The Python partition is one of the String Methods, which is useful to split the given string using the specified separator and return a tuple with three arguments. This Python partition function starts looking for the separator from the Left-Hand side. Once it finds the separator, it returns the string before the Separator as Tuple Item 1, Separator itself as Tuple Item 2, and the remaining sentence (or after the Separator) as Tuple Item 3.
The syntax of the partition function in Python Programming Language is
String_Value.partition(Separator)
Separator: This argument is required, and if you forget this argument, the Python partition function throws TypeError. If you pass the non-existing item as a separator, the partition function returns the whole string as Tuple Item 1 followed by two empty tuple items.
Return Value: It returns Tuple with three arguments. For example, If we have A*B*C and If we use * as a separator. The Python partition function search for * from left to right. Once it finds * it returns the string before the * symbol as Tuple Item 1 (A), * as Tuple Item 2, and the remaining text as Tuple Item 3 (B*C).
Even though there are multiple occurrences of the separator, the Python partition function looks for the first occurrence.
Python partition method Example
The following set of examples helps to understand the string partition in this Python Programming Language.
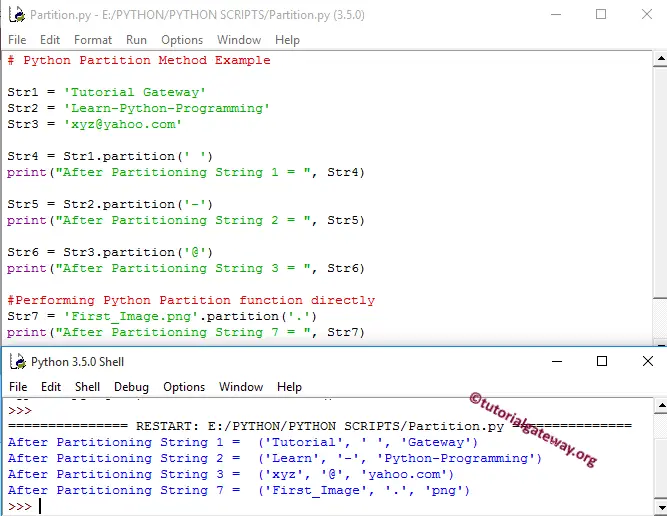
Str1 = 'Tutorial Gateway'
Str2 = 'Learn-Python-Programming'
Str3 = 'xyz@yahoo.com'
Str4 = Str1.partition(' ')
print("After Partitioning String 1 = ", Str4)
Str5 = Str2.partition('-')
print("After Partitioning String 2 = ", Str5)
Str6 = Str3.partition('@')
print("After Partitioning String 3 = ", Str6)
#Performing directly
Str7 = 'First_Image.png'.partition('.')
print("After Partitioning String 7 = ", Str7)
TIP: Please refer to rpartition article in String Method to understand the rpartition method, which performs the same operation but from right to left.
In this example, first, we declared three String variables Str1, Str2, and Str3. Next, we assigned the corresponding value using the following statement.
Str1 = 'Tutorial Gateway' Str2 = 'Learn-Python-Programming' Str3 = 'xyz@yahoo.com'
The following statement splits the Str1 into multiple parts based on the separator we specified (i.e., Empty Space) and prints the output.
Str4 = Str1.partition(' ')
It separates the Str2 into multiple parts based on the ‘_’ symbol and prints the output.
Str5 = Str2.partition('-')
The following Python function statement partition the Str3 string into multiple parts based on the ‘@’ symbol and prints the output.
Str6 = Str3.partition('@')
The below code uses directly on String.
Str7 = 'First_Image.png'.partition('.')
The below Python code looks for *, which doesn’t exist. So it returns the Tuple as (‘Tutorial Gateway’, ”, ”).
Str8 = Str1.partition('*')
