In this section, we discuss the difference between Python Dictionary copy and = Operator with practical examples. The Python Dictionary copy shallow copy the dictionary items to an entirely new dictionary. Whereas = operator creates an instance of the existing dictionary.
Difference between Python Dictionary copy and = Operator Example 1
In this example, we are showing how we can use these two options to copy the dictionary items to a new Dictionary. As you can see, they both the Python codes are giving the same result.
# Difference between Python Dictionary copy and = Operator
emp = {'name': 'John', 'age': 25 , 'job': 'HR', 'Sal': 725000}
print("Dictionary: ", emp)
print("Dictionary Length: ", len(emp))
newEmp = emp.copy()
print("\nDictionary: ", newEmp)
print("Dictionary Length: ", len(newEmp))
newEmp2 = emp
print("\nDictionary: ", newEmp2)
print("Dictionary Length: ", len(newEmp2))
Dictionary copy vs = equals operator output
Dictionary: {'name': 'John', 'age': 25, 'job': 'HR', 'Sal': 725000}
Dictionary Length: 4
Dictionary: {'name': 'John', 'age': 25, 'job': 'HR', 'Sal': 725000}
Dictionary Length: 4
Dictionary: {'name': 'John', 'age': 25, 'job': 'HR', 'Sal': 725000}
Dictionary Length: 4Differentiate Dictionary copy and = Operator Example 2
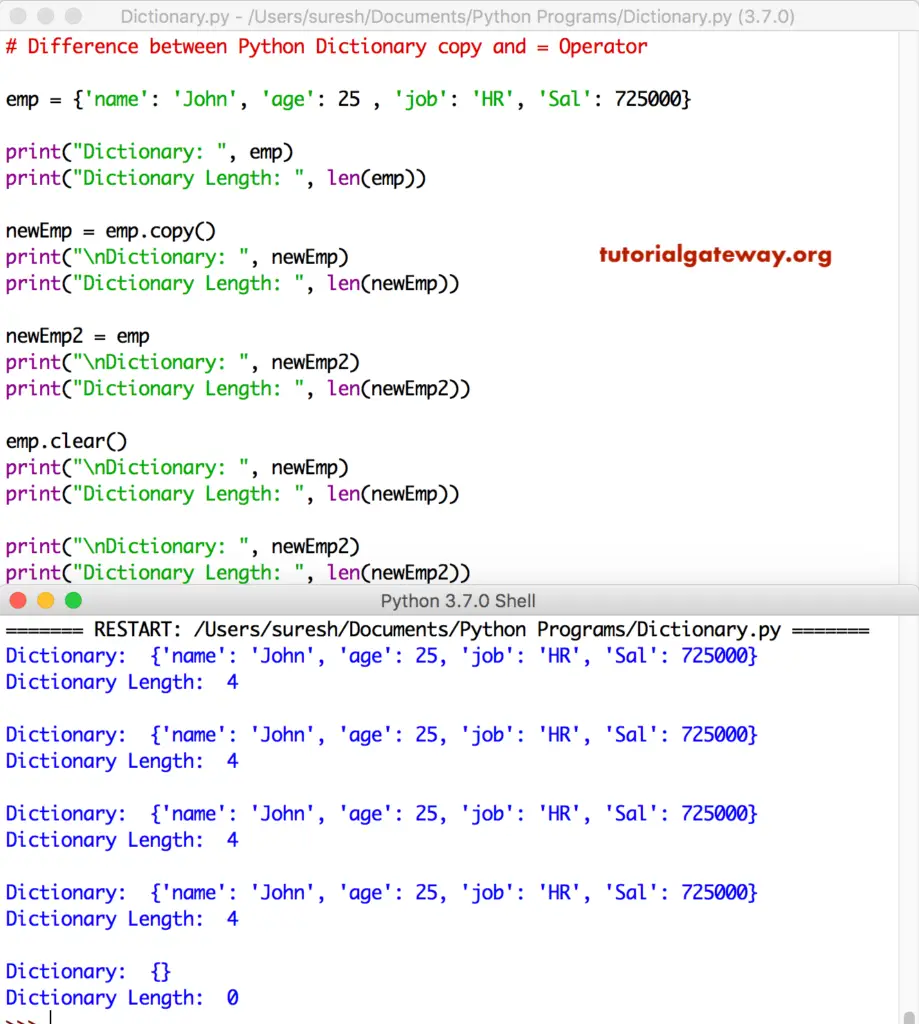
In this program, we are using a dictionary clear function to remove the items from the dictionary. If you observe carefully, when we removed items from emp, newEmp2 is also returning an empty set.
# Difference between Python Dictionary copy and = Operator
emp = {'name': 'John', 'age': 25 , 'job': 'HR', 'Sal': 725000}
print("Dictionary: ", emp)
print("Dictionary Length: ", len(emp))
newEmp = emp.copy()
print("\nDictionary: ", newEmp)
print("Dictionary Length: ", len(newEmp))
newEmp2 = emp
print("\nDictionary: ", newEmp2)
print("Dictionary Length: ", len(newEmp2))
emp.clear()
print("\nDictionary: ", newEmp)
print("Dictionary Length: ", len(newEmp))
print("\nDictionary: ", newEmp2)
print("Dictionary Length: ", len(newEmp2))