The C# Relational operators work on two operands and return the boolean value true (1) if the relation between two operands is satisfied. Otherwise, it returns false (0). The following C# Relational operators table shows different relational operators.
| Symbols | Operation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| = = | Equal To | 3 = = 2 returns false |
| > | Greater than | 3 > 2 returns true |
| < | Less than | 3 < 2 returns false |
| > = | Greater than or equal to | 3 > = 2 returns true |
| < = | Less than or equal to | 3 < = 2 returns false |
| != | Not Equal To | 3 ! = 2 returns true |
C# Relational Operators Example
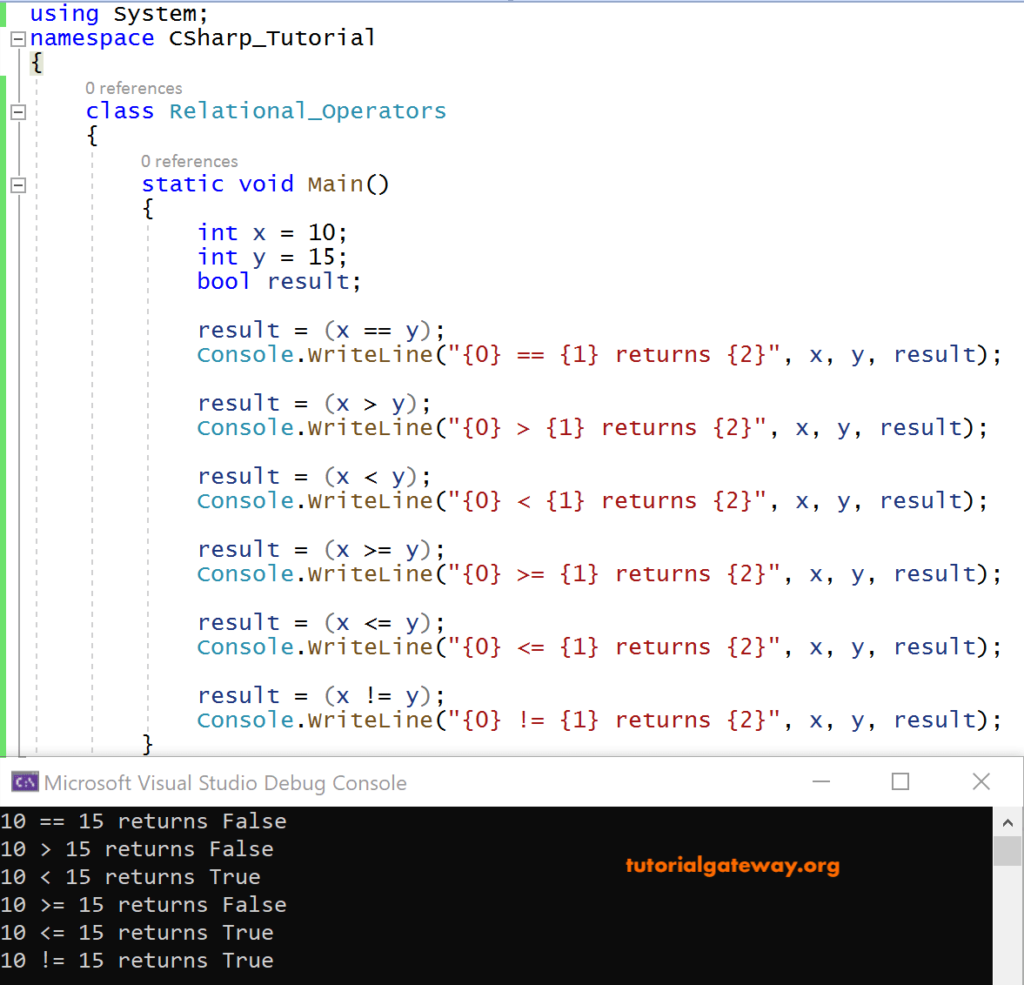
In the following C# code, we have taken two integer variables x and y. After applying different relational operators on them, the result stored in a Boolean variable result.
using System;
class Relational_Operators
{
static void Main()
{
int x = 10;
int y = 15;
bool result;
result= (x==y);
Console.WriteLine("{0} == {1} returns {2}", x, y, result);
result= (x>y);
Console.WriteLine("{0} > {1} returns {2}", x, y, result);
result= (x<y);
Console.WriteLine("{0} < {1} returns {2}", x, y, result);
result= (x>=y);
Console.WriteLine("{0} >= {1} returns {2}", x, y, result);
result= (x<=y)
Console.WriteLine("{0} <= {1} returns {2}", x, y, result);
result= (x != y);
Console.WriteLine("{0} != {1} returns {2}", x, y, result);
}
}
In the above C# example, integer variables x=10, y=15 are the two operands. And on applying relational operators on them, of the expression is satisfied, True is stored in the result otherwise False.