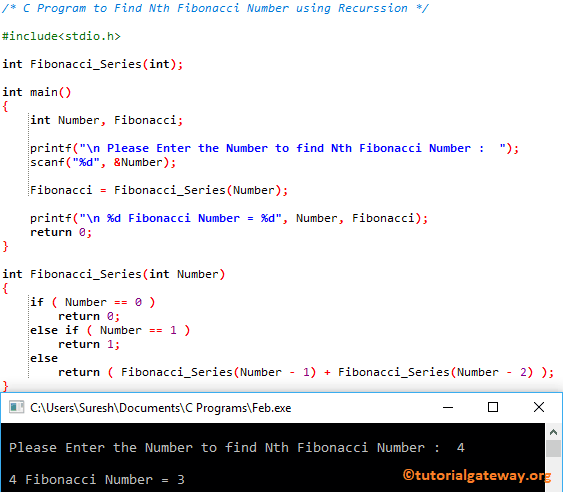
How to Write a C Program to Find Nth Fibonacci Number with example. For this, we are going to use the Recursion concept.
C Program to Find Nth Fibonacci Number using Recursion
This program allows the user to enter any positive integer and display the Fibonacci number at that position using Recursion. Please refer to the Fibonacci Series to understand this program.
#include<stdio.h>
int Fibonacci_Series(int);
int main()
{
int Number, Fibonacci;
printf("\n Please Enter the Number to find Nth Fibonacci Number : ");
scanf("%d", &Number);
Fibonacci = Fibonacci_Series(Number);
printf("\n %d Fibonacci Number = %d", Number, Fibonacci);
return 0;
}
int Fibonacci_Series(int Number)
{
if ( Number == 0 )
return 0;
else if ( Number == 1 )
return 1;
else
return ( Fibonacci_Series(Number - 1) + Fibonacci_Series(Number - 2) );
}
Let’s see the Else If statement inside the above specified C Programming functions
- if (Number == 0) – check whether the given number is 0 or not. If the condition result is TRUE, the function will return Zero.
- if (Number == 1) – check whether the specified number equals 1. If it is TRUE, the function will return One.
- If the number is greater than 1, the Program compiler will execute the statements inside the else block.
Within the Else block, we call the Fibonacci_Series function Recursively to display the Fibonacci numbers.
For example, Number = 2
(Fibonacci_series(Number- 2) + Fibonacci_series(Number – 1))
(Fibonacci_series(2 – 2) + Fibonacci_series(2 – 1))
It means, (Fibonacci_series (0)+ Fibonacci_series(1))
return (0 + 1) = return 1