The Java atan2 Function is one of the Java Math Library functions, which returns the angle (in radius) from the X-Axiss to the specified point (y, x).
Java atan2 Function Syntax
The basic syntax of the Math.atan2 in Java Programming language is shown below.
static double atan2(double y, double x); //Return Type is Double // In order to use in program: Math.atan2(double y, double x);
- X: It can be a double value or a valid numerical expression representing Cartesian X – Coordinate.
- Y: It can be a double value or a valid numerical expression representing Cartesian Y – Coordinate.
The Java Math.atan2 function will return the values between -π and π except for special cases that we specified below:
- If any argument is Not a Number, the Java atan2 Function will return NaN.
- If the first argument is positive, zero, and the second argument is positive double value, the result is Positive Zero.
- When the first argument is a positive double value and the second is positive infinity, the result is Positive Zero.
- If the first argument is negative zero, and the second is a negative double value, the Java atan2 result is Negative Zero.
- If the first argument is a negative double value, and the second is positive infinity, the result is Negative Zero.
- When the first argument is positive, zero, and the second argument is a negative double value. Alternatively, the first argument is a positive double value, and the second is negative infinity. The result is Closest to the PI value.
- If the first argument is negative, zero, and the second argument is a negative double value. Or the first argument is a negative double value, and the second is -ve infinity, the Java atan2 function result is Closest to -PI value.
- If the first argument is a positive double value, and the second argument is positive zero or negative zero. Or the first argument is positive infinity, and the second is negative double value; the result is Closest to the PI/2 value.
- When the first argument is a negative double value, and the second argument is positive zero or negative zero. Alternatively, if the first argument is negative infinity and the second is finite, the result will be Closest to the -PI/2 value.
- If both the first and second arguments are positive infinity, the result of the Java atan2 function is Closest to the PI/4 value.
- If the first argument is positive infinity and the second one is negative infinity, the result is Closer to the 3 * (PI/4) value.
- When the first argument is negative infinity and the second is positive infinity, the result is the Closest to the -PI/4 value.
- If both the first and second arguments are Negative infinity, the result is Closest to the -3 * (PI/4) value.
Java atan2 Function Example
The Math.atan2 Function in Java Programming returns the angle (in radius) from the X-Axis to the specified point (y, x). In this Java program, We find the same with positive and negative values and display the output.
package TrigonometricFunctions;
public class Atan2Method {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("\nATAN2 result of Zero Value = " + Math.atan2(0, 10));
System.out.println("ATAN2 result of Zero Value = " + Math.atan2(10, 0));
System.out.println("\nATAN2 result of Zero Value = " + Math.atan2(0, -5));
System.out.println("ATAN2 result of Zero Value = " + Math.atan2(-10, 0));
System.out.println("\nATAN2 result of Positive Value = " + Math.atan2(4, 5));
System.out.println("ATAN2 result of Positive Value = " + Math.atan2(6, 10));
System.out.println("\nATAN2 result of Negative Value = " + Math.atan2(-2.50, -5.50));
System.out.println("ATAN2 result of Negative Value = " + Math.atan2(-6.25, -12.75));
System.out.println("\nATAN2 result of Both Postive & Negative Value = " + Math.atan2(3.50, -9.50));
System.out.println("ATAN2 result of Both Postive & Negative Value = " + Math.atan2(-4.25, 10.75));
double x = Math.toRadians(30), y = Math.toRadians(90);
System.out.println("\nATAN2 result of Radians = " + Math.atan2(x, y));
}
}
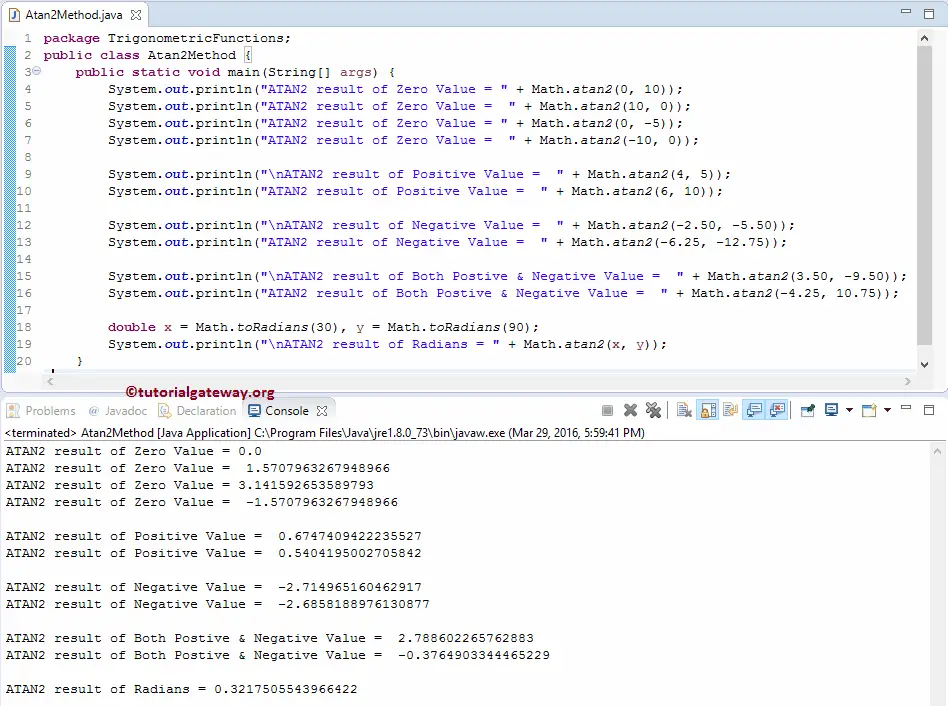
We used the Math.atan2 Function with zero as one argument and Positive or negative double values as the second. The following Java atan2 statements will find the corresponding values’ angle (in radius).
System.out.println("\nATAN2 result of Zero Value = " + Math.atan2(0, 10));
System.out.println("ATAN2 result of Zero Value = " + Math.atan2(10, 0));
System.out.println("\nATAN2 result of Zero Value = " + Math.atan2(0, -5));
System.out.println("ATAN2 result of Zero Value = " + Math.atan2(-10, 0));
Next, we used the Java Math.atan2 Function directly on Positive double values. Please refer to the Java tan and Java atan Function Java program to understand the Arc Tangent Function.
System.out.println("\nATAN2 result of Positive Value = " + Math.atan2(4, 5));
System.out.println("ATAN2 result of Positive Value = " + Math.atan2(6, 10));
Next, we used the Java atan2 Function on Negative double values.
System.out.println("\nATAN2 result of Negative Value = " + Math.atan2(-2.50, -5.50));
System.out.println("ATAN2 result of Negative Value = " + Math.atan2(-6.25, -12.75));
Here, we used the Java Math.atan2 Function directly on both Positive & Negative double values.
System.out.println("\nATAN2 result of Both Postive & Negative Value = " + Math.atan2(3.50, -9.50));
System.out.println("ATAN2 result of Both Postive & Negative Value = " + Math.atan2(-4.25, 10.75));
Next, We declared a variable of type Double and assigned the value. We used the toRadians Math function to convert 30, 90 into equivalent radiant. Lastly, we used System.out.println statement to print the result as output.
double x = Math.toRadians(30), y = Math.toRadians(90);
System.out.println("\nATAN2 result of Radians = " + Math.atan2(x, y));
