Unlike Static Methods, classmethod in Python is bound to a Class. So, we don’t have to create an instance or object to call this class method. A Python classmethod receives cls as an implicit first argument, just like a standard method receives self as the first argument. This cls allows you to access the instance’s class variables, methods, and static methods.
You can define any method as this one by using the Python @ decorator or classmethod() function. Either way, it works, but it is always advisable to go for the first option. The syntax of the classmethod def is
Class A:
@classmethod
def function_name(cls, arg1, arg2,....):
........
......
You can call the class method using CName.MName or CName().MName(). Both ways will return the result.
In this section, we show how to create or define a classmethod in Python programming language using the @ decorator and () function with examples.
Python classmethod using Decorator
In this example, we are creating a classmethod called message using the Python @classmethod decorator. Within this method, cls.__name__ returns the name (Employee), and cls.company returns the variable company value (Tutorial Gateway).
class Employee:
company = 'Tutorial Gateway'
@classmethod
def message(cls):
print('The Message is From %s' %cls.__name__)
print('The Company Name is %s' %cls.company)
Employee.message()
print('-----------')
Employee().message() # Other way of calling
The Message is From Employee
The Company Name is Tutorial Gateway
-----------
The Message is From Employee
The Company Name is Tutorial GatewayPython classmethod using function
Here, we are using the Python classmethod() function to create a class method. From the below Python code, the Employee.printValue statement converts the function to this.
class Employee:
value = 100
def printValue(cls):
print('The Value = %d' %cls.value)
Employee.printValue = classmethod(Employee.printValue)
Employee.printValue()
The Value = 100Call Static Method from Python classmethod
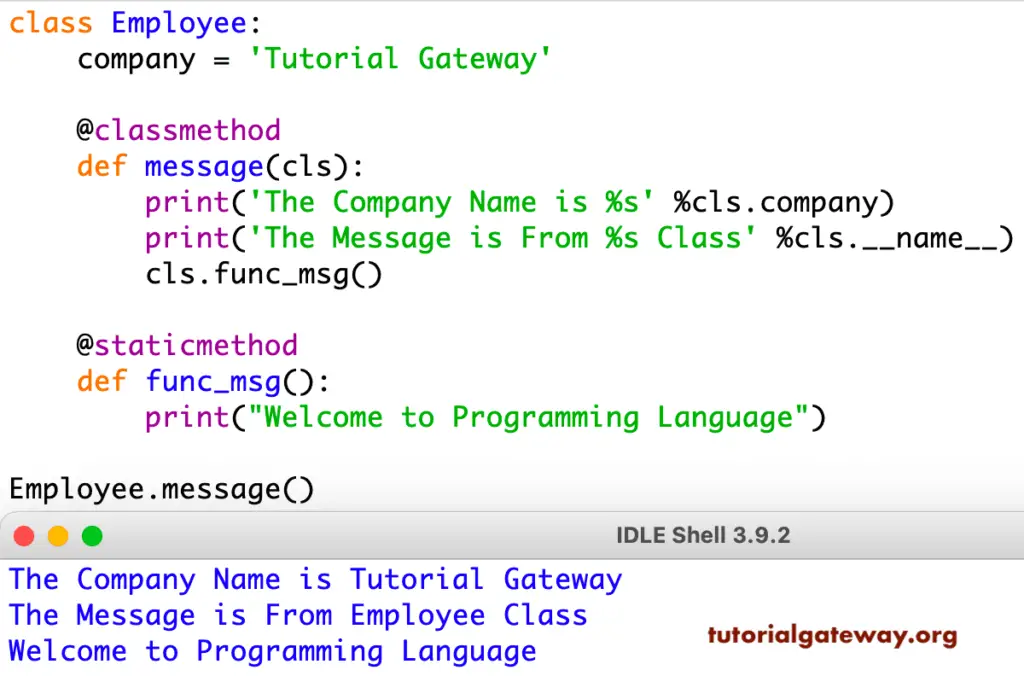
In this Python classmethod example, we show how to call Static Methods within the class method. Here, we created a staticmethod called func_msg(), which prints a welcome message. Next, we defined the message that returns a class variable company and the name. Within the same function, we are calling the staticmethod using the cls.methodname.
class Employee:
company = 'Tutorial Gateway'
@classmethod
def message(cls):
print('The Company Name is %s' %cls.company)
print('The Message is From %s Class' %cls.__name__)
cls.func_msg()
@staticmethod
def func_msg():
print("Welcome to Python Programming")
Employee.message()
Here, Instead of printing the message, we are finding the sum and average. First, we created a Static Method that accepts three arguments and returns some of those three. Next, we defined a Python classmethod that calls the static method using the cls. Within the function, it finds returns the average of the static method result.
class Employee:
company = 'Tutorial Gateway'
@staticmethod
def add(a, b, c):
return a + b + c
@classmethod
def avg(cls):
x = cls.add(10, 20, 40)
return (x / 3)
average = Employee.avg()
print('The Average Of three Numbers = ', average)
The Average Of three Numbers = 23.333333333333332Alter class variable using Python classmethod
In this example, we will create a classmethod that accepts an argument and assigns the value to the variable. It means that when you call this function, it replaces the company text with the new text that you provide as an argument value. It helps hide the variables and allows the end-users to work with them.
class Employee:
company = 'Tutorial Gateway'
@classmethod
def func_newName(cls, new_Name):
cls.company = new_Name
emp = Employee()
print(Employee.company)
print(emp.company)
print('----------')
Employee.func_newName('Coding')
print(Employee.company)
print(emp.company)
Tutorial Gateway
Tutorial Gateway
----------
Coding
CodingPython classmethod real-time Examples
For example, if the client receives the Employee information in a long string and details are separated by the – (or any other delimiter). Instead of performing splitting operations from his end, we can create a Python class method and allow them to use classmethod.
In this example, we initialized fullname, age, gender, and salary. Next, we created a classmethod that splits the given string based on – and returns those values. I suggest you refer to the split string article to understand the split function.
class Employee:
def __init__(self, fullname, age, gender, salary):
self.fullname = fullname
self.age = age
self.gender = gender
self.salary = salary
@classmethod
def func_string_split(cls, employee_str):
fullname, age, gender, salary = employee_str.split('-')
return cls(fullname, age, gender, salary)
emp_from_csv1 = 'Suresh-27-Male-120000'
emp_from_csv2 = 'John-29-Male-100000'
emp_from_csv3 = 'Tracy-25-Female-155000'
emp1 = Employee.func_string_split(emp_from_csv1)
print(emp1.fullname)
print(emp1.gender)
print(emp1.salary)
print(emp1.age)
print('----------')
emp3 = Employee.func_string_split(emp_from_csv3)
print(emp3.fullname)
print(emp3.gender)
print(emp3.age)
Suresh
Male
120000
27
----------
Tracy
Female
25It is another example of this one. Here, we are splitting the date string into Day, Month, and Year. Here, we used the map function for this splitting.
class Date:
def __init__(self, day = 0, month = 0, year = 0):
self.day = day
self.month = month
self.year = year
@classmethod
def string_to_Date(cls, string_Date):
day, month, year = map(int, string_Date.split('-'))
return cls(day, month, year)
dt = Date.string_to_Date('31-12-2018')
print(dt.day)
print(dt.month)
print(dt.year)
31
12
2018