that the stop value would be less than 5. In the fourth line, the dtype = int will convert the result to integers.
import numpy as np a = np.logspace(1, 3, num = 5) print(a) b = np.logspace(1.0, 5.0, num = 5, base = 2) print(b) c = np.logspace(1.0, 5.0, num = 5, endpoint = False, base = 2) print(c) d = np.logspace(1.0, 5.0, num = 5, base = 2, dtype = int) print(d)
[ 10. 31.6227766 100. 316.22776602 1000. ]
[ 2. 4. 8. 16. 32.]
[ 2. 3.48220225 6.06286627 10.55606329 18.37917368]
[ 2 4 8 16 32]Python numpy array logspace function
We used the arrays as the start and stopped values in this example.
np.logspace(start = [1, 5], stop = [5, 10], num = 6, base = 2) will generate 6 numbers vertically. The first column values start from 1 and end at 5, and the second column values from 5 to 10.
In the last line, we set the axis = 1. It will horizontally generate 7 evenly spaced log scale numbers where the first row starts from 1, ends at 5, and the second from 5 to 10.
import numpy as np a = np.logspace(start = [1, 5], stop = [5, 10], num = 6, base = 2) print(a) b = np.logspace(start = [1, 5], stop = [5, 10], num = 6, base = 2, dtype = int) print(b) c = np.logspace(start = [1, 5], stop = [5, 10], num = 7, base = 2, dtype = int, axis = 1) print(c)
[[ 2. 32. ]
[ 3.48220225 64. ]
[ 6.06286627 128. ]
[ 10.55606329 256. ]
[ 18.37917368 512. ]
[ 32. 1024. ]]
[[ 2 32]
[ 3 64]
[ 6 128]
[ 10 256]
[ 18 512]
[ 32 1024]]
[[ 2 3 5 8 12 20 32]
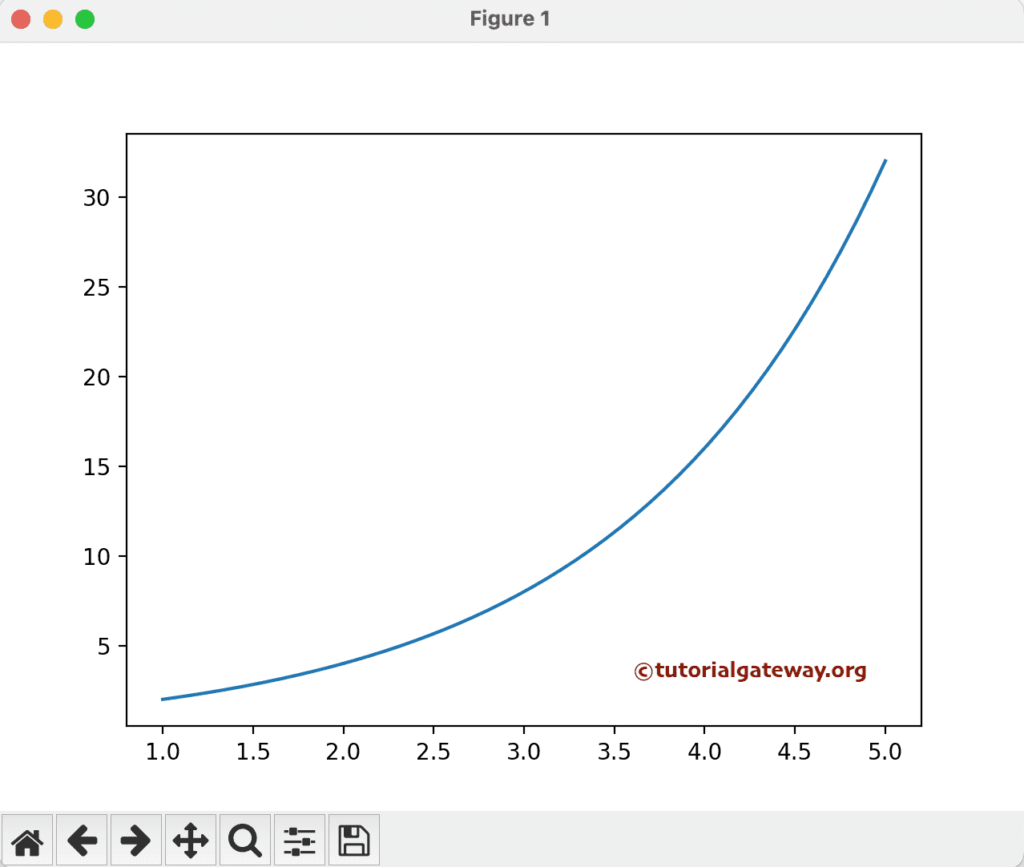
[ 32 57 101 181 322 574 1024]]In this example, we will generate a line chart using the values generated by the numpy logspace function.
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt a = np.linspace(1, 5) b = np.logspace(1, 5, base = 2) print(b) plt.plot(a, b) plt.show()