The SQL Server RIGHT function returns the rightmost characters from a given expression. The SQL RIGHT function uses its second argument to decide the number of characters it should return, and its syntax.
SELECT RIGHT(Character_Expression, Value) FROM [Source]
- Character_Expression: It will write the rightmost characters from this expression.
- Value: Number of characters it has to extract from the Character_Expression.
The index position in the SQL Server RIGHT Function will start from 1, Not 0. For this example, we use the below data
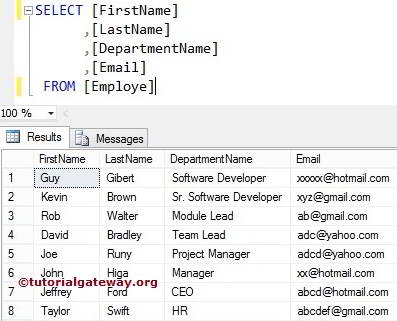
SQL Server RIGHT Function Example
The SQL RIGHT function returns the specified number of rightmost characters from the given string. For example, the following query returns the rightmost 6 and 20 characters from a variable.
First, we declared a Character expression with sample text. Next, we used this one to return the six rightmost characters from the @Character_Expression variable.
In the following line, We set the second argument = 20, which is greater than the string length. So, the RIGHT Function prints all the letters from the @Character_Expression
DECLARE @Charcater_Expression varchar(50) SET @Charcater_Expression = 'Learn SQL Server' --Using Positive Integer 6 SELECT RIGHT(@Charcater_Expression, 6) AS 'SQLRIGHT' --Searching from specific position – 20 SELECT RIGHT(@Charcater_Expression, 20) AS 'SQLRIGHT'
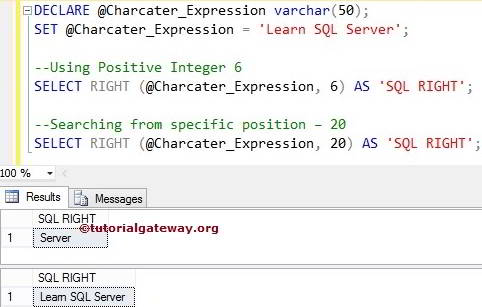
SQL Server RIGHT Example 2
The RIGHT function also allows you to select the rightmost characters from the column values. In this Server example, we print the rightmost nine words of all the records present inside the Email column
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[DepartmentName]
,[Email]
,RIGHT([Email], 9) AS [SQLRIGHT]
FROM [Employe]
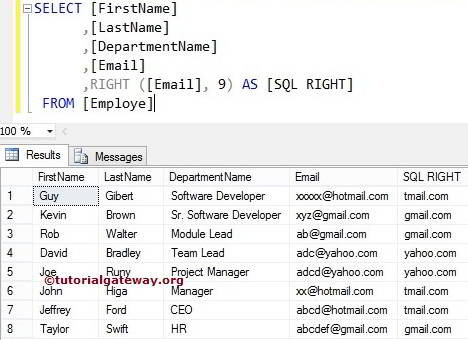
If you observe the above result, it is not getting the domain names perfectly because we are using fixed values. In the following String method example, we show how to use dynamic value as a second argument to return the domain names accurately.
How to Find Domain Names in the Email?
We will find the domain names present in the Email column using the SQL right Function.
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[DepartmentName]
,[Email]
,RIGHT(
[Email]
,(LEN([Email]) - CHARINDEX ('@', [Email]))
) AS [SQLRIGHT]
FROM [Employe]
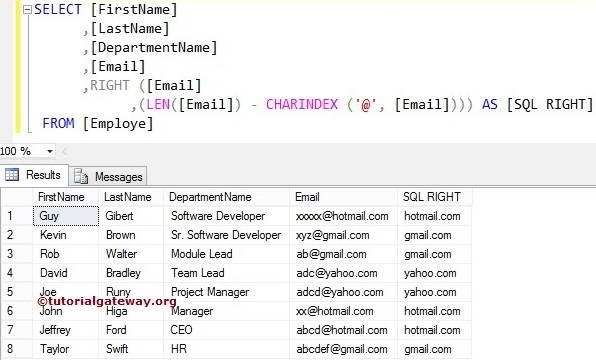
Within the right function, it will find the length of the Email using the LEN method.
LEN([Email])
It returns the index position of the @ symbol. It means the CHARINDEX method check for the index position of @ sign in every record.
CHARINDEX ('@', [Email])
We subtracted the index position from the Length of a string.
(LEN([Email]) - CHARINDEX ('@', [Email]))
