The Python numpy string functions are to alter the given string as per your requirement. The numpy string functions are: add, multiply, capitalize, title, upper, lower, center, split, splitlines, strip, join, replace, encode, and decode. For instance, the numpy string upper function converts to uppercase. These examples help you understand the string functions.
Python numpy add
The python numpy add function is used for string concatenation. In this example, we are using this numpy add function to add two strings
import numpy as np
print('Numpy String concatenation')
print(np.char.add(['Tutorial'], ['Gateway']))
numpy add function to perform string concatenation output
Numpy String concatenation
['TutorialGateway']This time we declared two different strings. Next, we used this char add function
import numpy as np fname = 'Suresh' company = ' Tutorial Gateway' print(np.char.add([fname], [company]))
char add function output.
['Suresh Tutorial Gateway']Here, we are concatenating a string variable and sample text
import numpy as np
fname = 'Suresh'
print('concatenation')
print(np.char.add([fname], [' Working at Tutorial Gateway']))
char add output
concatenation
['Suresh Working at Tutorial Gateway']Python numpy multiply
The multiply function is used to multiply or repeat a given string for a specified number of times. In this example, p.char.multiply(‘hello ‘, 2) repeats hello twice.
import numpy as np
print('---Numpy String multiply---')
print(np.char.multiply('hello ', 2))
print('-------')
fname = 'Numpy '
print(np.char.multiply(fname, 4))
print(np.char.multiply(fname, 6))
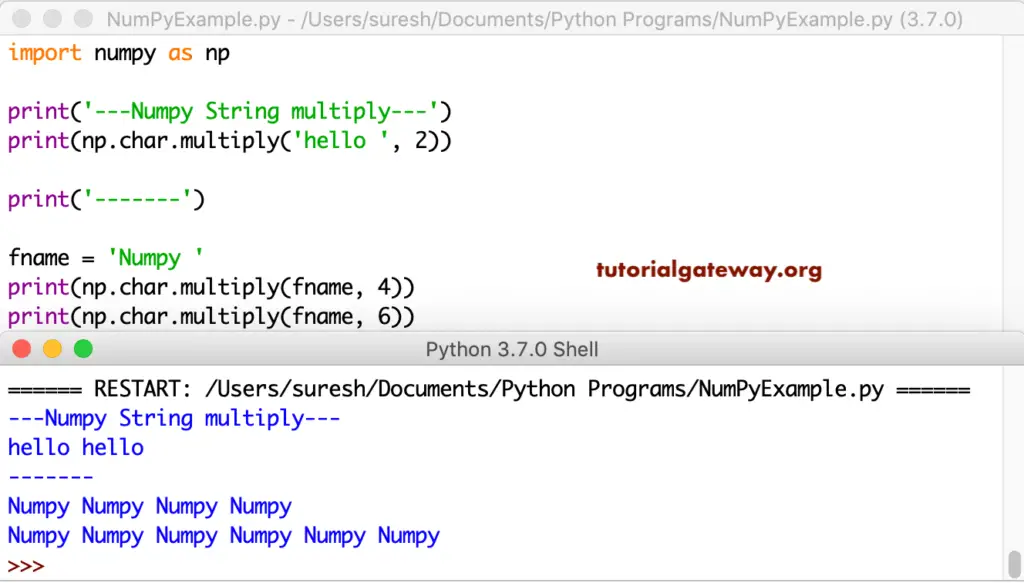
Python numpy capitalize
The capitalize function is used to capitalize or uppercase the first letter in a complete string.
import numpy as np
print('---Numpy String capitalize---')
print(np.char.capitalize('hello'))
print(np.char.capitalize('hello world'))
print('-------')
fname = 'numpy'
company = 'tutorial gateway'
print(np.char.capitalize(fname))
print(np.char.capitalize(company))
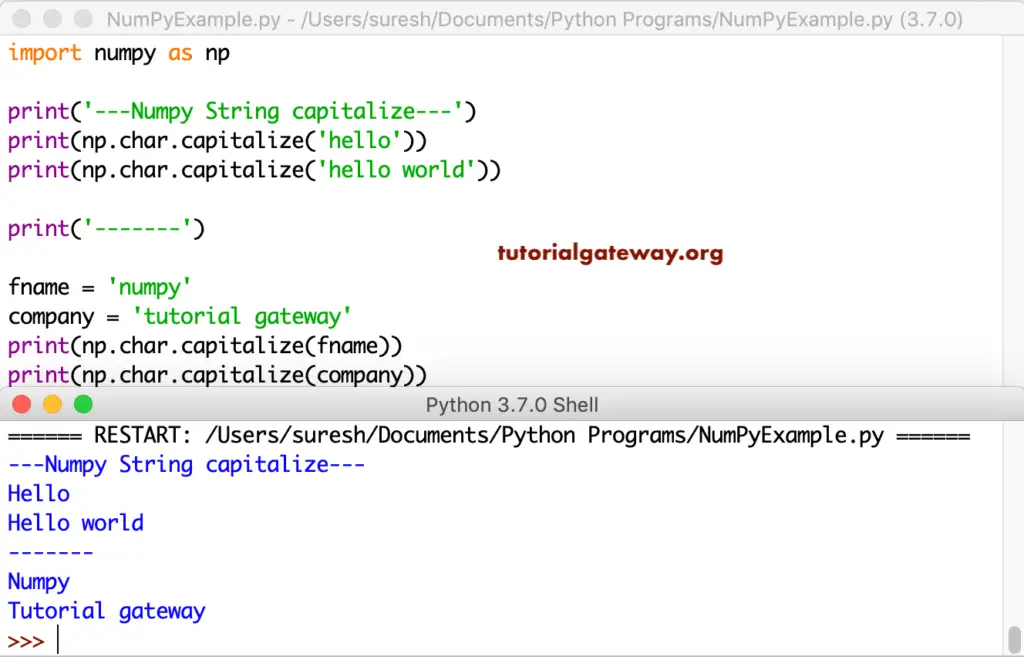
Python numpy title
The title function is to convert the first letter of each word to uppercase.
import numpy as np
print('---Numpy String title---')
print(np.char.title('hello'))
print(np.char.title('hello world'))
print(np.char.title('hi, how are you?'))
print('-------')
name = 'python'
company = 'tutorial gateway'
print(np.char.title(name))
print(np.char.title(company))
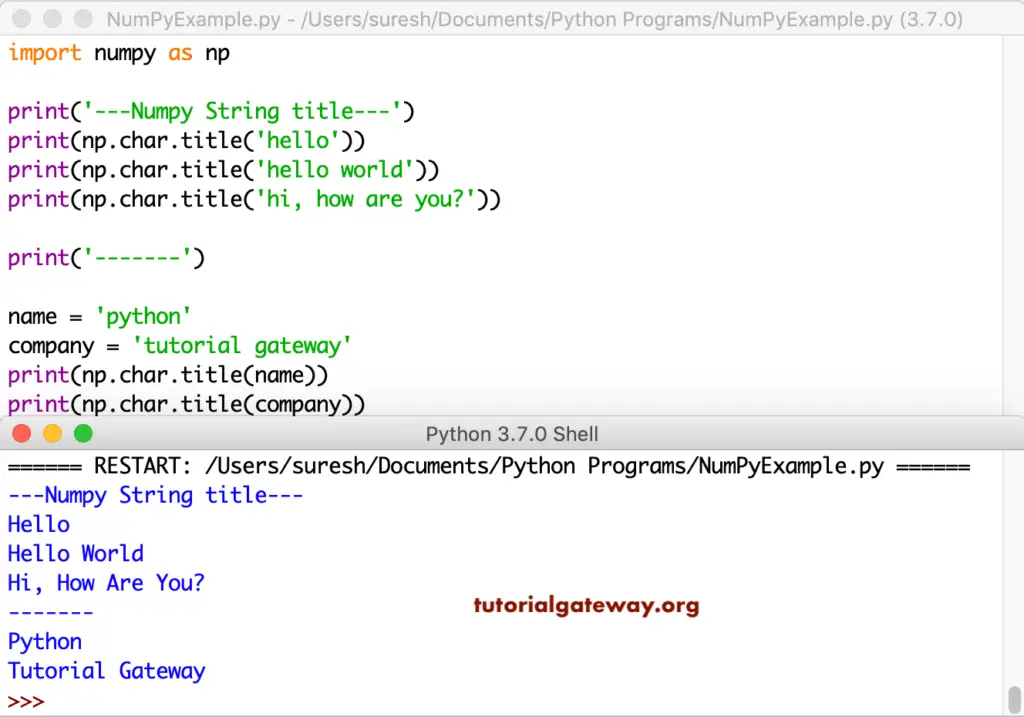
Python numpy upper
The upper converts all the letters in a string to uppercase
import numpy as np
print('---String upper---')
print(np.char.upper('hello'))
print(np.char.upper('hello world'))
print(np.char.upper('hi, how are you?'))
print('\n---Uppercase example 2----')
name = 'python'
company = 'tutorial gateway'
print(np.char.upper(name))
print(np.char.upper(company))
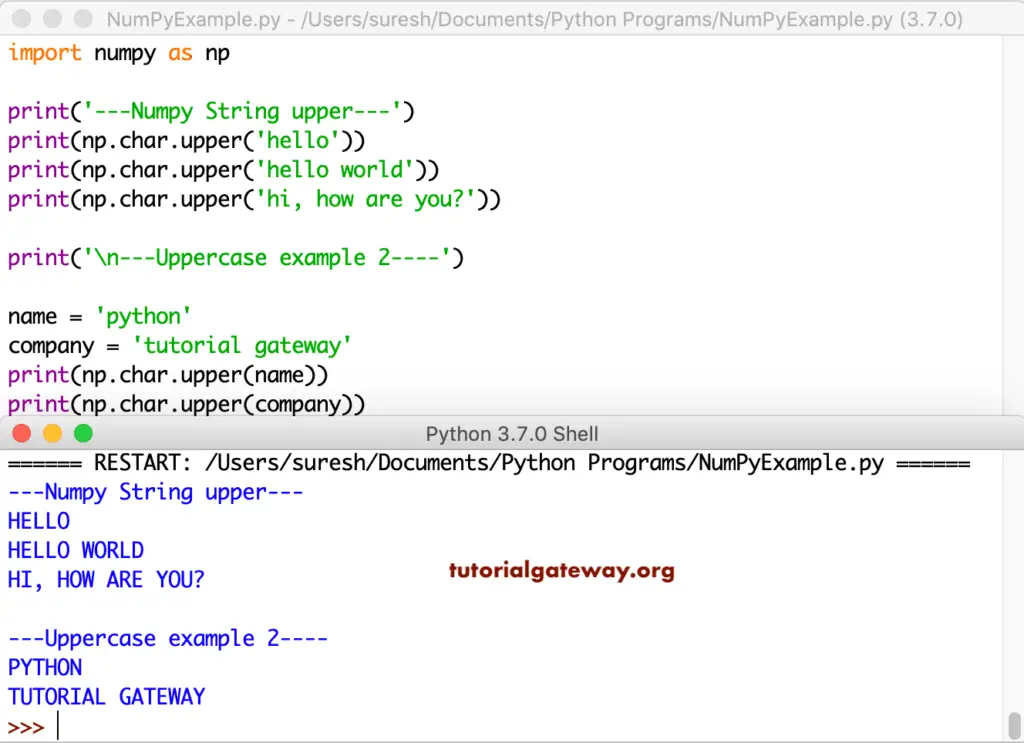
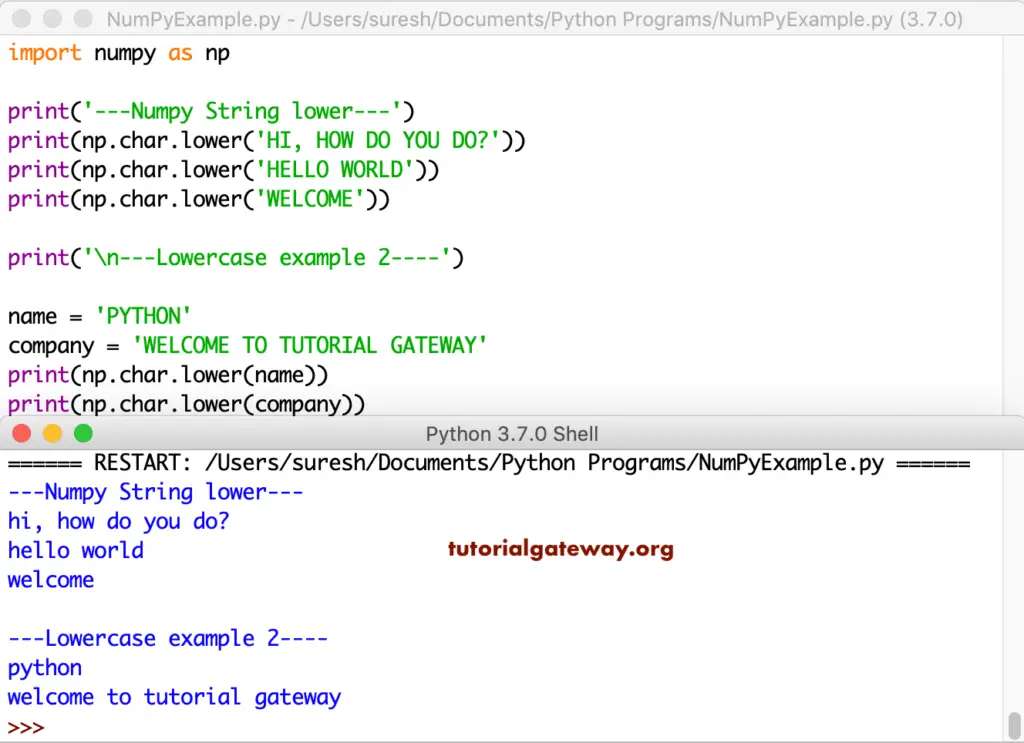
Python numpy lower
This lower converts all the characters in a string to lowercase
import numpy as np
print('---String lower---')
print(np.char.lower('HI, HOW DO YOU DO?'))
print(np.char.lower('HELLO WORLD'))
print(np.char.lower('WELCOME'))
print('\n---Lowercase example 2----')
name = 'PYTHON'
company = 'WELCOME TO TUTORIAL GATEWAY'
print(np.char.lower(name))
print(np.char.lower(company))
Python numpy center
The numpy center is for padding a string. The syntax of the Numpy center
np.char.center(‘string’, length, ‘char’)
If the given length is less than the original length, then Python removes the extra characters from the original string (trim)
If the length is greater than the original length, then those extra spaces are filled with the given character. As the name suggests, the original string is in the center position.
import numpy as np
print('---center---')
print(np.char.center('Hello', 11, '*'))
print(np.char.center('Welcome', 20, '#'))
print(np.char.center('Hello', 4, '*'))
print('\n--char center example----')
name = 'Python'
company = 'TutorialGateway'
print(np.char.center(name, 30, '@'))
print(np.char.center(company, 50, '$'))
print(np.char.center(company, 10, '$'))
center function output
---center---
***Hello***
######Welcome#######
Hell
---char center example----
@@@@@@@@@@@@Python@@@@@@@@@@@@
$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$TutorialGateway$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$
TutorialGaPython Numpy strip
The Numpy strip removes empty spaces from Both the right and left sides of a given string.
import numpy as np
msg1 = ' Hello'
msg2 = 'Python '
msg3 = ' Hello World '
print('Original Message = ', msg1)
print('Strip Left = ', np.char.strip(msg1))
print('\nOriginal Message = ', msg2)
print('Strip Right = ', np.char.strip(msg2))
print('\nOriginal Message = ', msg3)
print('Strip Left & Right = ', np.char.strip(msg3))
strip function output
Original Message = Hello
Strip Left = Hello
Original Message = Python
Strip Right = Python
Original Message = Hello World
Strip Left & Right = Hello WorldPython numpy split
The numpy split function splits the given string based on the specified separator
import numpy as np
print('---split---')
print(np.char.split('Hello World', sep = ' '))
print(np.char.split('hi,how are you?', sep = ' '))
print(np.char.split('hi,Python,Program', sep = ','))
print('\n----char split---')
msg = 'Welcome to Tutorial Gateway'
print(np.char.split(msg, sep = ' '))
msg2 = 'Welcome@Python@From@Tutorial@Gateway'
print(np.char.split(msg2, sep = '@'))
split function output
---split---
['Hello', 'World']
['hi,how', 'are', 'you?']
['hi', 'Python', 'Program']
----char split---
['Welcome', 'to', 'Tutorial', 'Gateway']
['Welcome', 'Python', 'From', 'Tutorial', 'Gateway']Python numpy splitlines
This numpy splitlines returns a list of lines in a given string. The numpy splitlines considers the line breaks \n and \r.
import numpy as np
msg = 'Hello\nWorld'
print(msg)
print('\n-- splitlines output----')
print(np.char.splitlines(msg))
print()
msg1 = 'Hi\rHow are you?'
print(msg1)
print('\n-- splitlines output----')
print(np.char.splitlines(msg1))
print()
msg2 = 'Hi\rHow are \nyou?'
print(msg2)
print('\n-- splitlines output----')
print(np.char.splitlines(msg2))
print('\n--- splitlines---')
print(np.char.splitlines('Hello\nWorld'))
splitlines function output
Hello
World
-- splitlines output----
['Hello', 'World']
Hi
How are you?
-- splitlines output----
['Hi', 'How are you?']
Hi
How are
you?
-- splitlines output----
['Hi', 'How are ', 'you?']
---splitlines---
['Hello', 'World']Python numpy join
The numpy join function joins the specified character(first Argument) after each character in a given string.
import numpy as np
print('--- join---')
print(np.char.join(':', 'HMS'))
print(np.char.join('/', 'dmy'))
print(np.char.join('-', 'dmy'))
print(np.char.join(' ', 'HelloWorld'))
print('\n----char join---')
print(np.char.join(['-', ':'], ['dmy', 'mdy']))
print(np.char.join(['@', '$', ':'], ['Hi', 'Hello', 'HMS']))
join function output
---join---
H:M:S
d/m/y
d-m-y
H e l l o W o r l d
----char join---
['d-m-y' 'm:d:y']
['H@i' 'H$e$l$l$o' 'H:M:S']Python numpy replace
The Python numpy replace function is used to replace the substring with a new string.
np.char.replace(original_string, old_string, new_string)
The Numpy replace function searches for an old string in an original. If it finds, the numpy replace function replace with new_string.
import numpy as np
print(np.char.replace('Hello', 'l', 'K'))
print(np.char.replace('tutorial', 't', 'M'))
print(np.char.replace('oh boy! welcome to you', 'o', 'X'))
print(np.char.replace('oh boy! welcome to you', 'o', 'SSh'))
replace function output
HeKKo
MuMorial
Xh bXy! welcXme tX yXu
SShh bSShy! welcSShme tSSh ySShuIt is another example of a numpy string replace function.
import numpy as np
msg1 = 'Hello World'
msg2 = 'xyz working in xyz position at xyz company'
print('Original Message = ', msg1)
print('Repalce l with T = ', np.char.replace(msg1, 'l', 'T'))
print('Repalce o with HMS = ', np.char.replace(msg1, 'o', 'HMS'))
print('\nOriginal Message = ', msg2)
print('Repalce o with T = ', np.char.replace(msg2, 'o', 'T'))
print('Repalce xyz with abc = ', np.char.replace(msg2, 'xyz', 'abc'))
replace function output
Original Message = Hello World
Repalce l with T = HeTTo WorTd
Repalce o with HMS = HellHMS WHMSrld
Original Message = xyz working in xyz position at xyz company
Repalce o with T = xyz wTrking in xyz pTsitiTn at xyz cTmpany
Repalce xyz with abc = abc working in abc position at abc companyPython numpy encode
The numpy encode is used to encode the string using the specified encoder. Here, np.char.encode(‘Hello’, ‘cp500’) encode Hello string using cp500
import numpy as np
print('---String encode---')
print(np.char.encode('Hello', 'cp500'))
print(np.char.encode('Hello', 'utf_16'))
print(np.char.encode('How are You?', 'cp500'))
print(np.char.encode('Welcome again!', 'utf_16'))
print('\n---char encode----')
name = 'Python'
company = 'Tutorial Gateway'
print(np.char.encode(name, 'cp500'))
print(np.char.encode(name, 'utf_16'))
print(np.char.encode(name, 'utf_16_le'))
print(np.char.encode(company, 'cp500'))
print(np.char.encode(company, 'utf_16'))
print(np.char.encode(company, 'utf_16_be'))
encode function output
---String encode---
b'\xc8\x85\x93\x93\x96'
b'\xff\xfeH\x00e\x00l\x00l\x00o'
b'\xc8\x96\xa6@\x81\x99\x85@\xe8\x96\xa4o'
b'\xff\xfeW\x00e\x00l\x00c\x00o\x00m\x00e\x00 \x00a\x00g\x00a\x00i\x00n\x00!'
---char encode----
b'\xd7\xa8\xa3\x88\x96\x95'
b'\xff\xfeP\x00y\x00t\x00h\x00o\x00n'
b'P\x00y\x00t\x00h\x00o\x00n'
b'\xe3\xa4\xa3\x96\x99\x89\x81\x93@\xc7\x81\xa3\x85\xa6\x81\xa8'
b'\xff\xfeT\x00u\x00t\x00o\x00r\x00i\x00a\x00l\x00 \x00G\x00a\x00t\x00e\x00w\x00a\x00y'
b'\x00T\x00u\x00t\x00o\x00r\x00i\x00a\x00l\x00 \x00G\x00a\x00t\x00e\x00w\x00a\x00y'Python numpy string decode
The numpy decode is used to decode the already encoded (numpy encode) string. Here, you have to specify the code that has to use for decoding a message. If you use the wrong code, then the decode function throws an error.
import numpy as np
print('---String decode---')
print(np.char.decode(b'\xc8\x85\x93\x93\x96', 'cp500'))
print('\n---char decode----')
name = b'\xd7\xa8\xa3\x88\x96\x95'
company = b'\xe3\xa4\xa3\x96\x99\x89\x81\x93@\xc7\x81\xa3\x85\xa6\x81\xa8'
print(np.char.decode(name, 'cp500'))
print(np.char.decode(company, 'cp500'))
print('\n---char decode----')
name = 'Python Numpy'
ecode = np.char.encode(name, 'cp500')
dcode = np.char.decode(ecode, 'cp500')
print('Original Message = ', name)
print('Encoded Message = ', ecode)
print('Decoded Message = ', dcode)
decode output
---String decode---
Hello
---char decode----
Python
Tutorial Gateway
---char decode----
Original Message = Python Numpy
Encoded Message = b'\xd7\xa8\xa3\x88\x96\x95@\xd5\xa4\x94\x97\xa8'
Decoded Message = Python Numpy