How to write MySQL Left Join with an example using Command Prompt and Workbench? The MySQL Left outer join is to return all the records (or rows) from the first table and match rows from the right table.
The basic syntax of MySQL Left Join is as shown below:
SELECT Table1.Column(s), Table2.Column(s)
FROM Table1
LEFT JOIN
Table2 ON
Table1.Common_Column = Table2.Common_Column
--OR We can Simply Write it as
SELECT Table1. Column(s), Table2. Column(s)
FROM Table1
LEFT OUTER JOIN Table2
ON Table1.Common_Column = Table2.Common_Column
It is optional for you to use the Outer Keyword because both are the same. Let us see the visual representation of the MySQL Left Outer join for better understanding.
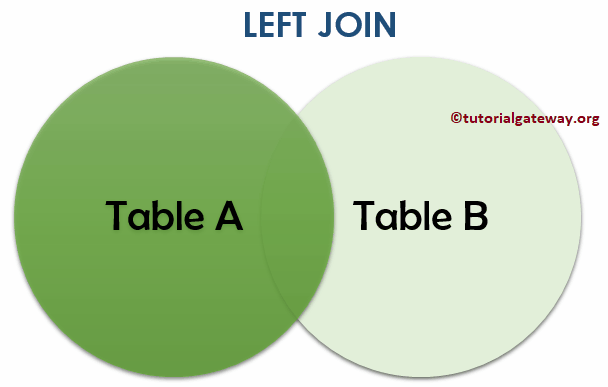
From the above image, you can easily understand that the MySQL Left Outer join displays all the records in Table A and matching records from Table B.
NOTE: All the Unmatched rows from MySQL right table will fill with NULL Values.
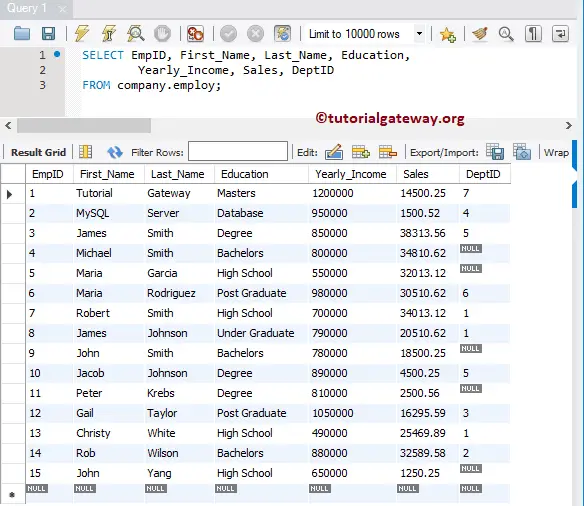
To demonstrate this MySQL Left outer join, we will use the Employ and Department tables present in our company Database. The data present in the employ is:
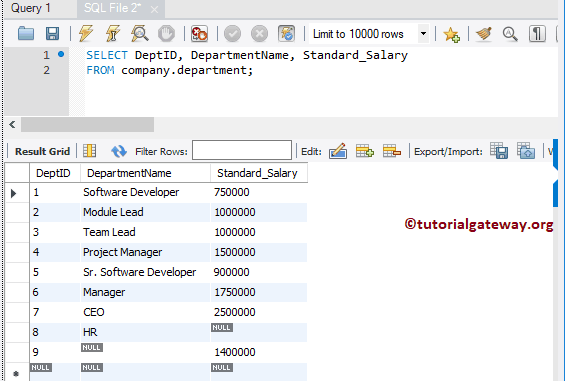
Data present in the Department are:
MySQL Left Join Examples
The following is the list of ways we can use this one to combine two tables or get information (records) from two or more tables.
MySQL Left Join Select * Example
The following query will display all the columns present in the employ table and matching records from the Department table.
USE company;
SELECT * FROM employ
LEFT JOIN department
ON employ.DeptID = department.DeptID;
If you observe the screenshot below, MySQL Left Join displays all 15 records from the Employ. But for [DeptID], Department Name, and Standard_Salary, it displays NULL Values for the EmpID numbers 4, 5, 9, 11, and 15.
It is because DeptID for those records in the Employ is NULL. So there are no matching records in the right table.
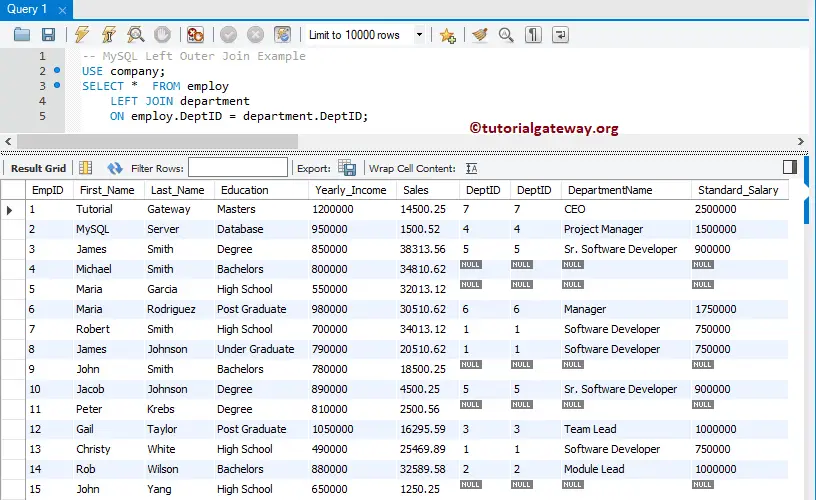
NOTE: The DeptID column is repeated twice, which might annoy the end user. To avoid unwanted columns, I suggest you select individual column names. Please avoid the SELECT * Statement.
Select a Few Columns Example
As we said before, please use the required columns after the SELECT Statement to avoid unwanted columns.
USE company;
SELECT First_Name, Last_Name, Education,
Yearly_Income, Sales,
DepartmentName, Standard_Salary
FROM employ
LEFT JOIN department
ON employ.DeptID = department.DeptID;
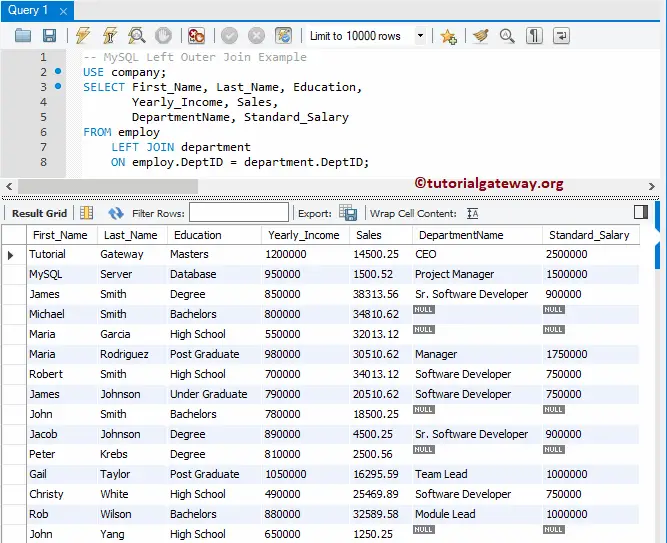
Ambiguous Columns in MySQL Left Join Example
The above-specified MySQL Left join query will work entirely as long as the column names from both employ and Department is different like above. But what happens if they had the same column names in both tables? Well, with the above-specified approach, you will end up in a mess. So, let us see how to resolve the issue.
Let me show you one practical example. As you can see, we are using the same left join query. But, we added DepID from the department as an additional column.
USE company;
SELECT First_Name, Last_Name, Education,
Yearly_Income, Sales,
DeptID, DepartmentName, Standard_Salary
FROM employ
LEFT JOIN department
ON employ.DeptID = department.DeptID;
As you can see, it throws an error: Ambiguous column DeptID. It is because the DeptID column is present in both tables, and the query doesn’t know which column you are asking it to display.
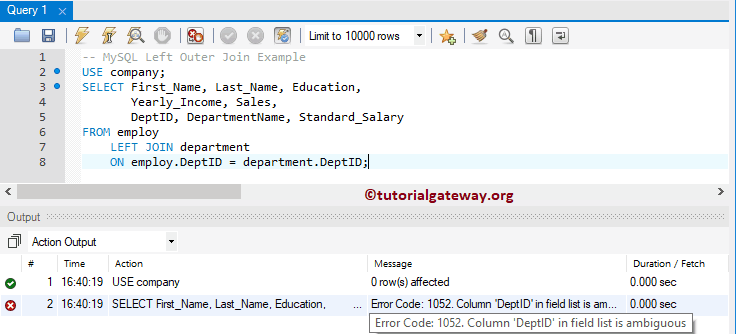
To resolve this issue, always use the table name before the column name. For example, the following query uses the ALIAS table name before the column names.
This approach informs the query that we are looking for DepID belonging to the department. We can simply write the above query as:
USE company;
SELECT emp.First_Name, emp.Last_Name, emp.Education,
emp.Yearly_Income, emp.Sales,
dept.DeptID, dept.DepartmentName, dept.Standard_Salary
FROM employ AS emp
LEFT JOIN department AS dept
ON emp.DeptID = dept.DeptID;
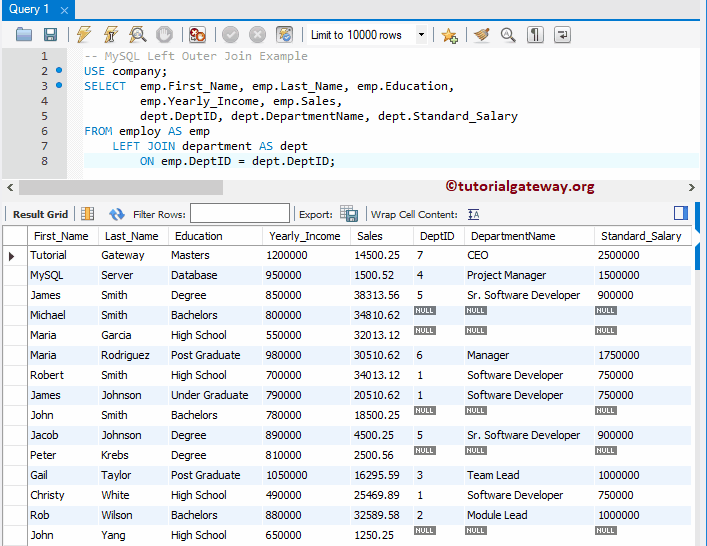
It is always a best practice to use the table name before the Column name in MySQL Left Outer Join. For example, SELECT employ.First_Name
MySQL Left Join using the Keyword
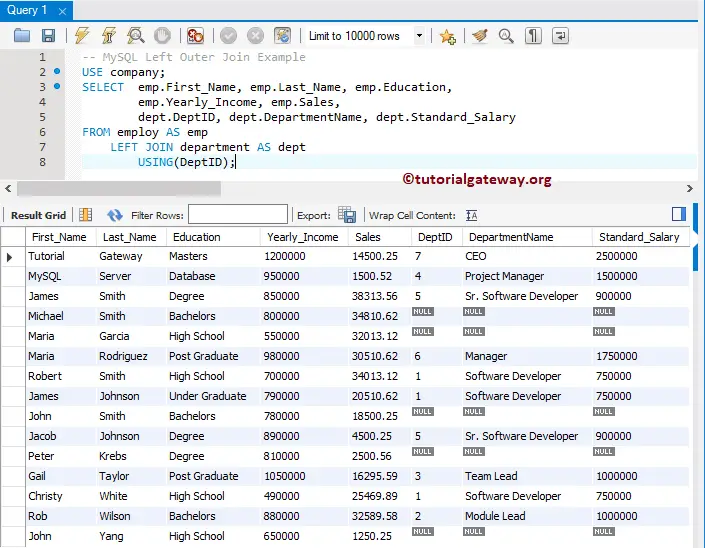
If the common column name in both tables is the same, you can use the Left Join with USING keyword. Since DeptID is the common column name in both tables, the above query can also return as
USE company;
SELECT emp.First_Name, emp.Last_Name, emp.Education,
emp.Yearly_Income, emp.Sales,
dept.DeptID, dept.DepartmentName, dept.Standard_Salary
FROM employ AS emp
LEFT JOIN department AS dept
USING(DeptID);
MySQL Left Join Multiple Conditions
Until now, we are showing the = operator as the condition to the employ and department tables. But you can replace = with < (less than), > (greater than), or not equal to operators.
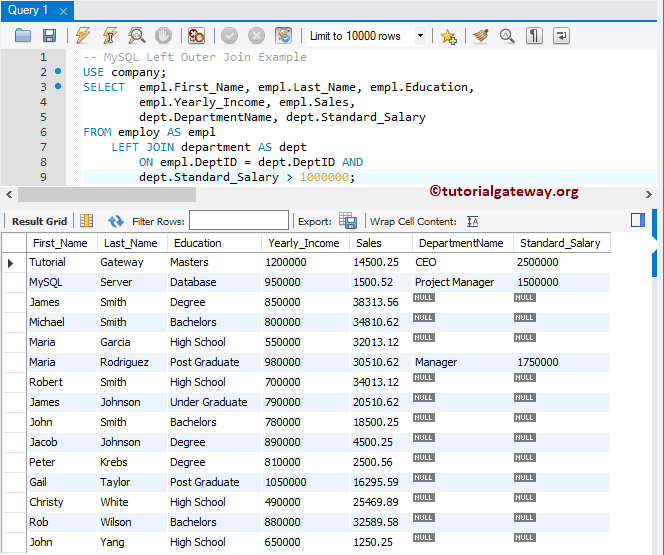
We use two conditions to connect those two tables in this example. The following query will display all the employee records and the matching department rows. Here matching records means the DeptID of both tables should match, and the Standard Salary should be greater than 1000000
USE company;
SELECT empl.First_Name, empl.Last_Name, empl.Education,
empl.Yearly_Income, empl.Sales,
dept.DepartmentName, dept.Standard_Salary
FROM employ AS empl
LEFT JOIN department AS dept
ON empl.DeptID = dept.DeptID AND
dept.Standard_Salary > 1000000;
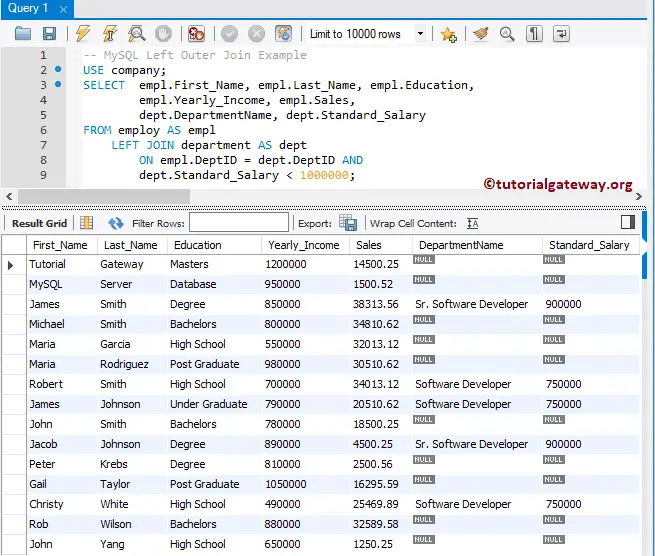
I think you are confused about the result. Let me replace the greater than symbol with less than. It means the DeptID of both tables should match, and the Standard Salary should be less than 1000000
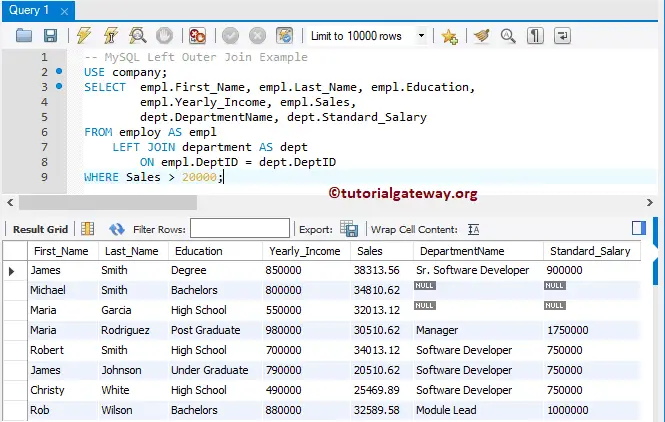
MySQL Left Join Where Clause Example
In this example, we will show you how to use the Where clause (to apply a filter). I suggest you refer Where Clause article.
USE company;
SELECT empl.First_Name, empl.Last_Name, empl.Education,
empl.Yearly_Income, empl.Sales,
dept.DepartmentName, dept.Standard_Salary
FROM employ AS empl
LEFT JOIN department AS dept
ON empl.DeptID = dept.DeptID
WHERE Sales > 20000;
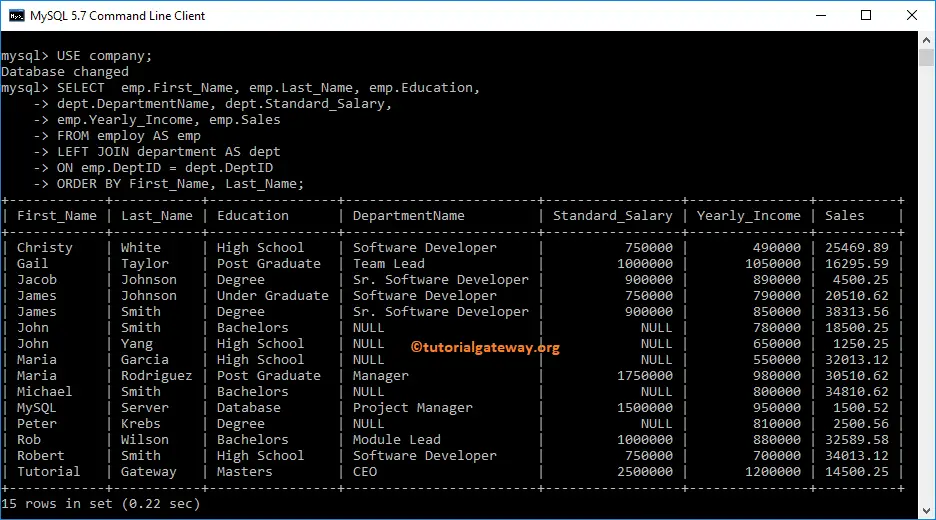
Command prompt Example
Let me show you, How to write it in the Command prompt. In this example, we will also show how to use the Order By clause along with it. I suggest you refer to the Order By article.
USE company;
SELECT empl.First_Name, empl.Last_Name, empl.Education,
depat.DepartmentName, depat.Standard_Salary,
empl.Yearly_Income, empl.Sales
FROM employ AS empl
LEFT JOIN department AS depat
ON empl.DeptID = depat.DeptID
ORDER BY First_Name, Last_Name;