How to write a C Program to Find Sum of series 1³+2³+3³+….+n³ using For Loop, Recursion, and Functions with example. This series 1³+2³+3³+….+n³ also called as Sum of cubes of n natural numbers in C. The Mathematical formula for C program to find Sum of series 1³+2³+3³+….+n³ = ( n (n+1) / 6)²
C Program to Find Sum of series 1³+2³+3³+….+n³
In this C program, the user asked to enter any positive integer. Next, using that value, the C compiler will find the sum of series 1³+2³+3³+….+n³ with the above formula.
/* Sum of Cubes of n Natural Numbers */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main()
{
int Number, Sum = 0;
printf("\n Please Enter any positive integer \n");
scanf(" %d",&Number);
Sum = pow(((Number * (Number + 1))/ 2), 2);
printf("\n The Sum of Series for %d = %d ",Number, Sum);
}
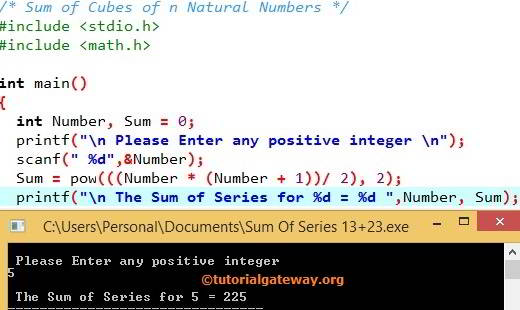
First, we declared 2 integer variables, and they are Number and Sum. In the next line, We are calculating the Sum of the series 1³+2³+3³+4³+5³ using the above formula.
Sum = pow (((Number * (Number + 1)) / 2), 2);
Sum = pow (((5 * (5 + 1)) / 2), 2);
Sum = pow (((5 * 6) / 2), 2);
Sum = pow ((30 / 2), 2);
Sum = pow (15, 2);
Sum = 15 * 15 = 225
The Final C Programming printf statement will print the Sum as output
printf("\n The Sum of Series for %d = %d ",Number, Sum);
So, the final output of the C Program to Find Sum of series 1³+2³+3³+….+n³ for 5 = 225
C Program to Find Sum of series 1³+2³+3³+….+n³ using For Loop
If you want to display the series order 1³+2³+3³+4³ in the output, then we have to add extra For Loop to display as below
/* Sum of Cubes of n Natural Numbers */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main()
{
int Number, i, Sum = 0;
printf("\nPlease Enter any positive integer \n");
scanf("%d",&Number);
Sum = pow(((Number * (Number + 1))/ 2), 2);
for(i =1; i<=Number;i++)
{
if (i != Number)
printf("%d^3 + ",i);
else
printf("%d^3 = %d ",i, Sum);
}
}
Please Enter any positive integer
4
1^3 + 2^3 + 3^3 + 4^3 = 100 The for loop inside the main function will traverse each member and displays the output
for(i =1; i<=Number;i++)
{
if (i != Number)
printf(" %d^3 + ",i);
else
printf(" %d^3 = %d ",i, Sum);
}
In the above output, the user-entered value is 4, Sum = 100. Now the compiler will enter into For Loop
First Iteration
i = 1 so the condition inside the for loop (i <= Number) is TRUE (1 <=4). Next, It will go to if condition (i != Number). It means (1 != 4) – Which is TRUE So, it will print the output as 1³+
i incremented to 2. It will do the same until i reaches 4. When it is equal 4, then if condition will fail so, the else statement is printed.
The final Output of this C program will be 1³+2³+3³+4³ = 100
C Program to Find Sum of series 1³+2³+3³+….+n³ using Functions
This C program finds the sum of series 1³+2³+3³+….+n³ using FUNCTIONS.
/* Sum of Cubes of n Natural Numbers */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
void Sum_Of_Series(int);
int main()
{
int Number;
printf("\n Please Enter any positive integer \n");
scanf("%d",&Number);
Sum_Of_Series(Number);
}
void Sum_Of_Series(int Number)
{
int i, Sum = 0;
Sum = pow (((Number * (Number + 1))/ 2), 2);;
for(i =1;i<=Number;i++)
{
if (i != Number)
printf("%d^3 + ",i);
else
printf(" %d^3 = %d ", i, Sum);
}
}
Please Enter any positive integer
6
1^3 + 2^3 + 3^3 + 4^3 + 5^3 + 6^3 = 441The first line of the program is the declaration of User Defined Function
Within the main() function,
void Sum_Of_Series(int);
Next, we called the user-defined function Sum_Of_Series().
Sum_Of_Series(Number);
When the compiler reaches the Sum_Of_Series(), it will jump to the function definition for the calculations. We already explained the logic in the above example.
C Program to Find Sum of series 1³+2³+3³+….+n³ using Recursion
This C program allows to enter the N value, and then it finds the s sum of series 1³+2³+3³+….+n³ using RECURSION
/* Sum of Cubes of n Natural Numbers */
#include <stdio.h>
int Sum_Of_Series(int);
int main()
{
int Number, Sum;
printf("\nPlease Enter any positive integer \n");
scanf("%d",&Number);
Sum =Sum_Of_Series(Number);
printf("\nSum of the Series = %d",Sum);
}
int Sum_Of_Series(int Number)
{
if(Number == 0)
return 0;
else
//Recursive Calling
return (Number * Number * Number) + Sum_Of_Series(Number-1);
}
Please Enter any positive integer
3
Sum of the Series = 36Function Definition
Within the Sum_Of_Series (Number) function, If the user entered Number is 0, then the function will return 0 else it will return
(Number * Number * Number) + Sum_Of_Series(Number-1);
Let us divide the above expression for better understanding
(Number * Number * Number) = Multiplying the number three times
Sum_Of_Series(Number – 1) = Calling the same function with 1 number minus
From the above output, User entered value is 3,
Sum of series 1³+2³+3³+….+n³ Recursion 1
Number = 3, which is Greater than 0 and Sum is 0, so
Sum = (Number * Number) + Sum_Of_Series(Number-1)
Sum = (3 * 3 * 3) + Sum_Of_Series (3 – 1)
Sum = 27 + Sum_Of_Series (2)
Sum value is = 27
Recursion 2
Number = 2, which is Greater than 0 and Sum is 27
Sum = (2 * 2 * 2) + Sum_Of_Series (2 – 1)
Sum = 8 + Sum_Of_Series (1)
Sum value is: 27 + 8 = 35
Recursion 3
Number = 1, which is Greater than 0 and Sum is 35 so,
Sum = (1 * 1 * 1) + Sum_Of_Series (1 – 1)
Sum = 1 + Sum_Of_Series (0)
Sum value is: 35 + 1 = 36
Recursion 4
Number = 0, which means the first if condition is True so that it will exit from the function. The final value of Sum is 36. We must use some conditions to exit the recursive calling. If you forgot, then the RECURSION function will execute countless times
