The Python numpy concatenate function is used to Join two or more arrays together and returns the ndarray as an output.
The syntax of the Python Numpy array concatenate function is.
numpy.concatenate((array1, array2,....), axis = 0)
- array1, array2,… are the arrays that you want to combine. The arrays that you pass to this function must have the same shape. However, you can choose arrays with different dimensions.
- axis – This is an optional argument with a default value as 0. Use this to specify in which way (horizontal or Vertical) concatenation should be done.
Python numpy concatenate array
In this example, we declared two ndarrays. Next, we used this function to join those two arrays.
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print(a)
b = np.array([4, 5, 6])
print(b)
print('\n---Result of a and b---')
print(np.concatenate((a, b)))
[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]
---Result of a and b---
[1 2 3 4 5 6]The Python Numpy concatenate function is not limited to joining two. You can use this function to combine more than two. Here, we are joining four different arrays using this function.
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print(a)
b = np.array([4, 5, 6])
print(b)
c = np.array([7, 8, 9])
print(c)
d = np.array([10, 11, 12])
print(d)
print('\n------')
print(np.concatenate((a, b, c, d)))
[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]
[7 8 9]
[10 11 12]
------
[ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12]Join 2D Array
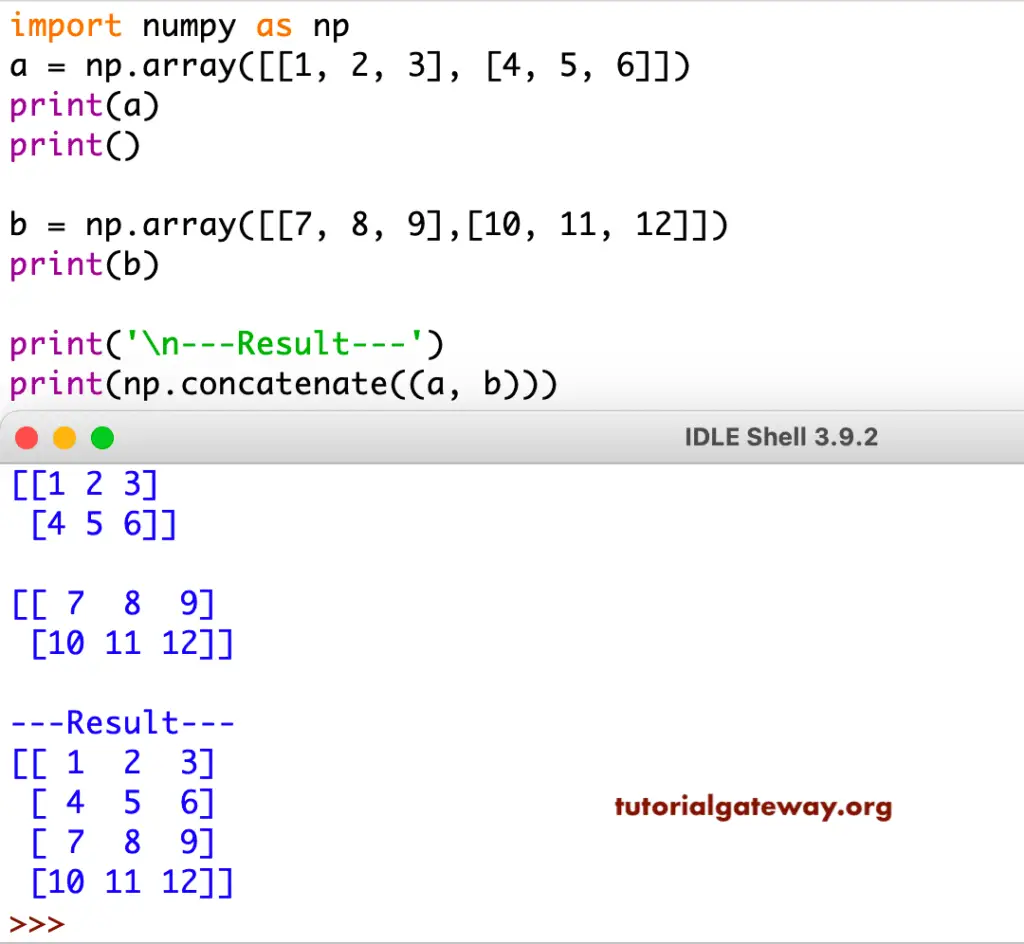
We are using Python Numpy concatenate function to join two dimensional arrays.
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
print(a)
print()
b = np.array([[7, 8, 9],[10, 11, 12]])
print(b)
print('\n---Result---')
print(np.concatenate((a, b)))
It is another example of concatenating 2D arrays.
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[10, 20, 30, 40]])
print(a)
b = np.array([[50 ,60, 70, 80], [90 ,100, 110, 120]])
print(b)
print('\n------')
print(np.concatenate((a, b)))
print('\n------')
print(np.concatenate((b, a)))
[[10 20 30 40]]
[[ 50 60 70 80]
[ 90 100 110 120]]
------
[[ 10 20 30 40]
[ 50 60 70 80]
[ 90 100 110 120]]
------
[[ 50 60 70 80]
[ 90 100 110 120]
[ 10 20 30 40]]Python Numpy concatenate 2D array with axis
Until now, we have been using this method without an axis parameter. This time, we use this parameter value while combining two-dimensional arrays. Remember, If the axis = 0, then the items in b are vertically appended to a. Whereas axis = 1 horizontally appends items in b to a.
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
print(a)
print()
b = np.array([[7, 8, 9],[10, 11, 12]])
print(b)
print('\n---2D---')
print(np.concatenate((a, b), axis = 0))
print('\n---2D---')
print(np.concatenate((a, b), axis = 1))
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]
[[ 7 8 9]
[10 11 12]]
---2D---
[[ 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6]
[ 7 8 9]
[10 11 12]]
---2D---
[[ 1 2 3 7 8 9]
[ 4 5 6 10 11 12]]In Python, you don’t have to specify the axis. I mean, you can directly use the value.
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[10, 20, 30], [40, 50, 60]])
print(a)
print()
b = np.array([[70, 80, 90],[100, 110, 120]])
print(b)
print('\n------')
print(np.concatenate((a, b), 0))
print('\n------')
print(np.concatenate((a, b), 1))
[[10 20 30]
[40 50 60]]
[[ 70 80 90]
[100 110 120]]
------
[[ 10 20 30]
[ 40 50 60]
[ 70 80 90]
[100 110 120]]
------
[[ 10 20 30 70 80 90]
[ 40 50 60 100 110 120]]Python Numpy concatenate 3D array
In this example, we are using Numpy concatenate function on three-dimensional arrays. First, we created two 3D random using randint. Next, we used this function with different axis values.
import numpy as np
a = np.array(np.random.randint(0, 10, size = (2, 3, 4)))
print(a)
print()
b = np.array(np.random.randint(11, 20, size = (2, 3, 4)))
print(b)
print('\n---Three Dimensional---')
print(np.concatenate((a, b), axis = -1))
Combining three Dimensional numpy output
[[[5 3 6 4]
[1 8 1 1]
[1 9 7 2]]
[[4 2 6 0]
[4 3 6 8]
[4 8 8 9]]]
[[[12 13 17 16]
[17 14 16 13]
[17 16 17 19]]
[[16 18 18 16]
[19 16 18 12]
[18 19 18 14]]]
---Three Dimensional---
[[[ 5 3 6 4 12 13 17 16]
[ 1 8 1 1 17 14 16 13]
[ 1 9 7 2 17 16 17 19]]
[[ 4 2 6 0 16 18 18 16]
[ 4 3 6 8 19 16 18 12]
[ 4 8 8 9 18 19 18 14]]]
>>> Another example of concatenating the three dimensional.
import numpy as np
a = np.array(np.random.randint(0, 10, size = (2, 3, 4)))
print(a)
print()
b = np.array(np.random.randint(11, 20, size = (2, 3, 4)))
print(b)
print('\n---Three Dimensional---')
print(np.concatenate((a, b), axis = -1))
[[[9 4 1 6]
[1 9 4 5]
[8 5 1 3]]
[[9 3 3 3]
[5 0 6 6]
[5 9 7 4]]]
[[[16 17 12 12]
[12 19 19 14]
[11 11 11 14]]
[[15 17 13 17]
[17 13 17 19]
[18 12 15 11]]]
---Three Dimensional---
[[[ 9 4 1 6 16 17 12 12]
[ 1 9 4 5 12 19 19 14]
[ 8 5 1 3 11 11 11 14]]
[[ 9 3 3 3 15 17 13 17]
[ 5 0 6 6 17 13 17 19]
[ 5 9 7 4 18 12 15 11]]]Concatenate Different size Arrays
Until now, we are working with the same size of arrays (joining the same size). Let me join different size using this function.
import numpy as np
x = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print(x)
y = np.array([4, 5])
print(y)
print('\n---Result---')
print(np.concatenate((x, y)))
print()
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
print(a)
print()
d = np.array([[7, 8, 9],[10, 11, 12], [13, 14, 15]])
print(d)
print('\n---Two Dimensional---')
print(np.concatenate((a, d), axis = 0))
print('\n---Two Dimensional---')
print(np.concatenate((d, a.T), axis = 1))
[1 2 3]
[4 5]
---Result---
[1 2 3 4 5]
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]
[[ 7 8 9]
[10 11 12]
[13 14 15]]
---Two Dimensional---
[[ 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6]
[ 7 8 9]
[10 11 12]
[13 14 15]]
---Two Dimensional---
[[ 7 8 9 1 4]
[10 11 12 2 5]
[13 14 15 3 6]]Python numpy hstack
The numpy hstack function horizontally appends the array items, which is similar to axis = 1.
import numpy as np
a = np.array([10, 20, 30, 40])
print(a)
b = np.array([50 ,60, 70, 80])
print(b)
print('\n--- hstack on one Dimensional ---')
print(np.hstack((a, b)))
[10 20 30 40]
[50 60 70 80]
--- hstack on one Dimensional ---
[10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80]Let me use this numpy hstack function to concatenate two dimensional arrays.
import numpy as np
a = np.array(np.random.randint(0, 10, size = (3, 3)))
print(a)
print()
b = np.array(np.random.randint(11, 20, size = (3, 3)))
print(b)
print('\n---hstack on Two Dimensional ---')
print(np.hstack((a, b)))
[[3 6 0]
[4 3 5]
[3 8 7]]
[[11 12 11]
[12 13 17]
[19 11 17]]
--- hstack on Two Dimensional ---
[[ 3 6 0 11 12 11]
[ 4 3 5 12 13 17]
[ 3 8 7 19 11 17]]Python numpy vstack
The numpy vstack function vertically appends the array items, which is similar to axis = 0.
import numpy as np
a = np.array([10, 20, 30, 40])
print(a)
b = np.array([50 ,60, 70, 80])
print(b)
print('\n--- vstack on one Dimensional ---')
print(np.vstack((a, b)))
[10 20 30 40]
[50 60 70 80]
--- vstack on one Dimensional ---
[[10 20 30 40]
[50 60 70 80]]We are using the vstack function to concatenate two-dimensionals.
import numpy as np
a = np.array(np.random.randint(0, 10, size = (3, 3)))
print(a)
print()
b = np.array(np.random.randint(11, 20, size = (3, 3)))
print(b)
print('\n--- vstack on Two Dimensional ---')
print(np.vstack((a, b)))
The vstack function combines two dimensional output
[[8 7 1]
[3 4 5]
[8 7 6]]
[[11 17 13]
[14 12 14]
[18 17 18]]
--- vstack on Two Dimensional ---
[[ 8 7 1]
[ 3 4 5]
[ 8 7 6]
[11 17 13]
[14 12 14]
[18 17 18]]