A variable in C# is nothing but a name given for a data value. The data value can be of any data type like string, float, int, etc. The syntax of the C# variable is
<data type> <variable-name> = <value>; (or) <data type> <variableName1>, <variableName2>,etc;
A C# variable can be declared and initialized at the same time, or, once declared, can be initialized later. The data value initialized to a variable can be changed throughout the program as long as it is accessible. But before using them, they should be initialized; otherwise, it gives a compile-time error while executing.
Let us see an example code using type string variables message1, message2.
using System;
namespace CSharp_Tutorial
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
string message1, message2;
message1 = "Welcome to Tutorial Gateway";
message2 = "You are learning C#.Net";
Console.WriteLine(message1);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine(message2);
}
}
}
OUTPUT
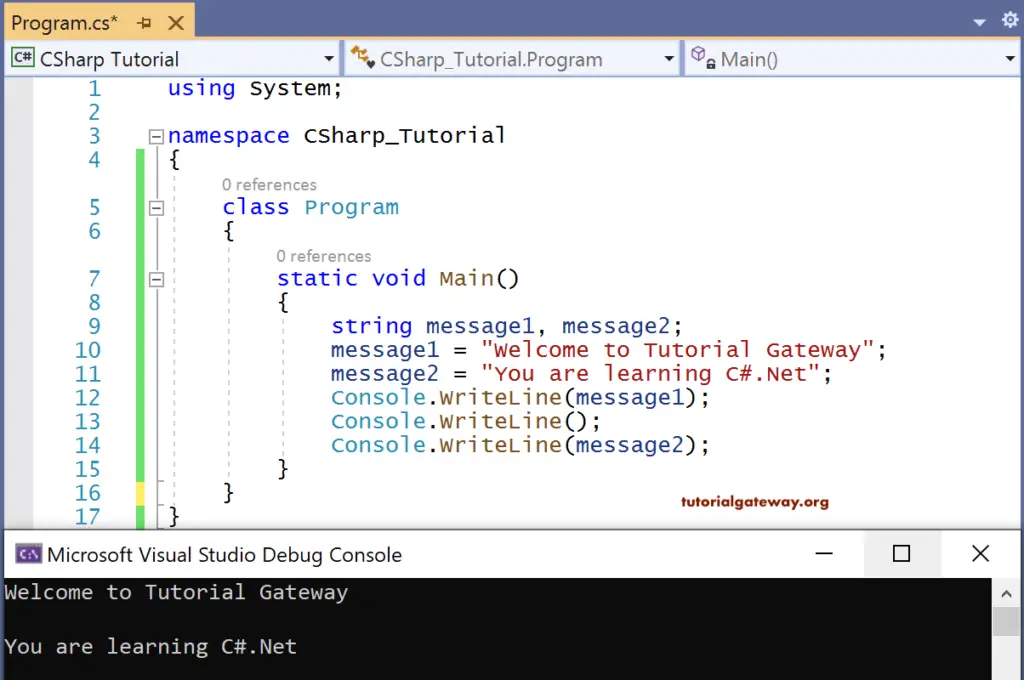
message 1 and message 2 are the two variables. Where message1 initializes with the string “Welcome to Tutorial Gateway”.
message2 will initialize with the string “You are learning C#.Net”.
These two strings will print onto the console using the console.Writeline(). Where console is the Class and Writeline() is a Console class method that prints the console’s value.
