Python Comparison Operators are called Relational operators, and they are mostly used either in IF Statements, for loop, and while loop. Python Comparison Operators are usually used to check the relationship between two variables. If the relation is true, it returns TRUE, and if the relation is false, then it will return output as FALSE.
The below table shows all of the Python comparison or relational Operators and their examples.
| Relational | Usage | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| > | a > b | a is greater than b | 7 > 3 returns True (1) |
| < | a < b | a is less than b | 7 < 3 returns False (0) |
| >= | a >= b | a is greater than or equal to b | 7 >= 3 => True (1) |
| <= | a<=b | a is less than or equal to b | 7 <= 3 return False (0) |
| == | a==b | a is equal to b | 7 == 3 returns False (0) |
| != | a != b | a is not equal to b | 7 != 3 returns True(1) |
Python Comparison Operators Example
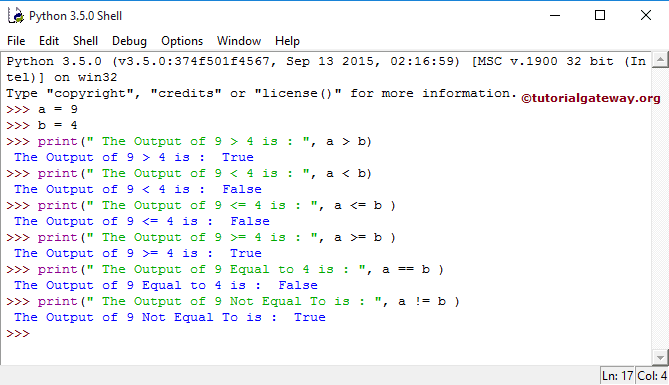
In this example, we declared two variables, a and b, and their values are 9 and 4. Next, we perform various comparison operations. I mean, we checked these values against those.
a = 9
b = 4
print(" The Output of 9 > 4 is : ", a>b )
print(" The Output of 9 < 4 is : ", a<b )
print(" The Output of 9 <= 4 is : ", a <= b )
print(" The Output of 9 >= 4 is : ", a >= b )
print(" The Output of 9 Equal to 4 is : ", a == b )
print(" The Output of 9 Not Equal To is : ", a != b )
How to use the Relational operator in IF Statement?
Using Python Relational or comparison operators in If statements. For this example, We use two variables, x, and y, and their values are 10 and 25. Here, we use these two variables in the If Statement to check the conditions using one of them.
>>> x = 10
>>> y = 25
>>> if x >= y:
print(" x value is Greater than or Equal to y ")
else:
print(" x value is Less than or Equal to y ")
x value is Less than or Equal to yIn this Python comparison or relational operator example, We assigned 2 integer values, x, y, and assigned the values 10 and 25.
>>> x = 10 >>> y = 25
If Condition: If x is greater than or equal to y, then the first print statement will execute
print(" x value is Greater than or Equal to y ")
If the first condition fails, then the second one executes.
print(" x value is Less than or Equal to y ")
Here, 10 is neither greater nor equal to 25. So, the Second statement was printed. Refer to the IF Statements and Loops in Python.
